2. 西北师范大学生命科学学院, 兰州 730070
2. College of Life Sciences, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou 730070, China
1996年发现并成功克隆出能与生长激素促分泌素(GHS)反应的G蛋白偶联受体,即生长激素促分泌素受体(growth hormone secretagogue receptor,GHSR)[1]。这种受体蛋白有2种天然形式,一种是具有功能的7次跨膜蛋白受体,即GHSR1a;另一种是缩短的无功能受体,即GHSR1b。Kojima于1999年首次从胃组织中发现了饥饿激素(ghrelin),并证明它是GHSR的唯一内源性配体[2]。ghrelin是一种28个氨基酸多肽,在肽链的第3个丝氨酸位点有1个8碳脂肪酸侧链,即酰基化侧链[2],该侧链的添加使得该位点能够被ghrelin-O-乙酰基转移酶(ghrelin O-acyltransferase,GOAT)酰基化[3]。一般而言,ghrelin有1个酰基化侧链,而没有该酰基化侧链的28个氨基酸肽链被称为非酰基化ghrelin(unacylated ghrelin,UAG)[2]。ghrelin在机体食欲、体重和脂肪代谢、胃肠功能及葡萄糖和脂类代谢等生理活动的调节中发挥着重要作用。因此,本文系统综述了ghrelin的结构、定位及其在能量代谢中的作用模式与分子机制。
1 ghrelin的结构组成及其加工人类的ghrelin基因位于第3号染色体(3p25-26),长约5 kb,由4个编码外显子(exon 1~4)和1个长为20 bp的第1外显子exon 0组成[4, 5]。exon 1~4编码117个氨基酸的ghrelin前体(preproghrelin),其中,exon 1编码preproghrelin信号肽,exon 1和2编码28个氨基酸的ghrelin多肽激素;exon 3编码23个氨基酸的肥胖抑制素(obestatin)[6];exon 2、3和4编码66个氨基酸的C-ghrelin,该多肽完全包含23个氨基酸的obestatin多肽序列[6, 7]。此外,进一步研究表明在ghrelin基因中还存在1个末端外显子(exon1)[4]。综上所述,如图1所示,人类ghrelin基因的结构,是由exon-1、0、1、2、3和4组成。
ghrelin基因的核心启动子约长200 bp,exon 1和内含子1(intron 1)参与转录调控,辅助核心启动子发挥功能。除此之外,在人和大鼠中,该基因N端还存在不同的调控区域,其中含一个具有活性的TATA盒子(TATA盒子)序列以及E盒子(E-box)序列。TATA box的缺失会降低人类ghrelin基因的转录活性,3个E-box序列可以结合上游刺激因子-1/2(upstream stimulatory factor-1/2,USF-1/USF-2),进而增强其转录活性[9]。上游调控序列还存在其他转录因子的结合位点,如核转录因子激活蛋白-1(activator protein-1,AP-1)、CCAAT增强子结合蛋白(CCAAT enhancer binding proteins,C/EBP)及cAMP反应元件结合蛋白(cAMP response elements binding protein,CREB)等[4]。人类ghrelin基因启动子区域包含的结合位 点也能够结合转录组因子,该类转录组因子主要 有转录因子激活蛋白-2(AP-2)、核转录因子-白细胞介素6(NF-IL6)、核转录因子-κB(NF-κB)、雌性激素及糖皮质激素结合元件的半结合位点因子[4, 10, 11]。且ghrelin基因存在多态性,但其与血液ghrelin的浓度改变无关[12]。
 | 图1 人ghrelin基因的结构
Fig. 1 Structure of the human ghrelin gene[8] |
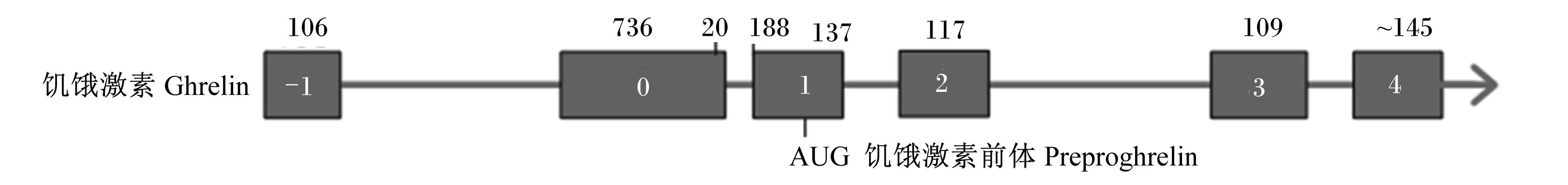
如图2所示,ghrelin基因有2个转录起始位点,转录2种不同的转录组本,即转录本A和转录本B,其中转录本A是该基因的主要转录形式,转录mRNA,该mRNA进一步翻译合成 preproghrelin,该前体分子由117个氨基酸组成,该氨基酸序列在哺乳动物中具有较高的保守性[4]。另外,大鼠和小鼠的ghrelin非常相似,且与人类的相比也仅有2个氨基酸的差异,即人类ghrelin中为Arg11和Val12,而在鼠中却为Lys11和Ala12[6]。牛和羊ghrelin为27个氨基酸的形式,只有17位的1个氨基酸不同(羊为脯氨酸,牛为精氨酸)[13]。
 | 图2 人ghrelin基因不同转录本
Fig. 2 Different transcripts of human ghrelin gene[4] |
此外,如图3所示,ghrelin基因经过“转录—剪接—翻译”3个阶段的加工后最终形成具有活性的preproghrelin[14]。
2 ghrelin的定位 2.1 ghrelin在下丘脑和垂体的定位免疫组化定位分析显示,ghrelin免疫阳性神经元主要分布于下丘脑弓状核,且该阳性神经元在弓状核腹侧部的分布尤其丰富[15]。免疫电镜进一步分析显示,在免疫阳性神经元胞体、突触及轴突末端ghrelin免疫阳性产物主要分布在直径约110 nm的密集颗粒小泡中,该结果表明,在弓状核中ghrelin可能作用于下丘脑或者被转运到下丘脑其他调节食欲的肽能神经元和垂体前叶的生长激素(GH)分泌细胞而发挥其作用[16]。而且,在下丘脑弓状核中ghrelin神经元是通过其复杂的神经元回路和其他相关神经元调控将信息传递到外周相关靶组织或靶器官来影响摄食行为和诱导GH释放的[17]。此外,通过反向液相色谱结合放射免疫和定量PCR分析进一步证实,在下丘脑中ghrelin主要来源并分布于弓状核[18, 19]。但是,有研究报道,ghrelin除了主要分布于弓状核神经元外,在下丘脑外侧区、弓状核、腹正中核、背内侧核、室旁核以及第三脑室室管膜层之间的一个连续体中均有表达[20]。 而且,王琳等[21]通过免疫组化和原位杂交分析,进一步证实ghrelin的蛋白及其mRNA在下丘脑弓状核、腹内侧核、正中隆起及室旁核中均有表达,其阳性神经纤维均投射至神经肽Y(NPY)及刺鼠基因相关蛋白(AgRP)神经元,且该蛋白在各核团细胞中的表达水平存在一定的差异。
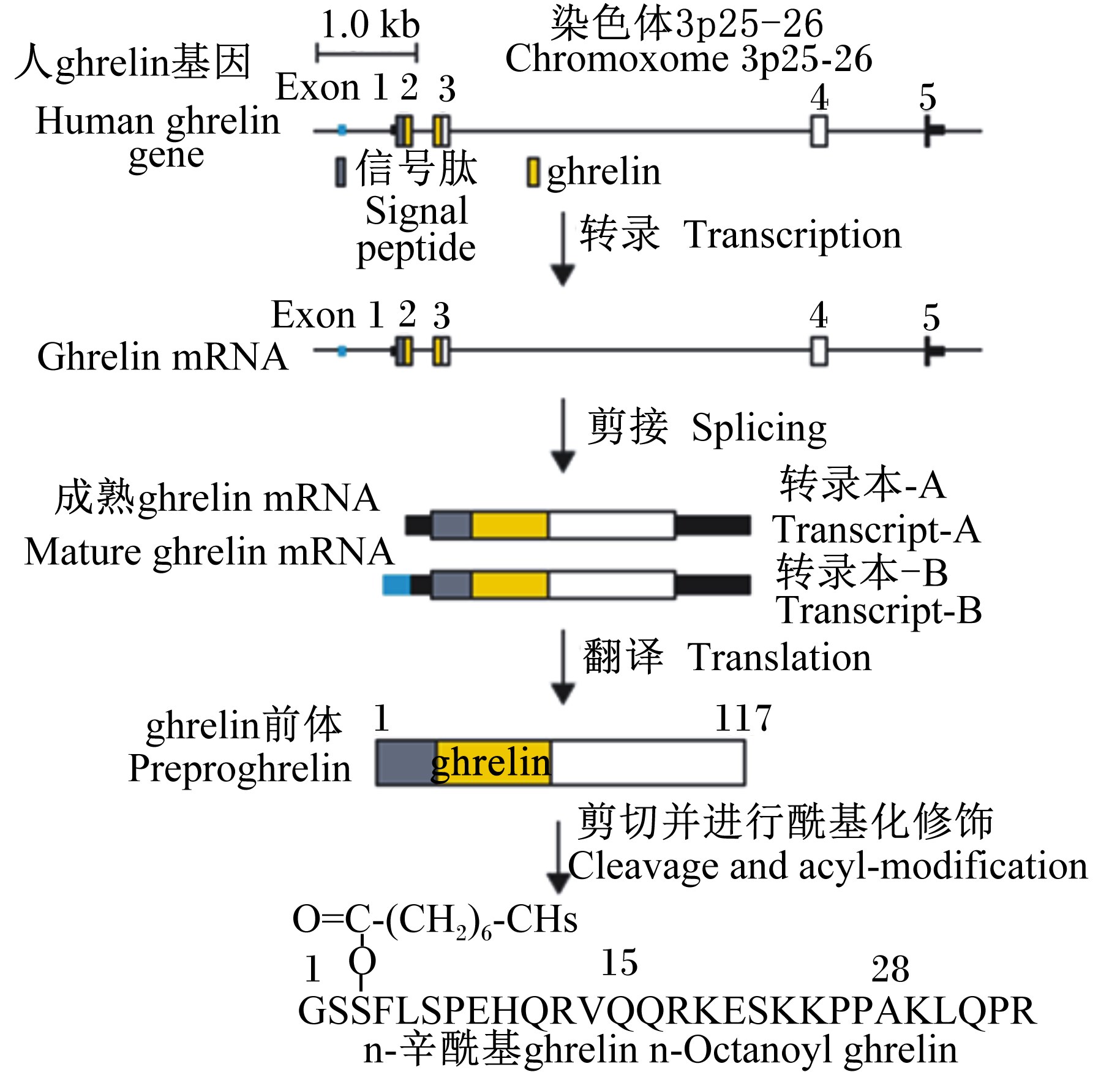 | 图3 人ghrelin基因加工成活性多肽
Fig. 3 From human ghrelin gene to an active peptide[14] |
在腺垂体中也有大量ghrelin阳性细胞的分布,但在神经垂体中尚未见到该阳性细胞的存在[21]。另有研究表明ghrelin在出生后的垂体中是持续高水平表达的,直到青春期该表达才开始下降[14]。此外,ghrelin在脑垂体中,以自分泌或旁分泌的形式也影响着GH的分泌[22, 23]。
2.2 ghrelin在外周组织的定位ghrelin产生于胃X/A样细胞,是血浆ghrelin的主要来源,并参与了摄食信号从胃部到大脑的反馈传递与交流[24, 25, 26]。在胃黏膜中,产生ghrelin的细胞呈封闭式卵圆形,尽管其表达位置靠近毛细血管网,但与胃的吸收功能无关[26]。在肠道中,ghrelin免疫阳性细胞在十二指肠、空肠、回肠及结肠中均有分布,但其表达水平从十二指肠到结肠是逐渐下降的[26, 27, 28]。
除此之外,在外周器官胰腺、睾丸、卵巢及肾脏等器官中也均有ghrelin的表达。例如,大鼠胰岛中有一类细胞能够分泌ghrelin[29, 30, 31],且在大鼠胰岛A细胞和B细胞中也均有GHSR的表达[32, 33];在人和大鼠睾丸间质细胞和支持细胞中也有ghrelin的表达[34, 35],且在睾丸粗线期精母细胞、支持细胞及间质细胞中也均有GHSR的存在[36];而且,在人卵巢成熟和未成熟黄体及门间质细胞中也均有ghrelin的表达[37]。此外,ghrelin mRNA也在肾脏中表达,尤其是在肾小球中[38, 39]。
3 ghrelin的酰基化ghrelin的酰基化是与其受体结合产生相应生物学效应的前提。从1999年发现ghrelin以来,人们一直高度关注着ghrelin激活酶的研究。到目前为止,人们发现了大量膜结合O型酰基化转移酶(membrane-bound O-acyl transferases,MBOAT)蛋白家族成员,主要包括MBOAT1-a/b、MBOAT2-a/b、MBOAT4、MBOAT5及LRC4等,但其中大多数的功能还是未知的,仅MBOAT4是目前功能已知的可酰基化ghrelin的MBOAT;而GOAT属于MBOAT4蛋白,GOAT除了能够酰基化ghrelin,还能够酰基化其他脂肪酸,如碘苯腈辛酸酯和肉豆蔻酸等,且ghrelin酰基化的修饰发生在C7和C12之间;该研究进一步分析表明,在脊椎动物中,即使在斑马鱼这样的低等物种中,GOAT也是高度保守的,且斑马鱼GOAT 60%的氨基酸与人的相同,均具有酰基化修饰作用;在不同物种的酰基化作用中,ghrelin N端序列均含有7个高度保守的酰基化氨基酸序列(即GSSFLSP),斑马鱼的 GOAT能够辛酰化人的 ghrelin;且辛酰基化和癸酰基化是ghrelin受体激活的最佳的配体[40]。另外,在小鼠中进一步研究表明,GOAT是ghrelin酰基化所必需的[3]。综上所述,ghrelin基因的结构保守性是GOAT酰基化的基础。
