引用本文

万春孟, 张铁涛, 吴学壮, 杨福合, 邢秀梅, 高秀华. 饲粮
L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂氨基酸消化率、血清氨基酸含量及血清生化指标的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2015, 27(12): 3789-3796.

WAN Chunmeng, ZHANG Tietao, WU Xuezhuang, YANG Fuhe, XING Xiumei, GAO Xiuhua. Effects of Dietary
L-Arginine Level on Amino Acid Digestibility, Serum Amino Acid Content and Serum Biochemical Indices of Growing Minks[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2015, 27(12): 3789-3796.

饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂氨基酸消化率、血清氨基酸含量及血清生化指标的影响
万春孟
1
, 张铁涛
2, 吴学壮
1, 杨福合
2, 邢秀梅
2, 高秀华
1

1. 中国农业科学院饲料研究所, 北京 100081;
2. 中国农业科学院特产研究所, 吉林省特种经济动物分子生物学省部共建重点实验室, 长春 130112
收稿日期: 2015-06-12
基金项目: 国家自然资源平台专项"特种经济动物种质资源共享平台"(2005DKA21102)
作者简介: 万春孟(1989-),男,山东青岛人,硕士研究生,从事动物营养与饲料科学研究。E-mail:932904711@qq.com
通讯作者: 高秀华,研究员,博士生导师,E-mail:xiuhuagao@126.com
摘要: 本试验旨在研究饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂氨基酸消化率、血清氨基酸含量及血清生化指标的影响。选取(60±3)日龄健康雄性水貂70只,随机分为7组,每组10个重复,每个重复为1只水貂。各组分别饲喂在基础饲粮中添加0(Ⅰ组)、0.20%(Ⅱ组)、0.40%(Ⅲ组)、0.60%(Ⅳ组)、0.80%(Ⅴ组)、1.00%(Ⅵ组)和1.20%(Ⅶ组)L-精氨酸的试验饲粮。预试期7 d,正试期60 d。结果表明:1)Ⅱ组水貂的丝氨酸、谷氨酸、脯氨酸、甘氨酸、丙氨酸、缬氨酸、异亮氨酸、酪氨酸、赖氨酸消化率显著或极显著高于组Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ、Ⅵ和Ⅶ组(P<0.05或P<0.01);Ⅱ组水貂的天冬氨酸、苏氨酸、亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸消化率显著或极显著高于Ⅲ和Ⅳ组(P<0.05或P<0.01)。2)Ⅵ和Ⅶ组水貂的血清精氨酸含量显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ组(P<0.05);水貂血清其他氨基酸含量各组间差异不显著(P>0.05)。3)Ⅳ组水貂血清总蛋白含量极显著高于Ⅴ和Ⅶ组(P<0.01),显著高于Ⅰ和Ⅵ组(P<0.05);Ⅲ和Ⅳ组水貂血清白蛋白含量极显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅴ、Ⅵ和Ⅶ组(P<0.01);Ⅳ组水貂血清球蛋白含量显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅴ和Ⅶ组(P<0.05);Ⅳ组水貂血清碱性磷酸酶活性显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅴ和Ⅶ组(P<0.05);Ⅳ组水貂血清乳酸脱氢酶活性显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅴ和Ⅶ组(P<0.05);各组水貂血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶和天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶活性差异不显著(P>0.05)。4)Ⅲ组水貂血清免疫球蛋白M含量显著高于Ⅰ组(P<0.05);Ⅱ、Ⅲ和Ⅳ组水貂血清补体3含量显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅴ、Ⅵ、Ⅶ组(P<0.05);各组水貂血清免疫球蛋白A、免疫球蛋白G和补体4含量差异不显著(P>0.05)。通过本试验的研究和回归分析发现,饲粮L-精氨酸添加水平为0.20%~0.41%(饲粮精氨酸总水平为1.65%~1.86%)时,育成期水貂能获得较好的氨基酸消化率和血清生化指标。
关键词:
精氨酸
育成期
水貂
氨基酸消化率
血清氨基酸含量
血清生化指标
Effects of Dietary L-Arginine Level on Amino Acid Digestibility, Serum Amino Acid Content and Serum Biochemical Indices of Growing Minks
WAN Chunmeng
1
, ZHANG Tietao
2, WU Xuezhuang
1, YANG Fuhe
2, XING Xiumei
2, GAO Xiuhua
1

1. Institute of Feed Research, Chinese Academy of Agriculture Sciences, Beijing 100081, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Special Animal Molecular Biology, Institute of Economic Animal and Plant Science, Chinese Academy of Agriculture Sciences, Changchun 130112, China
