2. 四川农业大学动物营养研究所, 成都 611130
2. Institute of Animal Nutrition, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu 611130, China
鱼类和哺乳动物一样,具有非特异性和特异性免疫功能,能通过黏膜屏障、组织和体液中各种免疫细胞和因子共同抵御病原入侵[1]。营养物质是鱼类健康和生长的重要保障。鱼类健康与其免疫功能密切相关[2]。因此,营养物质对鱼类免疫功能的影响是当前研究的新热点。精氨酸(arginine,Arg)是鱼类的必需氨基酸,能代谢产生具有免疫调节功能的活性物质,如一氧化氮(nitric oxide,NO),能激活巨噬细胞的吞噬活性[3]。研究表明:Arg能保护鱼鳃组织物理屏障功能,提高吞噬细胞吞噬功能和杀菌活性、溶菌酶杀菌活性、补体活性和特异性抗体滴度,增强鱼类免疫功能[4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];能抑制鱼类炎症反应,保护鱼体在免疫应答时免受自我损伤[8, 9]。本文简要总结Arg对鱼类免疫功能的影响及其机制,以期为进一步深入研究Arg对鱼类免疫功能的调控作用及其机制提供参考。
1 Arg对鱼类非特异性免疫功能的影响 1.1 对黏膜物理屏障功能的影响鱼类黏膜物理屏障包括上皮细胞和细胞间紧密连接,其中上皮细胞是具有选择透过性的半透膜[1]。氧化应激能使细胞膜上的蛋白质和脂肪氧化降解,破坏细胞膜结构[10]。蛋白质羰基(protein carbonyl,PC)和丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)分别是蛋白质和脂肪的氧化产物,其含量反映上皮细胞的氧化损伤程度[11]。鱼鳃直接接触水环境,具有气体交换和渗透调节功能,对鱼类至关重要。铜应激前在饲料中补充1.41% Arg饲喂草鱼8周,鳃组织MDA和PC含量分别降低42.9%和37.3%[9]。这表明Arg能减轻鳃组织氧化损伤,保护鳃上皮细胞完整性,增强应激条件下鱼鳃组织的物理屏障功能。上皮细胞结构完整性与其抗氧化能力有关,抗氧化酶活性和非酶抗氧化物质含量可反映鱼类抗氧化能力[10, 12]。抗氧化酶包括超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GPx)和谷胱甘肽硫转移酶(glutathione S-transferase,GST),谷胱甘肽(glutathione,GSH)则是重要的非酶抗氧化物质[11]。Arg能显著提高草鱼鳃组织SOD、CAT、GPx和GST活性及GSH含量[9, 13]。因此Arg能提高鱼类鳃组织抗氧化能力。转录因子NF-E2相关因子2(transcription factor nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor2,Nrf2)可上调SOD、CAT、GPx和GST基因的表达[10]。Wang等[9]在饲料中添加1.41% Arg后提高了草鱼鳃组织Nrf2 mRNA丰度。因此Arg能通过上调Nrf2基因表达,增强鱼鳃组织抗氧化酶基因表达而提高其活性。NO是Arg重要的代谢活性物质,能促进鱼类Nrf2基因的表达[10]。但目前未见Arg提高鱼鳃组织NO生成的相关报道。在塞内加尔鳎上的研究发现,饲料中添加0.8%和1.5% Arg时,头肾NO含量在正常养殖条件下分别提高25.0%和55.6%,应激条件下分别提高100%和245%[6],表明Arg可促进鱼体组织NO的产生。因此,Arg可能通过产生NO,上调组织Nrf2基因表达,促进抗氧化酶合成,提高组织抗氧化能力,保护鱼体在应激条件下的鳃上皮完整性,增强其屏障功能。但关于Arg对鱼类肠道和皮肤黏膜上皮细胞结构完整性的保护作用还未见相关报道,其保护鳃上皮细胞结构完整性的具体作用机制有待进一步研究。
由紧密连接蛋白颗粒重复排列形成的紧密连接是细胞间屏障结构[14]。紧密连接蛋白zonula occludens-1(ZO-1),occludin、claudin b和claudin 3是维系细胞间紧密连接结构的重要蛋白质,其基因表达下降可导致紧密连接结构和功能改变,损伤细胞间物理屏障功能[10, 15, 16]。研究表明,Arg能上调鱼鳃组织紧密连接蛋白基因表达,维持应激时鳃组织细胞间屏障功能正常。铜应激降低ZO-1、occludin、claudin b和claudin 3的表达,导致紧密连接破坏,削弱物理屏障功能[9, 11]。而铜应激前在草鱼饲料中补充1.41% Arg饲养8周,ZO-1、occludin、claudin b和claudin 3 mRNA丰度分别显著上升50.0%、71.4%、53.3%和53.8%[9]。关于Arg上调紧密连接蛋白基因表达的机制尚不清楚。研究表明,促炎因子如肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-1β(interleukin-1β,IL-1β)和白细胞介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)能够抑制紧密连接蛋白基因的表达[9, 11],而Arg能抑制鱼类肠道和鳃组织TNF-α、IL-1β和IL-6的表达[4, 8, 9]。因此,Arg可通过抑制TNF-α等促炎因子的表达,促进细胞间紧密连接蛋白合成,增强鱼类上皮细胞间物理屏障功能,但其具体机制尚待研究。