而且,通过GOAT基因敲除动物模型研究进一步证实,GOAT是唯一的ghrelin酰基化酶[41]。在人的胃和胰脏中,GOAT的mRNA大多数是冗余的,而在小鼠中,GOAT的mRNA大部分表达在ghrelin表达的细胞中[42],另外小部分表达在其他组织中,如心脏、肝脏和结肠等[3]。此外,生化水平分析表明,GOAT有2个非常重要的底物,即Proghrelin和短中链脂肪酸,GOAT对ghrelin进行酰基化的修饰主要发生在Ser3残基上[3];后来,发现在含有脂肪酸辅酶A和GOAT的情况下,去酰基化的ghrelin会被酰基化,但GOAT激活其底物是需要辅酶A硫脂的存在,短氨基酸序列GXSFX是GOAT酰基化识别位点,G、X、S和F是一个识别模型,其顺序分别是末端氨基酸甘氨酸(G),依次是任意氨基酸(X)、丝氨酸(S)和苯丙氨酸(F)[43, 44]。通过上述识别序列与ghrelin高度保守的N端序列比对,发现该识别序列对ghrelin具有极强的特异性,且ghrelin是GOAT唯一的多肽底物。而且,在胃和胰腺组织中GOAT和ghrelin是共表达,GOAT对ghrelin表现出酰基转移酶活性,胃是ghrelin酰基化最主要的场所,该酰基化产物的改变会引起机体的代谢适应[45, 46]。此外,有研究表明,在胰腺中GOAT催化产生酰基化ghrelin(acyl-ghrelin,AG),其进一步调节胰岛素(insulin)的分泌[3]。
4 ghrelin的功能大量研究表明,ghrelin在机体食欲、体重和脂肪代谢、胃肠功能、葡萄糖及脂类代谢等生理活动的调节中发挥着重要作用。
4.1 参与食欲调控在机体食欲的调控中,ghrelin对进食频率的调节发挥着非常重要的作用。在啮齿动物中,神经中枢注射ghrelin会诱发进食效应,其具有与NPY引起促食欲效应相同的功能[47];外周器官注射ghrelin,无论是在瘦人、胖人、健康人还是营养失调的人群中,都会增强饥饿感进而增加进食量,且在能量负平衡的条件下,体内循环的ghrelin水平均会上升[48]。然而,AG对进食的调控与代谢状态密切相关。例如,外源性AG能导致自由进食动物摄食过量,而对禁食或者长期限制进食的动物则没有产生影响[49]。但是,AG通过刺激能量摄入的促食欲效应主要发生在下丘脑[50, 51]。在下丘脑中,AG可能是通过哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1(mTORC1)/核糖体S6激酶1(S6K1)通路调控激活弓状核神经元的,尤其是其中NPY和AgRP神经元[52, 53]。下丘脑AG的主要来源:第一,通过体循环穿越血脑屏障到达下丘脑;第二,通过迷走神经的传入神经到达下丘脑;第三,下丘脑中直接被合成,通过旁分泌而发挥其作用[54]。此外,通过AgRP和NPY基因敲除鼠表现出对外周ghrelin的促食欲效应不敏感表明,ghrelin参与摄食和能量平衡的作用是由AgRP神经元介导的[55, 56];ghrelin还能增加AgRP和NPY mRNA的表达量[52, 57];且在前阿片黑素细胞皮质激素(POMC)神经元上能增加γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)能(GABAergic)抑制性突触而使AgRP神经元去极化[58, 59]。另外,大量研究已证实,在能量平衡调节中,ghrelin结合AgRP在γ-氨基丁酸功能的调控中发挥着重要作用[60, 61, 62]。此外,AgRP和NPY能使POMC神经元直接超极化并减少α-黑素细胞刺激素(α-MSH)的合成和释放,进一步抑制该类神经元的活性[63, 64, 65]。因此,AgRP神经元能够通过直接机制(γ-氨基丁酸能突触)和间接机制(MCR拮抗剂)负调节POMC的厌食效应,而ghrelin仅能够增加进食频率,但不会影响食量[47, 66, 67]。
然而,ghrelin也参与了有关食物线索激励机制的调控[68]。例如,给健康受试者静脉注射ghrelin,功能磁共振成像显示受试者观看食物图片时,脑中杏仁核、前额叶皮质、前脑岛及纹状体中部分神经元的应答反应增强,而这些部位与编码食物线索的激励价值有关联,其意味着ghrelin不仅参与能量均衡摄食的调节,也会通过增强对食物相关线索的刺激反应而寻求进食快乐的感受[68]。此外,ghrelin调节的进食享乐机制涉及其对多巴胺神经元活性的调控[69]。与其对NPY/AgRP神经元的影响相似,ghrelin通过解偶联蛋白2(uncoupling protein 2,UCP2)依赖的线粒体呼吸作用和扩散的升高以及活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)产量的下降直接激活多巴胺神经元[70]。除了直接影响奖励系统,ghrelin还能通过调节AgRP神经元活性间接调控多巴胺神经元。另一方面,发现预期进食前ghrelin的分泌量达到最高[67],进食后摄入的营养素会抑制ghrelin的水平[71];但食物摄入量对ghrelin水平降低的影响与摄入的热量和营养素含量成比例,而摄入的脂质对ghrelin的抑制作用却很小[72, 73]。
另外,大量研究表明,胃源性ghrelin的促食欲效应是通过GHSR1a介导的,但其与受体的作用可能也发生在下丘脑而影响食欲。例如,BIM-28163与GHSR1a的结合阻断了转染细胞中ghrelin与GHSR1a的作用,同时也阻断了ghrelin对GH分泌的刺激效应[74]。然而,通过比较GHSR1a配体BIM-28163对GH释放和食欲的影响表明,在下丘脑中可能还存在着与ghrelin结合的新型受体[74]。例如,相比之下,BIM-28163和ghrelin都能在下丘脑中共同刺激进食[74]。但是,脑室内的UAG,而非ghrelin,在野生型大鼠和GHSR基因敲除鼠中均能增加食物摄入量,表明在中枢食欲调控通路中有UAG受体[75]。例如,在禁食野生型雄鼠中,脑室内或腹腔内注射UAG(3 nmol)会导致该鼠的食物摄入量减少[76];然而,在禁食雄性C57B16鼠[77]或禁食DDY鼠脑室内注射UAG(7.5 nmol)均未发现有抑制进食的作用[75]。外周应用ghrelin而不是UAG能够增加摄食,但GHSR基因敲除鼠在外周注射ghrelin时,而未呈现促食欲效应[75, 78]。由此表明,通过ghrelin引起食欲的受体可能不仅仅是GHSR1a。
4.2 参与体重和脂肪代谢调控在机体体重和脂肪代谢的调控中,ghrelin在能量消耗的调节中发挥着非常重要的作用。在啮齿动物中,慢性注射ghrelin,在未改变进食量的情况下,就可增加体重和导致肥胖[47, 79]。ghrelin诱导的体重增加,主要体现在脂肪的积累,而纵向骨骼发育和去脂体重并不会发生变化[47]。这种效应可以用能量分配来解释,脂肪作为主要的能源物质,可以向碳水化合物转变[80, 81]。此外,在啮齿动物中,中枢注射ghrelin可以抑制下丘脑黑皮质素系统,来诱导白色脂肪组织生成脂肪[82, 83]。在小鼠中,同时敲除ghrelin及其受体会增加能量消耗和运动量,其表明ghrelin对能量消耗和运动量会有一定的抑制作用[81]。综上所述,ghrelin不仅参与饮食调节,还在能量消耗调节中发挥着重要作用。
此外,在人体中,血液ghrelin水平与肥胖、胰岛素抗性及体重增加成负相关性[84, 85];相反,与体重下降、低热量饮食及厌食性神经衰弱或神经萎缩等病理学特征成正相关性[86, 87]。在肥胖个体中,ghrelin低水平主要表现在补偿适应机制,这种机制的目的是降低饥饿刺激,其表明ghrelin自身不是肥胖的关键因素。但是,患有Prader-Willi综合征过量摄食的病人,其血液ghrelin水平较高[88]。此外,存在一些罕见的基因突变体,能够导致ghrelin自身,Preproghrelin或者ghrelin受体发生改变,但是这些改变与人类肥胖的关系很微弱,其影响远低于已知肥胖相关基因突变体的[89, 90, 91, 92, 93]。综上所述,尽管ghrelin不仅参与饮食调节,还在能量消耗调节中发挥着重要作用,但是,与肥胖相关基因相比,其可能对肥胖疾病的发生影响甚微。
4.3 参与肠胃功能调控在机体胃肠功能的调控中,ghrelin在进食和胃排空的调节中发挥着非常重要的作用。食物摄入是由机体中枢平衡机制调控的,但该机制是由肠胃引起的饱腹感和饥饿信号触发的。肠胃激素不仅影响大脑,且在脑中的表达水平远高于胃肠道[94]。肠胃激素对中枢神经系统神经元的影响或者是直接的或者是通过迷走神经传入介导的[95]。一些激素,如胆囊收缩素、瘦素、胰高血糖素样肽-1(glucagon-like peptide-1,GLP-1)及多肽YY3-36等,均能刺激迷走神经传入和激活导致抑制进食及胃排空的信号通路[96]。然而,ghrelin则是刺激进食并加速胃排空。在人体[97]、大鼠[98, 99]和小鼠[100, 101]中,AG是胃排空效应的强力促进剂,也是胃肠蠕动的刺激物。但该效应在狗中并未观察到[102]。GHSR缺失的小鼠中,胃排空确实存在延误[103]。这些小鼠胃部肌肉中,GHSR显著表达,神经细胞数量减少[103]。在胃肠道中,AG通过一种双向机制,即中枢和外周机制,诱导肌动活动[104]。中枢机制通过弓状核、迷走神经或者侧间隔中的NPY神经元介导[105]。膈下迷走神经切断术或者辣椒素治疗能够完全消除进食与ghrelin作用的生长激素释放,说明上述作用受迷走神经的调控[106]。此外,肠胃源性ghrelin的促食欲信号通过血液被传输到弓状核神经元上[107],或者通过迷走神经传入被传递到孤束核[106]。弓状核中,促食欲神经元表达NPY和AgRP[108],厌食神经元表达POMC、α-MSH和可卡因-苯丙胺调控转录肽(CART)[109, 110]。94% NPY神经元上检测到AgRP[108]并且它们的活化均能够启动进食[67]。在94%的NPY神经元中存在GHSR1a,与此同时90%的NPY细胞会被腹腔注射的ghrelin激活,其说明ghrelin对以上三者有直接作用[111]。虽然,ghrelin能直接激活促食欲的NPY/AgRP,但是它并不能通过同样来自NPY/AgRP的GABA直接抑制使食欲减退的POMC[20]。ghrelin能够增加POMC神经元上抑制性突触的数量,从而通过降低厌食信号来增加食物摄入量[112]。综上所述,ghrelin是通过血液传输和迷走神经传输厌食信号来调节进食和胃排空功能。