Abstract: This study was conducted to study the effects of dietary L-arginine(L-Arg) level on amino acid digestibility, serum amino acid content and serum biochemical indices of growing minks. Seventy healthy female mink at the age of 60 days were randomly divided into 7 groups with 10 replicates per group and 1 mink per replicate. The mink in 7 groups were fed experimental diets with L-Arg supplementation levels of 0(group Ⅰ), 0.20%(group Ⅱ), 0.40%(group Ⅲ), 0.60%(group Ⅳ), 0.80%(group Ⅴ), 1.00%(group Ⅵ) and 1.20%(group Ⅶ), respectively. The pre-test period lasted for 7 days and the trial lasted for 60 days. The results showed as follows:1) the digestibility of serine, glutamic acid, proline, glycine, alanine, valine, isoleucine, tyrosine and lysine in group Ⅱ was significantly higher than that in groups Ⅲ, Ⅳ, Ⅴ, Ⅵ and Ⅶ(P<0.05 or P<0.01). The digestibility of aspartic acid, threonine, leucine and phenylalanine digestibility in groups Ⅱ was significantly higher than that in groups Ⅲ and Ⅳ(P<0.05 or P<0.01). 2) The serum arginine content in groups Ⅵ and Ⅶ was significantly higher than that in groups Ⅰ, Ⅱ and Ⅲ(P<0.05). There were no significantly differences in the other serum amino acid contents among all groups(P>0.05). 3) The serum total protein content in groups Ⅳ was greatly significantly higher than that in groups Ⅴ and Ⅶ(P<0.01), and was significantly higher than that in groups Ⅰ and Ⅵ(P<0.05). The serum albumin content in group Ⅲ and Ⅳ was greatly significantly higher than that in groups Ⅰ, Ⅴ, Ⅵ and Ⅶ(P<0.01). The serum globulin content in group Ⅳ was significantly higher than that in groups Ⅰ, Ⅴ and Ⅶ(P<0.05). The serum alkaline phosphatase activity in group Ⅳ was significantly higher than that in groups Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅴ and Ⅶ(P<0.05). The serum lactic dehydrogenase activity in group Ⅳ was significantly higher than that in groups Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅴ and Ⅶ(P<0.05). There were no significantly differences in serum alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase activities among all groups(P>0.05). 4) The serum immunoglobulin M content in group Ⅲ was significantly higher than that in group Ⅰ(P<0.05). The serum complement 3 content in groups Ⅱ, Ⅲ and Ⅳ was significantly higher than that in groups Ⅰ, Ⅴ, Ⅵ and Ⅶ(P<0.05). There were no significantly differences in serum immunoglobulin A, immunoglobulin G and complement 4 contents among all groups(P>0.05). Through this trial study and regression analysis, when dietary L-Arg supplement level is 0.20% to 0.41%(dietary L-Arg total level is 1.65% to 1.86%), the growing minks can get better amino acid digestibility and serum biochemical indices.
Key words:
arginine
growing period
minks
amino acid digestibility
serum amino acid contents
serum biochemical indices
精氨酸是一种免疫营养剂,它能防止营养缺乏,而且能以特定方式刺激免疫细胞,增强免疫功能[1]。新生动物自身合成精氨酸的能力还没有发育完全,机体自身不能合成足够的精氨酸,因此需要在饲粮中补充精氨酸来满足动物的生长需要。但是在动物饲粮中添加过量的精氨酸后,精氨酸的吸收与色氨酸、赖氨酸和组氨酸等拮抗[2],从而影响多种氨基酸的消化率和血清氨基酸含量,同时增加饲粮的成本。因此,只有在饲粮中添加适量的精氨酸才有利于动物生长和各种氨基酸的消化吸收,提高饲粮转化率,增加养殖场的生产效益。血清生化指标是反映动物机体免疫功能、酶活性及脏器功能完整性的重要指标[3],同时,血清生化指标能够在一定程度上反映动物对饲粮蛋白质的利用情况。因此,测定水貂血清生化指标的变化有助于研究动物机体内的营养物质代谢变化情况[4]。目前与精氨酸相关的水貂血清生化指标的研究比较少,同时国内尚未明确给出水貂饲粮中精氨酸的适宜添加水平。因此,本文通过在水貂饲粮中添加不同水平的精氨酸,研究饲粮精氨酸水平对育成期水貂氨基酸消化率、血清氨基酸含量和血清生化指标的影响,为完善我国水貂饲养标准提供科学依据及探究精氨酸在水貂体内的营养作用机制奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验动物