1.2 对非特异性免疫细胞功能的影响吞噬细胞是血液和组织器官中重要的非特异性免疫细胞[1, 17]。血液中吞噬细胞可在血液中或迁移到组织中吞噬和杀灭病原[1]。研究表明,适宜水平Arg能提高鱼类吞噬细胞的吞噬能力和杀菌活性。Pohlenz等[18]报道,在培养液中添加0.05 mmol/L Arg,斑点叉尾 吞噬细胞吞噬能力由13.7上升至24.7,杀菌活性由34.6%上升至50.4%;进一步添加Arg至1 mmol/L,吞噬能力上升至39.7。建鲤血液中吞噬细胞的吞噬能力随饲料Arg水平增加至1.61%而上升,但过高水平的Arg降低血液中吞噬细胞的吞噬能力[4]。其可能原因在于过量Arg导致氨基酸不平衡,氨基酸利用率降低,从而降低吞噬细胞的吞噬能力。
吞噬细胞的吞噬能力与其数量和吞噬活性有关。头肾是白细胞的生成场所[17]。研究表明,Arg能提高鱼类头肾指数以及血液中单核细胞和淋巴细胞数量[4, 6, 13]。因此,Arg能促进头肾发育和吞噬细胞的生成,从而提高吞噬能力。吞噬指数和吞噬百分数可反映吞噬细胞的吞噬活性。在斑点叉尾 饲料中添加0.5%、1.0%、2.0%和4.0% Arg,用荧光染料标记的大肠杆菌在培养基检测吞噬细胞的吞噬能力,发现其吞噬指数分别为0.002、0.005、0.014和0.008,吞噬百分数分别为100%、80%、130%和245%,表明Arg提高了斑点叉尾 血液中吞噬细胞的吞噬活性[19]。因此,Arg可以通过提高吞噬细胞数量和吞噬活性来增强吞噬细胞的吞噬能力。
吞噬细胞呼吸爆发产生的活性氧可杀灭入侵的病原,超氧阴离子是一种重要的活性氧,其产生量可反映吞噬细胞的杀菌活性[20]。在饲料中补充1%和2% Arg,杂交狼鲈头肾巨噬细胞产生胞外超氧阴离子的量分别提高41.8%和21.9%,胞内超氧阴离子量分别提高43.9%和34.1%,表明Arg可通过提高鱼类吞噬细胞活性氧的产生量来增强其杀菌活性[21];但补充1% Arg对红鼓鱼头肾巨噬细胞超氧阴离子的产生无显著影响[19]。其差异的原因可能在于Arg促进不同种鱼吞噬细胞产生活性氧的剂量存在差异,Arg对红鼓鱼吞噬细胞活性氧产生的影响需要进一步研究。
吞噬细胞能通过一氧化氮合成酶(nitric oxide synthase,NOS)利用Arg产生NO,NO能增强吞噬细胞活性氧的杀菌活性[22]。Arg能提高塞内加尔鳎血液中NO含量[10]。饲料中补充2.19% Arg,建鲤头肾诱导型一氧化氮合成酶(induced NOS,iNOS)活性提高340%[4]。饲料中添加2.57% Arg,军曹鱼血清NOS活性提高25.9%[23]。因此,Arg可能促进头肾和血液吞噬细胞利用Arg合成NO,增强活性氧杀菌活性。在大鼠上的研究表明,胰岛素能通过磷脂酰肌醇三磷酸激酶(phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase,PI-3K)/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,PKB)途径提高iNOS活性,提高NO的产生量[24]。Arg注射能显著提高大鳞大麻哈鱼、虹鳟和条斑星鲽血浆胰岛素水平[25, 26]。由此可以推测:Arg可能通过提高鱼体胰岛素水平,经PI-3K/PKB途径上调NOS活性,促进NO的生成,增强吞噬细胞活性氧杀菌活性,但其具体作用机制有待研究。
1.3 对非特异性抗菌物质活性的影响溶菌酶是非常重要的抗菌物质,能溶解细菌细胞壁,激活补体旁路和吞噬细胞活性,参与非特异性免疫防御[1]。研究表明,Arg能提高鱼类血清溶菌酶活性。杂交狼鲈饲料中添加1%和2%的Arg,血清溶菌酶活性分别提高50.5%和33.2%[21]。建鲤血清中溶菌酶活性在Arg添加水平为1.27%时提高68.8%[4]。饲料补充1%~4% Arg显著提高大菱鲆和斑点叉尾 血清溶菌酶活性[6, 27]。因此,Arg能提高鱼类血清中溶菌酶活性,以增强鱼类的非特异性免疫功能。但不同种类的鱼其适宜Arg水平存在差异,而过高水平的Arg会降低鱼类血清中溶菌酶活性[4, 21]。关于Arg影响溶菌酶活性的机制已有相关报道。研究发现,Arg可提高塞内加尔鳎G-型溶菌酶基因表达水平,从而提高溶菌酶的活性[9]。但Arg调控溶菌酶基因表达的机制有待研究。
补体(complement,C)可以被抗原-抗体复合物激活或直接被抗原激活,结合到抗原表面;也可以被外源细菌凝集素和炎症初期产生的蛋白共同激活,辅助非特异性免疫和特异性免疫[28]。半数溶血值可反映补体活性。饲料中Arg水平为2.52%时,大口黑鲈血清补体经典激活途径半数溶血值提高64.5%[29];长期应激条件下,在大菱鲆饲料中补充1% Arg,补体旁路激活途径半数溶血值显著提高44.2%[6],表明适宜水平Arg能提高鱼类血液中补体活性。但过量Arg会降低补体活性[6, 29]。C3在补体系统激活过程中起着枢纽作用,参与补体激活的3条通路;C4是补体经典激活途径的重要分子[30]。幼建鲤饲料中添加1.85% Arg时,C3和C4活性分别提高44.3%和40.0%[4]。但是添加过量Arg,鱼类血液中C3和C4活性有下降趋势[4]。这表明适宜水平的Arg能通过提高C3和C4活性,促进补体系统的激活,提高鱼类非特异性免疫功能。关于Arg提高C3和C4活性,激活补体系统的机制尚待研究。
1.4 对炎症反应的影响炎症反应受多种炎症细胞因子调节,能清除病原菌和坏死崩解的细胞碎屑,但过度反应会造成组织自我损伤[31]。鱼类炎症细胞因子水平与炎症细胞因子基因表达密切相关[7]。白细胞介素-4(interleukin-4,IL-4)和白细胞介素-10(interleukin-10,IL-10)是重要的抗炎因子,能抑制促炎因子如TNF-α和IL-6的合成[32]。TNF-α、IL-1β和IL-6主要通过诱导产生以白细胞介素-8(interleukin-8,IL-8)为主的趋化因子诱发炎症反应[33]。在大西洋鲑和草鱼上的研究发现,Arg能抑制应激引起的组织IL-8 mRNA表达上升[7, 9],表明Arg能抑制鱼类的炎症应答。Jiang等[8]报道,脂多糖(LPS)应激时,饲料中添加1.85% Arg后建鲤肠道TNF-α、IL-1β和IL-6 mRNA丰度分别降低96%、100%和46%,而IL-10 mRNA丰度提高29%。在培养液中添加300 mg/L Arg能完全抑制LPS应激引起的建鲤肠上皮细胞促炎因子基因表达升高,提高抗炎因子IL-10 mRNA的表达[8]。因此,Arg能上调抗炎因子表达,抑制促炎因子表达,起到抗炎作用。