除此之外,AG通过一氧化氮(NO)依赖途径[113],利用剂量依赖的方式,诱导大鼠的胃酸分泌[114]。而且,与进食调控较为相似,UAG与AG的功能是相反的。在胃窦中,UAG抑制胃排空是一种间接的介导效应,即通过下丘脑激活厌食的CART和尿皮质激素基因的表达来调节的[76]。
4.4 参与葡萄糖和脂类代谢调控在机体葡萄糖和脂类代谢的调控中,ghrelin在胰岛素敏感性、肉碱软脂酰转移酶活性及NPY/AgRP神经元生物学功能的调节中发挥着非常重要的作用。此外,最近研究表明,弓状核AgRP神经元可通过ghrelin调节血糖的生物效应[115]。用GHS治疗老年人和肥胖受试者,发现能够诱导高血糖症和胰岛素耐受性,其说明ghrelin能微调胰岛素分泌和葡萄糖代谢[116]。有趣的是,静脉注射AG时胰岛素敏感度降低,AG与UAG合并注射能非常有效地改善这种状况[117]。AG直接以胰岛作为目标并且通过生长素依赖的通路[118]。与AG不同,UAG能够引起负能量平衡[76]。外周注射UAG可以阻断AG的促食欲效应,改善胰岛素敏感度并减少脂肪[119]。因此,酰基化和非酰基化的2种形式ghrelin都能发挥急性和长期的对葡萄糖代谢和胰岛素敏感度的调节[120]。AG能单独与GHSR作用而导致肥胖[121],因此,ghrelin参与控制AG/UAG有利于调控脂肪生成和脂类降解之间的平衡,并且有利于避免胰岛素耐受性的发展[118]。此外,ghrelin活化的分子机制与线粒体介导的G蛋白偶联受体对神经元的功能相关联[109]。ghrelin能刺激下丘脑腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶来抑制脂肪酸的生物合成、降低下丘脑中丙二酰辅酶A的浓度,从而激活肉碱软脂酰转移酶[122]。而且,腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMPK)-棕榈酰转移酶1(CPT1)轴的激活能改善线粒体的呼吸作用并通过UCP2减少ROS的生成,且UCP2能缓冲过多的ROS[112, 123]。因此,ghrelin不仅能调控中枢及外周的脂类代谢[122],而且,通过激活AMPK-CPT1-UCP2通路,还能维持NPY/AgRP神经元的生物学功能并增加其活性。综上所述,ghrelin不仅通过影响胰岛素敏感度参与葡萄糖的代谢,而且还通过影响肉碱软脂酰转移酶的活性及NPY/AgRP神经元的生物学功能参与脂类代谢。
5 小 结综上所述,在“下丘脑—垂体—消化道”能量代谢系统中,ghrelin作为“脂质传感器”,以“外分泌、自分泌和旁分泌”的分泌方式,通过“神经元突触、迷走神经或/和血液循环”传导,参与机体进食、体重、肠胃功能及脂肪、葡萄糖及脂类代谢等多项任务的调节,进一步在下丘脑中协同调控机体的能量代谢。在全球范围内,代谢性疾病患者与日俱增,严重影响着人类的健康与发展。到目前为止,尽管在该系统中ghrelin参与能量代谢调控的研究方面已取得巨大突破,但其具体的作用机理还需进一步深究。因此,本综述将为相关代谢性疾病病理研究及治疗药物的研发提供必要的信息与新思路。
| [1] | HOWARD A D,FEIGHNER S D,CULLY D F,et al.A receptor in pituitary and hypothalamus that functions in growth hormone release[J].Science,1996,273(5277):974-977.( 1) 1) |
| [2] | KOJIMA M,HOSODA H,DATE Y,et al.Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach[J].Nature,1999,402(6762):656-660.( 2) 2) |
| [3] | GUTIERREZ J A,SOLENBERG P J,PERKINS D R,et al.Ghrelin octanoylation mediated by an orphan lipid transferase[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2008,105(17):6320-6325.( 4) 4) |
| [4] | KANAMOTO N,AKAMIZU T,TAGAMI T,et al.Genomic structure and characterization of the 5'-flanking region of the human ghrelin gene[J].Endocrinology,2004,145(9):4144-4153.( 6) 6) |
| [5] | NAKAI N,KANEKO M,NAKAO N,et al.Identification of promoter region of ghrelin gene in human medullary thyroid carcinoma cell line[J].Life Sciences,2004,75(18):2193-2201.( 1) 1) |
| [6] | ZHANG J V,REN P G,AVSIAN-KRETCHMER O,et al.Obestatin,a peptide encoded by the ghrelin gene,opposes ghrelin's effects on food intake[J].Science,2005,310(5750):996-999.( 2) 2) |
| [7] | BANG A S,SOULE S G,YANDLE T G,et al.Characterisation of proghrelin peptides in mammalian tissue and plasma[J].Journal of Endocrinology,2007,192(2):313-323.( 1) 1) |
| [8] | SEIM I,COLLET C,HERINGTON A C,et al.Revised genomic structure of the human ghrelin gene and identification of novel exons,alternative splice variants and natural antisense transcripts[J].BMC Genomics,2007,8(1):298.( 1) 1) |
| [9] | WEI W,WANG G Y,QI X,et al.Characterization and regulation of the rat and human ghrelin promoters[J].Endocrinology,2005,146(3):1611-1625.( 1) 1) |
| [10] | KISHIMOTO M,OKIMURA Y,NAKATA H,et al.Cloning and characterization of the 5'-flanking region of the human ghrelin gene[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2003,305(1):186-192.( 1) 1) |
| [11] | TANAKA M,HAYASHIDA Y,IGUCHI T,et al.Organization of the mouse ghrelin gene and promoter:occurrence of a short noncoding first exon[J].Endocrinology,2001,142(8):3697-3700.( 1) 1) |
| [12] | VIVENZA D,RAPA A,CASTELLINO N,et al.G hrelin gene polymorphisms and ghrelin,insulin,IGF-Ⅰ,leptin and anthropometric data in children and adolescents[J].European Journal of Endocrinology,2004,151(1):127-133.( 1) 1) |
| [13] | 刘璐,夏利宁,姚刚,等.反刍动物Ghrelin研究进展[J].动物医学进展,2013,34(6):149-153.( 1) 1) |
| [14] | KOJIMA M,KANGAWA K.Ghrelin:structure and function[J].Physiological Reviews,2005,85(2):495-522.( 3) 3) |
| [15] | HORI Y,KAGEYAMA H,GUAN J L,et al.Synaptic interaction between ghrelin- and ghrelin-containing neurons in the rat hypothalamus[J].Regulatory Peptides,2008,145(1/2/3):122-127.( 1) 1) |
| [16] | LU S,GUAN J L,WANG Q P,et al.Immunocytochemical observation of ghrelin-containing neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus[J].Neuroscience Letters,2001,321(3):157-160.( 1) 1) |