在农业部长白山野生生物资源重点野外科学观测试验站的毛皮动物生产基地随机选择健康、体重相近的(60±3)日龄雌性水貂70只。
1.2 试验饲粮
水貂目前没有统一的饲养标准,参照前人对水貂营养需要量的研究结果[5]配制育成期水貂基础饲粮,其组成及营养水平见表1。
1.3 试验设计
将70只试验水貂随机分为7个组,每组10个重复,每个重复1只,通过方差分析调整各组间平均体重至差异不显著(P>0.05)。各组水貂分别饲喂在基础饲粮中添加0(Ⅰ组)、0.20%(Ⅱ组)、0.40%(Ⅲ组)、0.60%(Ⅳ组)、0.80%(Ⅴ组)、1.00%(Ⅵ组)和1.20%(Ⅶ组)L-精氨酸的试验饲粮。
1.4 饲养管理
试验开始前,对水貂接种犬瘟热和细小病毒疫苗。试验水貂均单笼饲养,每日07:30与15:30各饲喂1次,自由采食,自由饮水,每日记录实际采食量。预试期7 d,正试期60 d,试验从2014年7月9日到2014年9月14日。
1.5 消化代谢试验
试验开始42 d后,每组挑选6只体重相近的水貂进行消化代谢试验,消化代谢试验时间为2014年8月20日至2014年8月23日,共计4 d。采用全收粪法,消化代谢试验期间饲养管理与日常饲养管理相同。每天收集的粪便称重后按鲜重的5%加入10%硫酸溶液,并加少量甲苯防腐,保存于-20 ℃备用。将4 d的粪便混合均匀,先在80 ℃下杀菌2 h,然后降到65 ℃烘干至恒重,磨碎过40目筛,制成风干样本,以备实验室分析。
表 1
(Table 1)

表 1 基础饲粮组成及营养水平(风干基础)
Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of the basal diet (air-dry basis)
| %
| |
项目 Items | 含量 Content
| |
原料 Ingredients | |
膨化玉米粉 Extruded corn | 24.80 | |
膨化大豆 Extruded soybean | 25.00 | |
肉骨粉 Meat and bone meal | 15.00 | |
鱼粉 Fish meal | 15.00 | |
玉米蛋白粉 Corn gluten meal | 6.00 | |
乳酪粉 Cheese meal | 5.00 | |
赖氨酸 Lys | 0.40 | |
蛋氨酸 Met | 0.50 | |
食盐 NaCl | 0.30 | |
豆油 Soybean oil | 7.00 | |
预混料 Premix1) | 1.00 | |
合计 Total | 100.00 | |
营养水平 Nutrient levels2) | |
代谢能 ME/(MJ/kg) | 15.04 | |
粗蛋白质 CP | 33.66 | |
粗脂肪 EE | 15.97 | |
钙 Ca | 2.30 | |
总磷 TP | 1.38 | |
精氨酸 Arg | 1.45 | 1)预混料为每千克饲粮提供 The premix provided following per kg of the diet: VA 10 000 IU,VD3 2 000 IU,VE 100 IU,VB1 6 mg,VB2 10 mg,VB6 6 mg,VB12 0.1 mg,VK3 1 mg,VC 400 mg,烟酸 nicotinic acid 30 mg,泛酸 pantothenic acid 40 mg,生物素 biotin 0.2 mg,叶酸 folic acid 1 mg,胆碱 choline 400 mg,Fe 82 mg,Cu 20 mg,Mn 120 mg,Zn 50 mg,I 0.5 mg,Se 0.2 mg,Co 0.3 mg.
2)粗蛋白质、粗脂肪、钙、总磷、精氨酸为测定值,代谢能为计算值。CP,EE,Ca,TP and Arg were measured values,while ME was a calculated value.
|
|
表 1 基础饲粮组成及营养水平(风干基础)
Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of the basal diet (air-dry basis)
|
1.6 血清制备
饲养试验结束后,每组分别选取6只水貂,断指采血并消毒。每只采血5 mL,置于促凝固管中,静置待血清析出后3 500 r/min、4 ℃离心10 min。将分离出的血清分装在1.5 mL的Eppendorf管中,置于-80 ℃中保存、备用。
1.7 测定指标
盐酸水解法测定饲粮和粪便中的氨基酸含量,参考GB/T 5009.124—2003[6];用三氯乙酸沉淀血清中蛋白质后,用日立L-8900氨基酸分析仪测定血清中的氨基酸含量;血清天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(aspartate aminotransferase,AST)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(alanine aminotransferase,ALT)、碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,ALP)、乳酸脱氢酶(lactate dehydrogenase,LDH)活性及总蛋白(total protein,TP)、白蛋白(albumin,ALB)、免疫球蛋白A(immunoglobulin A,IgA)、免疫球蛋白G(immunoglobulin G,IgG)、免疫球蛋白M(immunoglobulin M,IgM)、补体3(complement 3,C3)和补体4(complement 4,C4)含量测定用试剂盒全部购自中生北控有限公司,按照试剂盒说明书操作使用VITAL-E全自动生化分析仪测定,血清球蛋白(globulin,GLOB)含量由TP和ALB含量差值计算获得。
1.8 数据统计
结果以“平均值±标准差”表示,试验数据采用SPSS 17.0软件进行统计分析,采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)进行差异显著性检验,其中P<0.05为差异显著,P<0.01为差异极显著。
2 结 果
2.1 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂氨基酸消化率的影响
由表2可知,在饲粮中添加不同水平的L-精氨酸对氨基酸消化率有极显著影响(P<0.01)。其中Ⅱ组水貂的丝氨酸、谷氨酸、脯氨酸、甘氨酸、丙氨酸、缬氨酸、异亮氨酸、酪氨酸、赖氨酸消化率显著或极显著高于组Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ、Ⅵ和Ⅶ组(P<0.05或P<0.01);Ⅱ组水貂的天冬氨酸、苏氨酸、亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸消化率显著或极显著高于Ⅲ和Ⅳ组(P<0.05或P<0.01)。
表 2