关于Arg调控鱼类炎症因子基因表达的机制尚不完全清楚。分布于免疫细胞以及腔道上皮细胞表面的跨膜蛋白Toll样受体4(Toll-like receptor 4,TLR4)识别细菌LPS和病毒后,经髓样分化因子(myeloid differentiation factor88,MyD88)依赖途径激活促细胞分裂素原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen activated protein kinases,MAPK)信号转导通路,激活核因子-κB(NF-κB),诱导促炎因子分泌[34]。胞外信号调节蛋白激酶(extracelluar-signal regulated kinase,ERK)、促分裂原活化蛋白激酶p38(mitogen-activated protein kinases p38,MAPKp38)和c-Jun氨基末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase,JNK)是MAPK信号转导通路的主要成员[23, 34]。研究发现,Arg能抑制人回肠癌细胞Caco-2 ERK和JNK磷酸化[15]。饲料中添加1.85% Arg,饲养建鲤63 d后进行LPS应激,发现Arg组肠道TLR4、MyD88、MAPKp38和NF-κB mRNA丰度分别下降33.3%、38.2%、35.7%和23.3%[8]。因此,Arg可通过抑制TLR4通路MyD88依赖途径,下调MAPK信号转导和NF-κB活性,抑制鱼体炎症应答。NO是半衰期很短的小分子化合物,Connelly等[35]用LPS刺激体外培养的小鼠巨噬细胞,发现外源性NO可抑制巨噬细胞NF-κB活化,降低IL-6和IL-8的浓度,表明NO具有抗炎作用。Arg能促进鱼类NO的生成[4, 5, 36]。胰岛素能通过PI-3K/PKB促进NO的合成,抑制小鼠炎症反应[24]。研究表明,Arg能提高鱼类胰岛素水平[25, 26, 37]。因此,Arg可能通过抑制TLR4通路MyD88依赖途径,降低NF-κB活性,或通过胰岛素-PI-3K/PKB信号途径直接作用提高NOS活性,进而提高NO水平,抑制促炎因子的表达,发挥其抗炎作用(图1),但具体机制有待研究。
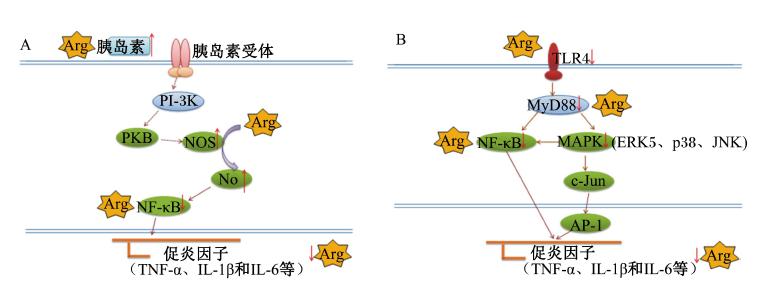 | 图1 Arg抑制鱼类炎症反应的可能通路 Fig. 1 The potential action pathway of Arg against inflammatory response in fish |
抗原经T淋巴细胞识别产生淋巴因子后,二者共同刺激B淋巴细胞分化为效应B淋巴细胞,分泌免疫球蛋白,介导体液免疫,杀伤病原体[19]。抗体滴度可反映组织中抗体含量。Pohlenz等[38]报道,饲料中添加4% Arg,受到灭活的爱德华氏菌应激时,斑点叉尾 血清抗体滴度提高18.2%;Arg补充条件下辅以相应的疫苗免疫,则血清、肠黏膜和胆汁抗体滴度分别提高230.0%、38.5%和195.5%。免疫球蛋白M(immuneglobulin M,IgM)是鱼类的主要抗体[39]。饲料中补充1.61% Arg,幼建鲤血清IgM滴度上升33.0%[13]。因此,Arg能提高免疫球蛋白滴度,增强鱼类特异性免疫功能。
Arg可通过促进鱼类淋巴细胞增殖,提高分泌IgM的B淋巴细胞的数量,以提高特异抗体滴度,增强鱼类特异性免疫功能。淋巴细胞主要包括T淋巴细胞和B淋巴细胞,二者共同介导体液免疫。淋巴细胞刺激指数可反映淋巴细胞增殖活性。Pohlenz等[18]报道,培养液中补充0.5和1.0 mmol/L Arg,斑点叉尾 淋巴细胞刺激指数较正常组分别提高155%和205%,LPS应激组分别提高28%和96%。IgM+细胞是能够分泌IgM的B淋巴细胞。Pohlenz等[38]报道,饲料中补充4% Arg,注射灭活爱德华氏菌后,斑点叉尾 血液中IgM+细胞含量提高2倍。这些结果表明:Arg能促进淋巴细胞增殖和B淋巴细胞分化为IgM+细胞,分泌IgM,增强体液免疫功能。关于Arg促进鱼B淋巴细胞增殖分化的机制尚待研究。免疫球蛋白的分泌受辅助性T(helper T,Th)细胞的调节,Th-2细胞可分泌IL-4和IL-10等细胞因子,促进免疫球蛋白的分泌[40]。Arg能提高建鲤IL-10 mRNA的丰度[8]。因此,Arg可能通过影响Th-2细胞IL-10分泌量,提高IgM+细胞分泌免疫球蛋白的能力,提高特异性抗体滴度,增强鱼类体液免疫功能,但具体机制有待研究。
2.2 对细胞免疫功能的影响T淋巴细胞表面具有特异性抗原受体,能与抗原特异性结合,介导细胞免疫杀伤抗原[17]。Pohlenz等[27, 38]报道,Arg能提高斑点叉尾 头肾、脾脏和血液中淋巴细胞活性。肾脏和脾脏是T淋巴细胞生成的主要场所,血液中淋巴细胞主要是T细胞。这揭示Arg可能促进T淋巴细胞增殖,增强细胞免疫功能。体外培养T淋巴细胞的研究表明,Arg能促进凝集素刺激时军曹鱼T淋巴细胞的增殖[23]。因此,Arg可通过促进T淋巴细胞增殖,以增强鱼类的细胞免疫功能。关于Arg促进鱼类T淋巴细胞增殖分化的机制尚待研究。在陆生动物上的研究表明Arg调节淋巴细胞增殖与IL-2无关,可能与Arg酶或Arg代谢产物相关,具体机制有待进一步研究[41]。