| [17] | KAGEYAMA H,TAKENOYA F,SHIBA K,et al.Neuronal circuits involving ghrelin in the hypothalamus-mediated regulation of feeding[J].Neuropeptides,2010,44(2):133-138.( 1) 1) |
| [18] | KAGEYAMA H,KITAMURA Y,HOSONO T,et al.Visualization of ghrelin-producing neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus using ghrelin-EGFP transgenic mice[J].Regulatory Peptides,2008,145(1/2/3):116-121.( 1) 1) |
| [19] | MONDAL M S,DATE Y,YAMAGUCHI H,et al.Identification of ghrelin and its receptor in neurons of the rat arcuate nucleus[J].Regulatory Peptides,2005,126(1/2):55-59.( 1) 1) |
| [20] | COWLEY M A,SMITH R G,DIANO S,et al.The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis[J].Neuron,2003,37(4):649-661.( 2) 2) |
| [21] | 王琳,方富贵,章孝荣,等.Ghrelin及其mRNA在大鼠下丘脑和垂体上的定位[J].畜牧兽医学报,2011,42(1):131-135.( 2) 2) |
| [22] | KORBONITS M,BUSTIN S A,KOJIMA M,et al.The Expression of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor ligand ghrelin in normal and abnormal human pituitary and other neuroendocrine tumors[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2001,86(2):881-887.( 1) 1) |
| [23] | KORBONITS M,KOJIMA M,KANGAWA K,et al.Presence of ghrelin in normal and adenomatous human pituitary[J].Endocrine,2001,14(1):101-104.( 1) 1) |
| [24] | ARIYASU H,TAKAYA K,TAGAMI T,et al.Stomach is a major source of circulating ghrelin,and feeding state determines plasma ghrelin-like immunoreactivity levels in humans[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2001,86(10):4753-4758.( 1) 1) |
| [25] | DORNONVILLE DE LA COUR C,BJÖRKQVIST M,SANDVIK A K,et al.A-like cells in the rat stomach contain ghrelin and do not operate under gastrin control[J].Regulatory Peptides,2001,99(2/3):141-150.( 1) 1) |
| [26] | DATE Y,KOJIMA M,HOSODA H,et al.Ghrelin,a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide,is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans[J].Endocrinology,2000,141(11):4255-4261.( 2) 2) |
| [27] | HOSODA H,KOJIMA M,MATSUO H,et al.Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin:two major forms of rat ghrelin peptide in gastrointestinal tissue[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2000,279(3):909-913.( 1) 1) |
| [28] | SAKATA I,NAKAMURA K,YAMAZAKI M,et al.Ghrelin-producing cells exist as two types of cells,closed- and opened-type cells,in the rat gastrointestinal tract[J].Peptides,2002,23(3):531-536.( 1) 1) |
| [29] | IWAKURA H,HOSODA K,SON C,et al.Analysis of rat insulin II promoter-ghrelin transgenic mice and rat glucagon promoter-ghrelin transgenic mice[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,2005,280(15):15247-15256.( 1) 1) |
| [30] | KOJIMA M,HOSODA H,KANGAWA K.Purification and distribution of ghrelin:the natural endogenous ligand for the growth hormone secretagogue receptor[J].Hormone Research in Paediatrics,2004,56(Suppl.1):93-97.( 1) 1) |
| [31] | PRADO C L,PUGH-BERNARD A E,ELGHAZI L,et al.Ghrelin cells replace insulin-producing β cells in two mouse models of pancreas development[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2004,101(9):2924-2929.( 1) 1) |
| [32] | DATE Y,NAKAZATO M,HASHIGUCHI S,et al.Ghrelin is present in pancreatic α-cells of humans and rats and stimulates insulin secretion[J].Diabetes,2002,51(1):124-129.( 1) 1) |
| [33] | KAGEYAMA H,FUNAHASHI H,HIRAYAMA M,et al.Morphological analysis of ghrelin and its receptor distribution in the rat pancreas[J].Regulatory Peptides,2005,126(1/2):67-71.( 1) 1) |
| [34] | TENA-SEMPERE M,BARREIRO M L,GONZÁLEZ L C,et al.Novel expression and functional role of ghrelin in rat testis[J].Endocrinology,2002,143(2):717-725.( 1) 1) |
| [35] | BARREIRO M L,GAYTÁN F,CAMINOS J E,et al.Cellular location and hormonal regulation of ghrelin expression in rat testis[J].Biology of Reproduction,2002,67(6):1768-1776.( 1) 1) |
| [36] | GAYTAN F,BARREIRO M L,CAMINOS J E,et al.Expression of ghrelin and its functional receptor,the type 1a growth hormone secretagogue receptor,in normal human testis and testicular tumors[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2004,89(1):400-409.( 1) 1) |
| [37] | CAMINOS J E,TENA-SEMPERE M,GAYTÁN F,et al.Expression of ghrelin in the cyclic and pregnant rat ovary[J].Endocrinology,2003,144(4):1594-1602.( 1) 1) |