(Table 2)

表 2 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂氨基酸消化率的影响
Table 2 Effects of dietary L-Arg level on amino acid digestibility of growing minks
| %
| |
项目 Items |
组别 Groups
|
P值
P-value
| |
Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | Ⅶ | |
天冬氨酸 Asp | 89.56 ±2.60Aa | 89.51 ±2.87Aa | 84.63 ±2.14Bbc | 82.45 ±2.88Bc | 85.42 ±2.38ABbc | 83.51 ±2.30Bbc | 86.86 ±3.18ABab | 0.001 | |
丝氨酸 Ser | 88.35 ±1.05ABab | 90.46 ±2.85Aa | 86.40 ±1.73ABCbc | 84.06 ±2.57BCcd | 85.49 ±3.34ABCbc | 80.88 ±5.21Cd | 84.54 ±4.05BCbcd | 0.001 | |
苏氨酸 Thr | 91.97 ±0.73Aa | 92.08 ±2.08Aa | 88.08 ±1.40ABb | 86.31 ±2.65Bb | 88.99 ±4.32ABab | 85.70 ±5.22Bb | 88.99 ±1.79ABab | 0.003 | |
谷氨酸 Glu | 92.08 ±1.39ABab | 92.92 ±2.28Aa | 88.46 ±3.02BCcd | 87.03 ±3.26Ccd | 89.52 ±1.91ABCbc | 86.16 ±2.58Cd | 89.03 ±2.08ABCcd | 0.001 | |
脯氨酸 Pro | 89.75 ±1.59BCab | 91.46 ±2.35Aa | 85.91 ±3.00BCcd | 83.22 ±3.80Cd | 87.46 ±2.28ABCbc | 84.26 ±2.83Ccd | 84.01 ±4.07Ccd | 0.001 | |
甘氨酸 Gly | 85.33 ±1.81ABa | 88.27 ±2.73Aa | 80.97 ±3.12BCb | 78.34 ±3.47Cb | 80.94 ±3.04BCb | 78.58 ±2.94Cb | 80.47 ±3.31BCb | 0.001 | |
丙氨酸 Ala | 85.33 ±1.81ABa | 88.27 ±2.73Aa | 80.97 ±3.12BCb | 78.34 ±3.47Cb | 80.94 ±3.04BCb | 78.58 ±2.94Cb | 80.47 ±3.31BCb | 0.001 | |
半胱氨酸 Cys | 87.61 ±2.63Aab | 88.78 ±2.37Aa | 86.88 ±1.45Aab | 81.43 ±3.27Bcd | 86.96 ±2.03Aab | 84.51 ±4.78ABbc | 79.94 ±4.93Bd | 0.001 | |
缬氨酸 Val | 87.96 ±2.08ABab | 89.09 ±2.43Aa | 83.21 ±2.57Ccd | 81.03 ±3.07Cd | 84.93 ±2.97ABCbc | 81.08 ±1.54Cd | 84.01 ±3.76BCcd | 0.001 | |
甲硫氨酸 Met | 93.14 ±1.54Aab | 93.19 ±1.77Aab | 94.84 ±0.95Aa | 88.10 ±2.78Bc | 94.04 ±2.09Aab | 93.74 ±2.30Aab | 91.81 ±1.90Ab | 0.001 | |
异亮氨酸 Ile | 88.81 ±1.70ABab | 90.04 ±2.40Aa | 84.36 ±2.42Ccde | 82.38 ±2.96Ce | 86.17 ±2.48ABCbc | 82.75 ±1.72Cde | 85.61 ±3.18BCcd | 0.001 | |
亮氨酸 Leu | 92.11 ±1.32ABa | 92.54 ±1.75Aa | 87.59 ±2.13CDcd | 86.13 ±2.73Dd | 90.43 ±1.75ABCab | 86.79 ±1.01Dcd | 89.00 ±2.76BCDbc | 0.001 | |
酪氨酸 Tyr | 92.97 ±1.13Aa | 93.26 ±1.86Aa | 90.83 ±1.21ABb | 88.75 ±1.96Bb | 90.52 ±1.90ABb | 88.85 ±2.44Bb | 89.63 ±1.32Bb | 0.001 | |
苯丙氨酸 Phe | 91.25 ±1.48ABa | 92.05 ±1.77Aa | 87.01 ±1.77CDEcd | 85.52 ±2.38Ed | 89.88 ±1.85ABCab | 86.77 ±1.00DEcd | 88.81 ±1.88BCDbc | 0.001 | |
赖氨酸 Lys | 93.35 ±1.26ABb | 95.56 ±1.27Aa | 92.50 ±1.27Bbc | 89.73 ±2.10Cd | 91.52 ±1.43BCbc | 92.34 ±1.68Bbc | 90.89 ±0.89BCcd | 0.001 | |
组氨酸 His | 93.04 ±1.02ABab | 93.71 ±1.56Aa | 90.76 ±1.53BCDcd | 89.30 ±2.32CDde | 91.83 ±1.67ABCabc | 88.72 ±1.88De | 91.10 ±0.96ABCDbcd | 0.001 | |
精氨酸 Arg | 95.59 ±0.69Aa | 95.33 ±0.41Aa | 94.76 ±0.71ABabc | 95.07 ±1.16ABabc | 94.27 ±1.09ABbc | 94.01 ±0.89Bc | 94.08 ±0.64Bc | 0.001 | 同行数据肩标不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.01),相同或无字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。下表同。
In the same row,values with different small letter superscripts mean significant difference (P<0.05),and with different capital letter superscripts mean significant difference (P<0.01),while with the same or no letter superscripts mean no significant difference (P>0.05). The same as below.