3 小 结综上所述,Arg能提高鱼鳃组织的黏膜物理屏障功能;提高吞噬细胞吞噬能力和杀菌活性,提高抗菌物质杀菌活性,以增强鱼类非特异性免疫功能;促进B淋巴细胞分泌免疫球蛋白,提高T淋巴细胞活性,以增强鱼类特异性免疫功能;抑制TLR4和MAPK通路,上调抗炎因子的表达,下调促炎因子的表达,发挥抗炎作用,保护鱼体免受免疫应答的自我损伤。但目前研究仅集中在斑点叉尾 、建鲤、大菱鲆、草鱼、杂交狼鲈和大口黑鲈等几种鱼类,Arg对鱼类黏膜化学屏障功能和免疫细胞增殖分化的影响及其机制有待进一步研究。
| [1] | ZHU L Y,NIE L,ZHU G,et al.Advances in research of fish immune-relevant genes:a comparative overview of innate and adaptive immunity in teleosts[J]. Developmental & Comparative Immunology,2013,39 (1/2):39-62. ( 4) 4)
|
| [2] | KIRON V.Fish immune system and its nutritional modulation for preventive health care[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology,2012,173(1/2):111-133. ( 1) 1)
|
| [3] | WEST N E J,QIAN H S,GUZIK T J,et al.Nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) gene transfer modifies venous bypass graft remodeling:effects on vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation and superoxide production[J]. Circulation,2001,104(13):1526-1532. ( 1) 1)
|
| [4] | CHEN G F,LIU Y,JIANG J,et al.Effect of dietary arginine on the immune response and gene expression in head kidney and spleen following infection of Jian carp with Aeromonas hydrophila[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2015,44(1):195-202. ( 10) 10)
|
| [5] | COSTAS B,CONCEIÇÀO L E C,DIAS J,et al.Dietary arginine and repeated handling increase disease resistance and modulate innate immune mechanisms of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup,1858)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2011,31(6):838-847. ( 2) 2)
|
| [6] | COSTAS B,GÊGO P C N P,CONCEIÇÀ L E C,et al.Dietary arginine supplementation decreases plasma cortisol levels and modulates immune mechanisms in chronically stressed turbot (Scophthalmus maximus)[J]. Aquaculture Nutrition,2013,19(Suppl.1):25-38. ( 6) 6)
|
| [7] | HOLEN E,ESPE M,ANDERSEN S M,et al.A co culture approach show that polyamine turnover is affected during inflammation in Atlantic salmon immune and liver cells and that arginine and LPS exerts opposite effects on p38MAPK signaling[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2014,37(2):286-298. ( 3) 3)
|
| [8] | JIANG J,SHI D,ZHOU X Q,et al.In vitro and in vivo protective effect of arginine against lipopolysaccharide induced inflammatory response in the intestine of juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var.Jian)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2015,42(2):457-464. ( 6) 6)
|