| [38] | GNANAPAVAN S,KOLA B,BUSTIN S A,et al.The tissue distribution of the mRNA of ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor,GHS-R,in humans[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2002,87(6):2988-2988.( 1) 1) |
| [39] | MORI K,YOSHIMOTO A,TAKAYA K,et al.Kidney produces a novel acylated peptide,ghrelin[J].FEBS Letters,2000,486(3):213-216.( 1) 1) |
| [40] | YANG J,BROWN M S,LIANG G S,et al.Identification of the acyltransferase that octanoylates ghrelin,an appetite-stimulating peptide hormone[J].Cell,2008,132(3):387-396.( 1) 1) |
| [41] | KIRCHNER H,GUTIERREZ J A,SOLENBERG P J,et al.GOAT links dietary lipids with the endocrine control of energy balance[J].Nature Medicine,2009,15(7):741-745.( 1) 1) |
| [42] | SAKATA I,YANG J,LEE C E,et al.Colocalization of ghrelin O-acyltransferase and ghrelin in gastric mucosal cells[J].American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism,2009,297(1):E134-E141.( 1) 1) |
| [43] | OHGUSU H,SHIROUZU K,NAKAMURA Y,et al.Ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) has a preference for n-hexanoyl-CoA over n-octanoyl-CoA as an acyl donor[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2009,386(1):153-158.( 1) 1) |
| [44] | YANG J,ZHAO T J,GOLDSTEIN J L,et al.Inhibition of ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) by octanoylated pentapeptides[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2008,105(31):10750-10755.( 1) 1) |
| [45] | MARTOS-MORENO G Á,BARRIOS V,SORIANO-GUILLÉN L,et al.Relationship between adiponectin levels,acylated ghrelin levels,and short-term body mass index changes in children with diabetes mellitus type 1 at diagnosis and after insulin therapy[J].European Journal of Endocrinology,2006,155(5):757-761.( 1) 1) |
| [46] | WORTLEY K E,DEL RINCON J-P,MURRAY J D,et al.Absence of ghrelin protects against early-onset obesity[J].The Journal of Clinical Investigation,2005,115(12):3573-3578.( 1) 1) |
| [47] | TSCHÖP M,SMILEY D L,HEIMAN M L.Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents[J].Nature,2000,407(6806):908-913.( 3) 3) |
| [48] | WREN A M,SEAL L J,COHEN M A,et al.Ghrelin enhances appetite and increases food intake in humans[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2001,86(12):5992.( 1) 1) |
| [49] | ALEN F,CRESPO I,RAMÍREZ-LÓPEZ M T,et al.Ghrelin-induced orexigenic effect in rats depends on the metabolic status and is counteracted by peripheral CB1 receptor antagonism[J].PLoS One,2013,8(4):e60918.( 1) 1) |
| [50] | WREN A M,SMALL C J,WARD H L,et al.The novel hypothalamic peptide ghrelin stimulates food intake and growth hormone secretion[J].Endocrinology,2000,141(11):4325-4328.( 1) 1) |
| [51] | JÖNSSON E.The role of ghrelin in energy balance regulation in fish[J].General and Comparative Endocrinology,2013,187:79-85.( 1) 1) |
| [52] | NAKAZATO M,MURAKAMI N,DATE Y,et al.A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding[J].Nature,2001,409(6817):194-198.( 2) 2) |
| [53] | STEVANOVIC D,TRAJKOVIC V,MVLLER-LVHLHOFF S,et al.Ghrelin-induced food intake and adiposity depend on central mTORC1/S6K1 signaling[J].Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,2013,381(1/2):280-290.( 1) 1) |
| [54] | LIM C T,KOLA B,KORBONITS M.The ghrelin/GOAT/GHS-R system and energy metabolism[J].Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders,2011,12(3):173-186.( 1) 1) |
| [55] | CHEN H Y,TRUMBAUER M E,CHEN A S,et al.Orexigenic action of peripheral ghrelin is mediated by neuropeptide Y and agouti-related protein[J].Endocrinology,2004,145(6):2607-2612.( 1) 1) |
| [56] | LUQUET S,PHILLIPS C T,PALMITER R D.NPY/AgRP neurons are not essential for feeding responses to glucoprivation[J].Peptides,2007,28(2):214-225.( 1) 1) |
| [57] | KAMEGAI J,TAMURA H,SHIMIZU T,et al.Chronic central infusion of ghrelin increases hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and agouti-related protein mRNA levels and body weight in rats[J].Diabetes,2001,50(11):2438-2443.( 1) 1) |
| [58] | YANG Y L,ATASOY D,SU H H,et al.Hunger states switch a flip-flop memory circuit via a synaptic AMPK-dependent positive feedback loop[J].Cell,2011,146(6):992-1003.( 1) 1) |
| [59] | ATASOY D,BETLEY J N,SU H H,et al.Deconstruction of a neural circuit for hunger[J].Nature,2012,488(7410):172-177.( 1) 1) |
| [60] | WU Q,BOYLE M P,PALMITER R D.Loss of GABAergic signaling by AgRP neurons to the parabrachial nucleus leads to starvation[J].Cell,2009,137(7):1225-1234.( 1) 1) |