|
|
表 2 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂氨基酸消化率的影响
Table 2 Effects of dietary L-Arg level on amino acid digestibility of growing minks
|
2.2 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂血清氨基酸含量的影响
由表3可知,Ⅵ和Ⅶ组水貂的血清精氨酸含 量显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ组(P<0.05);水貂血清其他氨基酸含量各组间差异不显著(P>0.05)。
表 3
(Table 3)

表 3 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂血清氨基酸含量的影响
Table 3 Effects of dietary L-Arg level on serum amino acids content of growing minks
| nmol/L
| |
项目 Items |
组别 Groups
|
P值
P-value
| |
Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | Ⅶ | |
天冬氨酸 Asp | 15.33±1.83 | 15.75±0.69 | 14.61±1.23 | 11.97±0.90 | 14.22±0.69 | 11.22±0.36 | 14.97±1.35 | 0.885 | |
丝氨酸 Ser | 28.14±0.72 | 19.74±0.42 | 22.92±0.93 | 20.46±0.39 | 20.79±2.19 | 17.43±2.07 | 21.33±0.75 | 0.450 | |
苏氨酸 Thr | 26.31±0.90 | 18.21±1.44 | 16.47±1.71 | 16.11±0.93 | 13.20±0.69 | 16.80±0.96 | 21.30±1.83 | 0.384 | |
谷氨酸 Glu | 39.51±1.89 | 41.37±2.73 | 40.35±0.66 | 37.83±2.55 | 36.93±1.68 | 37.26±1.59 | 37.77±0.90 | 0.298 | |
脯氨酸 Pro | 12.21±1.29 | 9.54±0.78 | 14.40±1.59 | 8.10±0.63 | 9.69±0.15 | 9.18±0.84 | 12.90±1.50 | 0.470 | |
甘氨酸 Gly | 28.80±0.90 | 26.91±2.70 | 30.00±1.29 | 26.43±2.31 | 18.21±1.77 | 21.57±2.31 | 22.29±0.75 | 0.337 | |
丙氨酸 Ala | 55.62±1.11 | 54.69±2.01 | 44.43±0.09 | 49.62±2.13 | 48.78±2.88 | 50.43±2.73 | 54.66±1.95 | 0.958 | |
缬氨酸 Val | 26.70±1.14 | 26.04±2.76 | 24.48±2.88 | 22.05±1.83 | 22.20±2.40 | 20.49±1.20 | 24.72±2.79 | 0.909 | |
半胱氨酸Cys | 1.02±0.03 | 1.29±0.18 | 0.87±0.09 | 0.81±0.45 | 0.63±0.09 | 0.63±0.06 | 0.75±0.09 | 0.289 | |
蛋氨酸Met | 1.98±0.27 | 2.19±0.24 | 2.85±0.15 | 1.89±0.06 | 1.83±0.21 | 1.68±0.21 | 1.65±0.18 | 0.287 | |
异亮氨酸Ile | 7.62±0.45 | 6.93±0.81 | 5.22±0.57 | 4.74±0.21 | 4.86±0.63 | 4.68±0.51 | 5.55±0.75 | 0.259 | |
亮氨酸 Leu | 42.48±0.81 | 36.42±1.17 | 36.45±2.25 | 35.46±4.65 | 33.75±4.20 | 32.07±2.79 | 32.97±2.01 | 0.353 | |