| [9] | WANG B,FENG L,JIANG W D,et al.Copper-induced tight junction mRNA expression changes,apoptosis and antioxidant responses via NF-κB,TOR and Nrf2 signaling molecules in the gills of fish:preventive role of arginine[J]. Aquatic toxicology,2015,158:125-137. ( 9) 9)
|
| [10] | ZHAO J,FENG L,LIU Y,et al.Effect of dietary isoleucine on the immunity,antioxidant status,tight junctions and microflora in the intestine of juvenile Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var.Jian)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2014,41(2):663-673. ( 6) 6)
|
| [11] | WEN H L,FENG L,JIANG W D,et al.Dietary tryptophan modulates intestinal immune response,barrier function,antioxidant status and gene expression of TOR and Nrf2 in young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2014,40(1):275-287. ( 4) 4)
|
| [12] | LUSHCHAK V I.Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals[J]. Aquatic Toxicology,2011,101(1):13-30. ( 1) 1)
|
| [13] | WANG B,LIU Y,FENG L,et al.Effects of dietary arginine supplementation on growth performance,flesh quality,muscle antioxidant capacity and antioxidant-related signalling molecule expression in young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,167:91-99. ( 3) 3)
|
| [14] | DELERIVE P,FRUCHART J C,STAELS B.Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in inflammation control[J]. The Journal of Endocrinol,2001,169:453-459. ( 1) 1)
|
| [15] | NIKLASSON L.Intestinal mucosal immunology of salmonids response to stress and infection and crosstalk with the physical barrier[D]. Ph.D.Thesis.Geoteborg:University of Gothenburg,2013. ( 2) 2)
|
| [16] | BEUTHEU S,GHOUZALI I,GALAS L,et al.Glutamine and arginine improve permeability and tight junction protein expression in methotrexate-treated Caco-2 cells[J]. Clinical Nutrition,2013,32(5):863-869. ( 1) 1)
|
| [17] | FUJITA H,CHIBA H,YOKOZAKI H,et al.Differential expression and subcellular localization of Claudin-7,-8,-12,-13,and -15 along the mouse intestine[J]. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry,2006,54(8):933-944. ( 3) 3)
|
| [18] | POHLENZ C,BUENTELLO A,MWANGI W,et al.Arginine and glutamine supplementation to culture media improves the performance of various channel catfish immune cells[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2012,32(5):762-768. ( 2) 2)
|
| [19] | BUENTELLO J A,REYES-BECERRIL M,ROMERO-GERALDO M D J,et al.Effects of dietary arginine on hematological parameters and innate immune function of channel catfish[J]. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health,2007,19(3):195-203. ( 3) 3)
|