| [61] | WU Q,CLARK M S,PALMITER R D.Deciphering a neuronal circuit that mediates appetite[J].Nature,2012,483(7391):594-597.( 1) 1) |
| [62] | WU Q,PALMITER R D.GABAergic signaling by AgRP neurons prevents anorexia via a melanocortin-independent mechanism[J].European Journal of Pharmacology,2011,660(1):21-27.( 1) 1) |
| [63] | ROSEBERRY A G,LIU H Y,JACKSON A C,et al.Neuropeptide Y-mediated inhibition of proopiomelanocortin neurons in the arcuate nucleus shows enhanced desensitization in ob/ob mice[J].Neuron,2004,41(5):711-722.( 1) 1) |
| [64] | SMITH M A,HISADOME K,AL-QASSAB H,et al.Melanocortins and agouti-related protein modulate the excitability of two arcuate nucleus neuron populations by alteration of resting potassium conductances[J].The Journal of physiology,2007,578(2):425-438.( 1) 1) |
| [65] | CYR N E,TOORIE A M,STEGER J S,et al.Mechanisms by which the orexigen NPY regulates anorexigenic α-MSH and TRH[J].America Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism,2013,304(6):E640-E650.( 1) 1) |
| [66] | CUMMINGS D E,NALEID A M,FIGLEWICZ LATTEMANN D P.Editorial:ghrelin:a link between energy homeostasis and drug abuse?[J].Addiction Biology,2007,12(1):1-5.( 1) 1) |
| [67] | CUMMINGS D E,PURNELL J Q,FRAYO R S,et al.A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans[J].Diabetes,2001,50(8):1714-1719.( 3) 3) |
| [68] | MALIK S,MCGLONE F,BEDROSSIAN D,et al.Ghrelin modulates brain activity in areas that control appetitive behavior[J].Cell Metabolism,2008,7(5):400-409.( 2) 2) |
| [69] | DIETRICH M O,BOBER J,FERREIRA J G,et al.AgRP neurons regulate development of dopamine neuronal plasticity and nonfood-associated behaviors[J].Nature Neuroscience,2012,15(8):1108-1110.( 1) 1) |
| [70] | ANDREWS Z B,ERION D,BEILER R,et al.Ghrelin promotes and protects nigrostriatal dopamine function via a UCP2-dependent mitochondrial mechanism[J].The Journal of Neuroscience,2009,29(45):14057-14065.( 1) 1) |
| [71] | TSCHÖP M,WAWARTA R,RIEPL R L,et al.Post-prandial decrease of circulating human ghrelin levels[J].Journal of Endocrinological Investigation,2001,24(6):RC19-RC21.( 1) 1) |
| [72] | FOSTER-SCHUBERT K E,OVERDUIN J,PRUDOM C E,et al.Acyl and total ghrelin are suppressed strongly by ingested proteins,weakly by lipids,and biphasically by carbohydrates[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2008,93(5):1971-1979.( 1) 1) |
| [73] | MONTELEONE P,BENCIVENGA R,LONGOBARDI N,et al.Differential responses of circulating ghrelin to high-fat or high-carbohydrate meal in healthy women[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2003,88(11):5510-5514.( 1) 1) |
| [74] | HALEM H A,TAYLOR J E,DONG J Z,et al.A novel growth hormone secretagogue-1a receptor antagonist that blocks ghrelin-induced growth hormone secretion but induces increased body weight gain[J].Neuroendocrinology,2005,81(5):339-349.( 2) 2) |
| [75] | TOSHINAI K,YAMAGUCHI H,SUN Y X,et al.Des-acyl ghrelin induces food intake by a mechanism independent of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor[J].Endocrinology,2006,147(5):2306-2314.( 2) 2) |
| [76] | ASAKAWA A,INUI A,FUJIMIYA M,et al.Stomach regulates energy balance via acylated ghrelin and desacyl ghrelin[J].Gut,2005,54(1):18-24.( 3) 3) |
| [77] | NEARY N M,DRUCE M R,SMALL C J,et al.Acylated ghrelin stimulates food intake in the fed and fasted states but desacylated ghrelin has no effect[J].Gut,2006,55(1):135.( 1) 1) |
| [78] | SUN Y X,WANG P,ZHENG H,et al.Ghrelin stimulation of growth hormone release and appetite is mediated through the growth hormone secretagogue receptor[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2004,101(13):4679-4684.( 1) 1) |
| [79] | THEANDER-CARRILLO C,WIEDMER P,CETTOUR-ROSE P,et al.Ghrelin action in the brain controls adipocyte metabolism[J].The Journal of Clinical Investigation,2006,116(7):1983-1993.( 1) 1) |
| [80] | LONGO K A,CHAROENTHONGTRAKUL S,GIULIANA D J,et al.Improved insulin sensitivity and metabolic flexibility in ghrelin receptor knockout mice[J].Regulatory Peptides,2008,150(1/2/3):55-61.( 1) 1) |
| [81] | PFLUGER P T,KIRCHNER H,GVNNEL S,et al.Simultaneous deletion of ghrelin and its receptor increases motor activity and energy expenditure[J].American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2008,294(3):G610-G618.( 2) 2) |