酪氨酸 Tyr | 8.55±0.18 | 6.78±0.78 | 6.18±0.63 | 6.48±0.36 | 5.25±0.93 | 6.45±0.78 | 5.58±0.36 | 0.634 | |
苯丙氨酸 Phe | 8.22±0.36 | 6.60±0.78 | 6.18±0.33 | 5.88±0.33 | 5.76±0.84 | 6.30±0.48 | 4.56±0.45 | 0.669 | |
鸟氨酸 Orn | 5.10±0.66 | 4.89±0.51 | 5.25±0.60 | 5.43±0.48 | 4.86±0.51 | 4.80±0.63 | 4.83±0.48 | 0.796 | |
赖氨酸 Lys | 28.05±0.87 | 24.09±1.23 | 24.42±0.90 | 23.64±1.50 | 21.33±0.93 | 21.03±0.63 | 21.36±1.17 | 0.235 | |
组氨酸 His | 6.18±0.60 | 5.25±0.51 | 5.37±0.81 | 5.97±0.87 | 5.10±0.21 | 5.22±0.39 | 6.39±0.54 | 0.801 | |
精氨酸 Arg | 9.84±1.56b | 9.90±0.81b | 10.23±1.11b | 11.58±0.54ab | 13.37±1.38ab | 18.39±1.47a | 17.07±0.72a | 0.047 |
|
表 3 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂血清氨基酸含量的影响
Table 3 Effects of dietary L-Arg level on serum amino acids content of growing minks
|
2.3 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂血清生化指标的影响
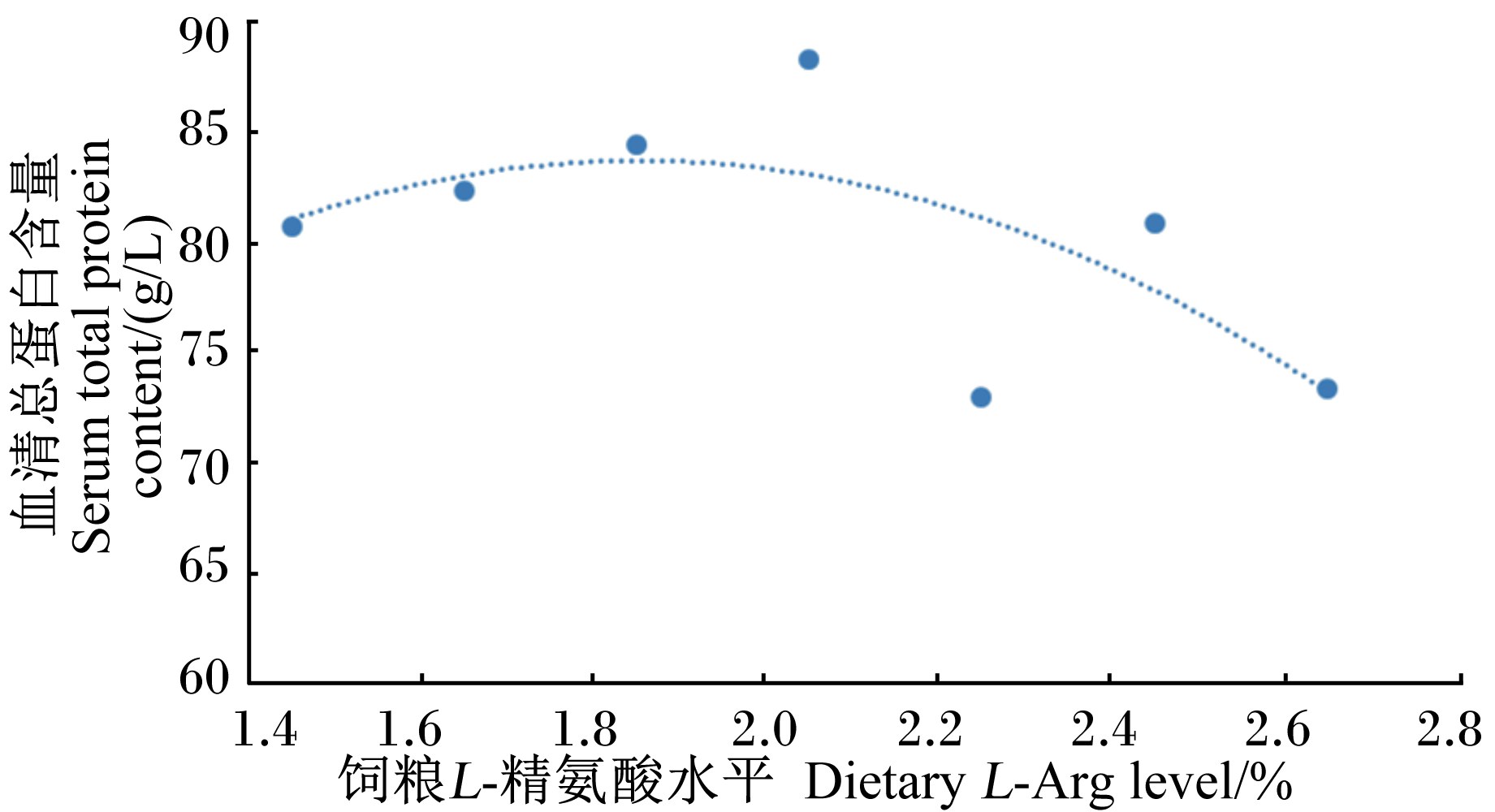
由表4可知,Ⅳ组水貂血清TP含量极显著高于Ⅴ和Ⅶ组(P<0.01),显著高于Ⅰ和Ⅵ组(P<0.05);Ⅲ和Ⅳ组水貂血清ALB含量极显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅴ、Ⅵ和Ⅶ组(P<0.01);Ⅳ组水貂血清GLOB含量显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅴ和Ⅶ组(P<0.05);Ⅳ组水貂血清ALP活性显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅴ和Ⅶ组(P<0.05);Ⅳ组水貂血清LDH活性显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅴ和Ⅶ组(P<0.05);各组水貂血清ALT和AST活性差异不显著(P>0.05)。
以血清TP含量为指标,建立的回归方程为:
Y=-16.464X2+60.993X+27.289 (R2=0.448,P<0.01)。
式中:Y为血清TP含量(g/L),X为饲粮L-精氨酸水平。通过回归曲线得出,当饲粮L-精氨酸水平为1.86%时,血清TP含量最高。
表 4
(Table 4)

表 4 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂血清常规生化指标的影响
Table 4 Effects of dietary L-Arg level on serum routine biochemical indices of growing minks
|
项目 Items |
组别 Groups
|
P值
P-value
| |
Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | Ⅶ | |
总蛋白 TP/(g/L) | 80.78 ±1.87ABb | 82.42 ±4.21Aab | 84.46 ±1.25Aab | 88.40 ±1.48Aa | 73.08 ±6.66Bc | 80.95 ±5.29ABb | 73.40 ±2.45Bc | 0.001 | |