| [20] | CHENG Z Y,BUENTELLO A,GATLIN D M Ⅲ.Effects of dietary arginine and glutamine on growth performance,immune responses and intestinal structure of red drum,Sciaenops ocellatus[J]. Aquaculture,2011,319(1/2):247-252. ( 1) 1)
|
| [21] | CHENG Z Y,GATLIN D M Ⅲ,BUENTELLO A.Dietary supplementation of arginine and/or glutamine influences growth performance,immune responses and intestinal morphology of hybrid striped bass (Morone chrysops×Morone saxatilis)[J]. Aquaculture,2012,362-363:39-43. ( 3) 3)
|
| [22] | WEYTS F A A,FLIK G,VERBURG-VAN KEMENADE B M L.Cortisol inhibits apoptosis in carp neutrophilic granulocytes[J]. Developmental & Comparative Immunology,1998,22(5/6):563-572. ( 1) 1)
|
| [23] | REN W K,CHEN S,YIN J,et al.Dietary arginine supplementation of mice alters the microbial population and activates intestinal innate immunity[J]. The Journal of Nutrition,2014,144(6):988-995. ( 3) 3)
|
| [24] | GAO F,GAO E H, YUE T L,et al.Nitric oxide mediates the antiapoptotic effect of insulin in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion:the roles of PI3-kinase,Akt,and endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation[J]. Circulation,2002,105(12):1497-1502. ( 2) 2)
|
| [25] | PLISETSKAYA E M,BUCHELLI-NARVAEZ L I,HARDY R W.Effects of injected and dietary arginine on plasma insulin levels and growth of pacific salmon and rainbow trout[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A:Physiology,1991,98(1):165-170. ( 2) 2)
|
| [26] | ANDOH T.Amino acids are more important insulinotropins than glucose in a teleost fish,barfin flounder (Verasper moseri)[J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology,2007,151(3):308-317. ( 2) 2)
|
| [27] | POHLENZ C,BUENTELLO A,HELLAND S L J,et al.Effects of dietary arginine supplementation on growth,protein optimization and innate immune response of channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque 1818)[J]. Aquaculture Research,2014,45(3):491-500. ( 2) 2)
|
| [28] | HOLLAND M C H,LAMBRIS J D.The complement system in teleosts[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2002,12(5):399-420. ( 1) 1)
|
| [29] | ZHOU H,CHEN N,QIU X,et al.Arginine requirement and effect of arginine intake on immunity in largemouth bass,Micropterus salmoides[J]. Aquaculture Nutrition,2012,18(1):107-116. ( 2) 2)
|
| [30] | JENKINS J A,OURTH D D.Opsonic effect of the alternative complement pathway on channel catfish peripheral blood phagocytes[J]. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology,1993,39(4):447-459. ( 1) 1)