| [82] | NOGUEIRAS R,WIEDMER P,PEREZ-TILVE D,et al.The central melanocortin system directly controls peripheral lipid metabolism[J].The Journal of Clinical Investigation,2007,117(11):3475-3488.( 1) 1) |
| [83] | SANGIAO-ALVARELLOS S,VÁZQUEZ M J,VARELA L,et al.Central ghrelin regulates peripheral lipid metabolism in a growth hormone-independent fashion[J].Endocrinology,2009,150(10):4562-4574.( 1) 1) |
| [84] | MCLAUGHLIN T,ABBASI F,LAMENDOLA C,et al.Plasma ghrelin concentrations are decreased in insulin-resistant obese adults relative to equally obese insulin-sensitive controls[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2004,89(4):1630-1635.( 1) 1) |
| [85] | TSCHÖP M,WEYER C,TATARANNI P A,et al.Circulating ghrelin levels are decreased in human obesity[J].Diabetes,2001,50(4):707-709.( 1) 1) |
| [86] | CUMMINGS D E,WEIGLE D S,FRAYO R S,et al.Plasma ghrelin levels after diet-induced weight loss or gastric bypass surgery[J].New England Journal of Medicine,2002,346(21):1623-1630.( 1) 1) |
| [87] | NAGAYA N,UEMATSU M,KOJIMA M,et al.Elevated circulating level of ghrelin in cachexia associated with chronic heart failure:relationships between ghrelin and anabolic/catabolic factors[J].Circulation,2001,104(17):2034-2038.( 1) 1) |
| [88] | DELPARIGI A,TSCHÖP M,HEIMAN M L,et al.High circulating ghrelin:a potential cause for hyperphagia and obesity in prader-willi syndrome[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2002,87(12):5461-5464.( 1) 1) |
| [89] | HINNEY A,HOCH A,GELLER F,et al.Ghrelin gene:identification of missense variants and a frameshift mutation in extremely obese children and adolescents and healthy normal weight students[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2002,87(6):2716-2716.( 1) 1) |
| [90] | KORBONITS M,GUEORGUIEV M,O'GRADY E,et al.A variation in the ghrelin gene increases weight and decreases insulin secretion in tall,obese children[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2002,87(8):4005-4008.( 1) 1) |
| [91] | PANTEL J,LEGENDRE M,CABROL S,et al.Loss of constitutive activity of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor in familial short stature[J].Journal of Clinical Investigation,2006,116(3):760-768.( 1) 1) |
| [92] | UKKOLA O,RAVUSSIN E,JACOBSON P,et al.Mutations in the preproghrelin/ghrelin gene associated with obesity in humans[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolish,2001,86(8):3996-3999.( 1) 1) |
| [93] | UKKOLA O,RAVUSSIN E,JACOBSON P,et al.Role of ghrelin polymorphisms in obesity based on three different studies[J].Obesity Research,2002,10(8):782-791.( 1) 1) |
| [94] | DOCKRAY G J.Immunochemical evidence of cholecystokinin-like peptides in brain[J].1976,264(5586):568-570.( 1) 1) |
| [95] | DAVISON J S.Activation of vagal gastric mechanoreceptors by cholecystokinin[C]//Proceedings of the Western Pharmacology Society.[S.l.]:[s.n.],1986.( 1) 1) |
| [96] | DOCKRAY G J.The G. L. brown lecture regulatory peptides and the neuroendocrinology of gut-brain relationS[J].Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology,1988,73(5):703-727.( 1) 1) |
| [97] | TACK J,DEPOORTERE I,BISSCHOPS R,et al.Influence of ghrelin on interdigestive gastrointestinal motility in humans[J].Gut,2006,55(3):327-333.( 1) 1) |
| [98] | TRUDEL L,TOMASETTO C,RIO M C,et al.Ghrelin/motilin-related peptide is a potent prokinetic to reverse gastric postoperative ileus in rat[J].American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2002,282(6):G948-G952.( 1) 1) |
| [99] | XU L,GONG Y L,WANG H B,et al.The stimulating effect of ghrelin on gastric motility and firing activity of gastric-distension-sensitive hippocampal neurons and its underlying regulation by the hypothalamus[J].Experimental Physiology,2014,99(1):123-135.( 1) 1) |
| [100] | ARIGA H,TSUKAMOTO K,CHEN C,et al.Endogenous acyl ghrelin is involved in mediating spontaneous phase Ⅲ-like contractions of the rat stomach[J].Neurogastroenterology & Motility,2007,19(8):675-680.( 1) 1) |
| [101] | ZHENG J,ARIGA H,TANIGUCHI H,et al.Ghrelin regulates gastric phase Ⅲ-like contractions in freely moving conscious mice[J].Neurogastroenterology & Motility,2009,21(1):78-84.( 1) 1) |