白蛋白 ALB/(g/L) | 42.42 ±1.47BCbc | 44.64 ±2.44ABab | 46.89 ±1.77Aa | 47.97 ±1.20Aa | 36.09 ±4.38Dd | 41.71 ±1.78BCbc | 39.02 ±1.28CDcd | 0.001 | |
球蛋白 GLOB/(g/L) | 36.90 ±1.32b | 37.98 ±1.29ab | 37.85 ±0.49ab | 41.12 ±1.91a | 34.75 ±5.44b | 42.55 ±4.17a | 35.79 ±2.84b | 0.112 | |
丙氨酸氨基 转移酶 ALT/(U/L) | 81.36 ±10.02 | 82.32 ±11.11 | 81.06 ±10.29 | 81.72 ±10.98 | 87.78 ±12.25 | 82.92 ±13.30 | 78.08 ±10.05 | 0.746 | |
天门冬氨酸 氨基转移酶 AST/(U/L) | 101.61 ±12.28 | 98.26 ±10.80 | 90.62 ±11.09 | 109.56 ±10.70 | 98.26 ±11.45 | 100.44 ±12.89 | 97.70 ±10.79 | 0.061 | |
碱性磷酸酶 ALP/(U/L) | 171.13 ±15.40ABab | 160.69 ±14.73Ba | 184.02 ±10.61ABabc | 208.72 ±15.53Ac | 161.96 ±16.69ABa | 202.66 ±16.99ABbc | 166.70 ±16.10ABa | 0.016 | |
乳酸脱氢酶 LDH/(U/L) | 1 289.49 ±106.76c | 1 286.67 ±129.00c | 1 367.10 ±149.29abc | 1 707.02 ±176.12a | 1 335.58 ±112.55bc | 1 678.09 ±121.86ab | 1 249.18 ±118.08c | 0.015 |
|
表 4 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂血清常规生化指标的影响
Table 4 Effects of dietary L-Arg level on serum routine biochemical indices of growing minks
|
2.4 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂血清免疫生化指标的影响
由表5可知,Ⅲ组水貂血清IgM含量显著高于Ⅰ组(P<0.05);Ⅱ、Ⅲ和Ⅳ组水貂血清C3含量显著高于Ⅰ、Ⅴ、Ⅵ、Ⅶ组(P<0.05);各组水貂血清IgA、IgG和C4含量差异不显著(P>0.05)。
3 讨 论
3.1 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂氨基酸消化率和血清氨基酸含量的影响
在本试验中,对照组(Ⅰ组)和Ⅱ组的氨基酸消化率高于其他各组。这说明当饲粮中的L-精氨酸水平过高时,会显著影响饲粮中氨基酸的消化率。Wu等[2]研究发现,精氨酸的吸收与色氨酸、赖氨酸和组氨酸等拮抗。因此,当饲粮中精氨酸水平过高时会影响色氨酸、赖氨酸和组氨酸等多种氨基酸的消化吸收,从而影响多种氨基酸的消化率。这与本试验的研究结果基本一致。血清中游离氨基酸含量在一定程度上可以反映动物体内氨基酸代谢状况[7]。当饲粮氨基酸不能满足动物需要时血清游离氨基酸含量偏低;在满足动物需要的前提下,进一步平衡饲粮氨基酸组成也可降 低血清游离氨基酸含量,这是由于氨基酸在体内 向不同组织器官的分流比例更趋合理继而利用效率提高的原因。血清氨基酸含量通常与饲料中相应氨基酸含量一致,有研究发现增加饲粮中某种氨基酸含量会使血清中该氨基酸含量升高[8]。在本试验中,随着饲粮中精氨酸含量的增加,水貂血清中游离氨基酸含量没有表现出差异。但是,随着饲粮精氨酸水平的增加,血清中精氨酸的含量逐渐增加,这与前人的研究结果[7, 8]一致。
表 5
(Table 5)

表 5 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂血清免疫生化指标的影响
Table 5 Effects of dietary L-Arg level on serum immune biochemical indices of growing mink
| g/L
| |
项目 Items |
组别 Groups
|
P值
P-value
| |
Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | Ⅶ | |
免疫球蛋白A IgA | 0.38±0.04 | 0.39±0.05 | 0.34±0.04 | 0.35±0.03 | 0.38±0.02 | 0.36±0.05 | 0.40±0.04 | 0.722 | |
免疫球蛋白M IgM | 0.52±0.06b | 0.58±0.02ab | 0.64±0.04a | 0.58±0.06ab | 0.58±0.06ab | 0.58±0.08ab | 0.59±0.06ab | 0.232 | |
免疫球蛋白G IgG | 7.29±0.38 | 7.85±0.67 | 6.62±0.70 | 7.53±0.72 | 6.62±0.28 | 6.57±0.52 | 6.32±0.23 | 0.308 | |
补体3 C3 | 0.32±0.01b | 0.33±0.01a | 0.33±0.01a | 0.33±0.01a | 0.32±0.01b | 0.32±0.01b | 0.32±0.01b | 0.040 | |
补体4 C4 | 0.10±0.04 | 0.12±0.03 | 0.10±0.05 | 0.11±0.05 | 0.06±0.03 | 0.08±0.04 | 0.06±0.03 | 0.594 |
|
表 5 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂血清免疫生化指标的影响
Table 5 Effects of dietary L-Arg level on serum immune biochemical indices of growing mink
|
3.2 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂血清常规生化指标的影响
血清中蛋白质类物质的含量与动物采食的饲粮具有相关性[9]。血液中的TP由ALB和GLOB组成,血液中的蛋白质指标是反映机体蛋白质合成代谢和营养状况的重要标志,血液中TP含量高是蛋白质代谢旺盛的表现,有利于促进动物的生长和提高饲料转化率[10]。ALT与AST主要分布在肝细胞内,其中ALT主要分布在肝细胞质中,AST主要分布在肝细胞浆和肝细胞线粒体中,可以反映机体中肝脏合成蛋白质的能力和肝脏功能的状况[11]。同时,ALP和LDH活性可以反映肝脏和肾脏的功能状况,AST和ALT活性反映蛋白质代谢和氨基酸利用水平[12]。潘杰等[13]研究发现,在仔猪饲粮中添加精氨酸后,仔猪血清中TP、ALB含量以及ALP、谷丙转氨酶活性均高于对照组。在本试验中,在育成期水貂饲粮中添加适宜的精氨酸后能显著的提高水貂血清中的TP、ALB和GLOB含量,这说明在育成期水貂饲粮中添加适宜的精氨酸后能显著提高育成期水貂对蛋白质的消化代谢,促进育成期水貂的生化和对饲粮的转化率[10]。同时,在饲粮中添加适宜的精氨酸后显著提高了育成期水貂血清中的ALP和LDH的活性,这说明在育成期水貂饲粮中添加适宜的精氨酸能提高肝脏和肾脏的的功能状况。因此,在动物饲粮中添加适宜的L-精氨酸能提高的蛋白质的消化代谢,同时能提高肝脏和肾脏的的功能状况。
3.3 饲粮L-精氨酸水平对育成期水貂血清免疫生化指标的影响
免疫球蛋白是血清TP的组成部分,能够直接反映水貂机体免疫能力。补体是存在于正常人和动物血清与组织液中的一组经活化后具有酶活性的蛋白质。免疫球蛋白是构成体液免疫作用的主要物质,它与补体结合后可杀死细菌和病毒[14]。精氨酸能够改善机体的体液免疫功能。李新国等[15]研究发现,在7日龄断奶仔猪饲粮中添加梯度的精氨酸,在试验第14天发现精氨酸显著提高了仔猪血清免疫球蛋白的含量。在本试验中,在育成期水貂饲粮中添加适宜的精氨酸能显著提高育成期水貂血清中的IgM和C3的含量,该试验结果与前人的研究结果[14, 15]基本一致。因此,在育成期水貂饲粮中添加适宜的精氨酸能提高育成期水貂的免疫功能。
4 结 论
通过本试验的研究和回归分析发现,饲粮L-精氨酸添加水平为0.20%~0.41%(饲粮精氨酸总水平为1.65%~1.86%)时,育成期水貂能获得较好的氨基酸消化率和血清生化指标。
 1)
1)
 2)
2)
 1)
1)
 1)
1)
 1)
1)
 1)
1)
 2)
2)
 2)
2)
 1)
1)
 2)
2)
 1)
1)
 1)
1)
 1)
1)
 2)
2)
 2)
2)