|
| [31] | ZHANG G Y,HAN J Y,WELCH E J,et al.Lipopolysaccharide stimulates platelet secretion and potentiates platelet aggregation via TLR4/MyD88 and the cGMP-dependent protein kinase pathway[J]. Journal of Immunology,2009,182(12):7997-8004. ( 1) 1)
|
| [32] | FOEY A D,PARRY S L,WILLIAMS L M,et al.Regulation of monocyte IL-10 synthesis by endogenous IL-1 and TNF-α Role of the p38 and p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinases[J]. The Journal of Immunology,1998,160(2):920-928. ( 1) 1)
|
| [33] | REDDY K P,MARKOWITZ J E,RUCHELLI E D.Lamina propria and Circulating interleukin-8 in newly and previously diagnosed pediatric inflammatory bowel disease patients[J]. Digestive Diseases and Sciences,2007,52(2):365-372. ( 1) 1)
|
| [34] | TSE K H,CHOW K B S,LEUNG W K,et al.Lipopolysaccharide differentially modulates expression of cytokines and cyclooxygenases in dorsal root ganglion cells via Toll-like receptor-4 dependent pathways[J]. Neuroscience,2014,267:241-251. ( 1) 1)
|
| [35] | CONNELLY L,PALACIOS-CALLENDER M,AMEIXA C,et al.Biphasic regulation of NF-KB activity underlies the pro- and ant-inflammatory actions of nitric oxide[J]. Journal of Immunology,2001,166(3):3873- 3881. ( 1) 1)
|
| [36] | REN M C,AI Q H,MAI K S.Dietary arginine requirement of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum)[J]. Aquaculture Research,2014,45(2):225-233. ( 1) 1)
|
| [37] | ANDOH T.Stress inhibits insulin release induced by feeding and arginine injection in barfin flounder Verasper moseri[J]. Fisheries Science,2014,80(2):311-316. ( 1) 1)
|
| [38] | POHLENZ C,BUENTELLO A,CRISCITIELLO M F,et al.Synergies between vaccination and dietary arginine and glutamine supplementation improve the immune response of channel catfish against Edwardsiella ictaluri[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2012,33(3):543-551. ( 3) 3)
|
| [39] | ACTON R T,WEINHEIMER P F,HALL S J,et al.Tetrameric immune macroglobulins in three orders of bony fishes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1971,68(1):107-111. ( 1) 1)
|
| [40] | BURTON O T,NOVAL RIVAS M,ZHOU J S,et al.Immunoglobulin E signal inhibition during allergen ingestion leads to reversal of established food allergy and induction of regulatory T cells[J]. Immunity,2014,41(1):141-151. ( 1) 1)
|
| [41] | YU H R,KUO H C,HUANG L T,et al.L-arginine modulates neonatal lymphocyte proliferation through an interleukin-2 independent pathway[J]. Immunology,2014,143(2):184-192. ( 1) 1)
|