| [102] | OHNO T,MOCHIKI E,KUWANO H.The roles of motilin and ghrelin in gastrointestinal motility[J].International Journal of Peptides,2010,2010:Article ID 820794.( 1) 1) |
| [103] | YANG C G,WANG W G,YAN J,et al.Gastric motility in ghrelin receptor knockout mice[J].Molecular Medicine Reports,2013,7(1):83-88.( 1) 1) |
| [104] | KORBONITS M,GOLDSTONE A P,GUEORGUIEV M,et al.Ghrelin-a hormone with multiple functions[J].Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology,2004,25(1):27-68.( 1) 1) |
| [105] | GONG Y L,XU L,GUO F F,et al.Effects of ghrelin on gastric distension sensitive neurons and gastric motility in the lateral septum and arcuate nucleus regulation[J].Journal of Gastroenterology,2014,49(2):219-230.( 1) 1) |
| [106] | DATE Y.Ghrelin and the vagus nerve[J].Methods in Enzymology,2012,514:261-269.( 2) 2) |
| [107] | HEWSON A K,DICKSON S L.Systemic administration of ghrelin induces Fos and Egr-1 proteins in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus of fasted and fed rats[J].Journal of Neuroendocrinology,2000,12(11):1047-1049.( 1) 1) |
| [108] | HAHN T M,BREININGER J F,BASKIN D G,et al.Coexpression of Agrp and NPY in fasting-activated hypothalamic neurons[J].Nature Neuroscience,1998,1(4):271-272.( 2) 2) |
| [109] | ANDREWS Z B.Central mechanisms involved in the orexigenic actions of ghrelin[J].Peptides,2011,32(11):2248-2255.( 2) 2) |
| [110] | ZHENG H Y,CORKERN M,STOYANOVA I,et al.Peptides that regulate food intake:appetite-inducing accumbens manipulation activates hypothalamic orexin neurons and inhibits POMC neurons[J].America Journal of Physiology:Regulatory,Integrative Comparative Physiology,2003,284(6):R1436-R1444.( 1) 1) |
| [111] | WANG L X,SAINT-PIERRE D H,TACH Y.Peripheral ghrelin selectively increases Fos expression in neuropeptide Y-synthesizing neurons in mouse hypothalamic arcuate nucleus[J].Neuroscience Letters,2002,325(1):47-51.( 1) 1) |
| [112] | ANDREWS Z B,LIU Z W,WALLLINGFORD N,et al.UCP2 mediates ghrelin's action on NPY/AgRP neurons by lowering free radicals[J].Nature,2008,454(7206):846-851.( 2) 2) |
| [113] | BILGIN H M,TUMER C,DIKEN H,et al.Role of ghrelin in the regulation of gastric acid secretion involving nitrergic mechanisms in rats[J].Physiological Research,2008,57(4):563-568.( 1) 1) |
| [114] | MASUDA Y,TANAKA T,INOMATA N,et al.Ghrelin stimulates gastric acid secretion and motility in rats[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2000,276(3):905-908.( 1) 1) |
| [115] | WANG Q,LIU C,UCHIDA A,et al.Arcuate AgRP neurons mediate orexigenic and glucoregulatory actions of ghrelin[J].Molecular Metabolism,2014,3(1):64-72.( 1) 1) |
| [116] | MULLER A F,JANSSEN J A,HOFLAND L J,et al.Blockade of the growth hormone (GH) receptor unmasks rapid GH-releasing peptide-6-mediated tissue-specific insulin resistance[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2001,86(2):590-593.( 1) 1) |
| [117] | GAUNA C,MEYLER F M,JANSSEN J A M J L,et al.Administration of acylated ghrelin reduces insulin sensitivity,whereas the combination of acylated plus unacylated ghrelin strongly improves insulin sensitivity[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2004,89(10):5035-5042.( 1) 1) |
| [118] | DELHANTY P J D,VAN DER LELY A J.Ghrelin and glucose homeostasis[J].Peptides,2011,32(11):2309-2318.( 2) 2) |
| [119] | ZHANG W Z,CHAI B X,LI J Y,et al.Effect of des-acyl ghrelin on adiposity and glucose metabolism[J].Endocrinology,2008,149(9):4710-4716.( 1) 1) |
| [120] | VAN DER LELY A J.Ghrelin and new metabolic frontiers[J].Hormone Research in Paediatrics,2009,71(Suppl.1):129-133.( 1) 1) |
| [121] | MUCCIOLI G,PONS N,GHÈ C,et al.Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin both inhibit isoproterenol-induced lipolysis in rat adipocytes via a non-type 1a growth hormone secretagogue receptor[J].European Journal of Pharmacology,2004,498(1/2/3):27-35.( 1) 1) |
| [122] | LÔPEZ M,LAGE R,SAHA A K,et al.Hypothalamic fatty acid metabolism mediates the orexigenic action of ghrelin[J].Cell Metabolisn,2008,7(5):389-399.( 1) 1) |
| [123] | ANDREWS Z B,HORVATH B,BARNSTABLE C J,et al.Uncoupling protein-2 is critical for nigral dopamine cell survival in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease[J].The Journal of Neuroscience,2005,25(1):184-191.( 1) 1) |




