2. 西南科技大学生命科学与工程学院, 绵阳 621010
2. School of Life Science and Engineering, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang 621010, China
磷是动物体所必需的矿物质元素之一,对机体的生理功能和代谢功能起着重要的作用。但植物性饲料中磷含量较低,而且60%~80%是以植酸盐的形式存在,由于单胃动物体内缺少分解植酸盐的内源酶系统,因而极少能被单胃动物所利用[1]。为提高动物生长性能,有必要在饲粮中添加无机磷以满足动物的营养需要量,目前使用较为广泛的无机磷主要包括磷酸氢钙(dicalcium phosphate, DCP)和磷酸二氢钙(monocalcium phosphate, MCP)[2-4]。前期研究表明,通过使用线性回归模型分析饲粮总磷摄入量与动物可消化磷之间的关系,可推导出饲料原料中磷的真消化率和猪内源磷排泄量[5-8]。影响饲粮中磷的消化率的因素有多种,包括饲粮磷水平、钙磷比、植酸酶活性以及饲粮中粗纤维和碳水化合物的组成和含量等[8-14]。Nortey等[14]研究发现,以小麦作为基础饲粮,使用小麦次粉部分替换基础饲粮的小麦,结果表明,磷的表观回肠和全肠道消化率随着小麦次粉替换小麦水平的增加而显著降低。以上结果表明,饲粮中碳水化合物组成及含量显著影响磷的消化利用效率。因此,为提高生长猪对饲料中无机磷的利用效率,应弄清楚无机磷中磷的消化率是否受到基础饲粮组成的影响。考虑到玉米和小麦在植酸酶活性和饲粮碳水化合物组成上存在显著差异,且二者是猪饲粮中主要的能量饲料,本试验通过在玉米-豆粕型饲粮和小麦-豆粕型饲粮中分别添加不同水平DCP和MCP,比较基础饲粮组成对DCP和MCP中无机磷的全肠道真消化率(true total tract digestibility, TTTD)的影响。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验设计和饲养管理试验在动物营养学国家重点实验室昌平试验基地进行。试验1选用10头平均体重(30.4±1.8)kg的“杜×长×大”三元杂交阉公猪,采用10×8不完全拉丁方设计,分别饲喂含有5种DCP添加水平的玉米-豆粕型和含有5种DCP添加水平的小麦-豆粕型饲粮,进行8期消化试验,试验1饲粮组成及营养水平见表 1。试验2选用10头平均体重为(30.9±1.5)kg的“杜×长×大”三元杂交阉公猪,按照10×8不完全拉丁方设计,分别饲喂含有5种MCP添加水平的玉米-豆粕型和含有5种MCP添加水平的小麦-豆粕型饲粮,进行8期消化试验,试验2饲粮组成及营养水平见表 2。试验动物于不锈钢代谢笼内饲养,自然光照,室温控制在20℃左右。每期消化试验包括5 d的饲粮适应期和2 d的粪便收集期。采食量根据试验动物体重的4%计算得出,分2次分别于每天08:00和17:00饲喂,试验期间试验动物自由饮水。
|
|
表 1 试验1饲粮组成及营养水平(饲喂基础) Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of diets used in experiment 1 (as-fed basis) |
|
|
表 2 试验2饲粮组成和营养水平(饲喂基础) Table 2 Composition and nutrient levels of diets used in experiment 2 (as-fed basis) |
试验经过5 d饲粮适应期后,在试验期的第6天和第7天08:00至18:00收集试验动物排出的全部粪便。收集粪便样品后立即置于-20℃冰箱中冷冻保存,待试验结束后将每头猪收集的全部粪便样品混合均匀后,置于65℃烘箱干燥后粉碎待测。
1.3 测定指标与方法试验饲粮的常规营养成分及粪便样品的干物质、总磷含量的测定参考张丽英[15]测定方法,三氧化二铬含量参考Fenton等[16]提出的方法进行测定。
1.4 磷的消化率计算方法磷的表观全肠道消化率(apparent total tract digestibility, ATTD)按照以下公式计算:

|
总粪磷排泄量根据以下公式计算:
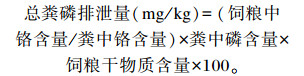
|
全肠道的可消化磷含量计算根据以下公式:
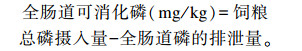
|
使用线性回归法测定磷的TTTD按照公式:
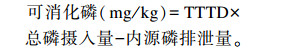
|
如上述公式所描述,使用全肠道可消化磷含量与饲粮总磷摄入量做回归方程,得出的回归方程斜率即为饲粮中磷的TTTD。
1.5 统计分析使用SAS 9.3统计分析软件中的一般线性模型(GLM)程序进行方差分析和显著性检验,并进行多重比较。结果以平均值±标准误表示,差异显著水平为P < 0.05和P < 0.01。
2 结果与分析试验期间所有生长猪健康状况正常,并按照相应的采食量采食完所有试验饲粮。
2.1 饲粮添加DCP对生长猪磷消化率的影响(试验1)由表 3可知,总粪磷排泄量、全肠道可消化磷含量及磷的ATTD均随着DCP在玉米-豆粕型饲粮和小麦-豆粕型饲粮中添加水平的增加而线性增加(P < 0.01),且总粪磷排泄量和磷的ATTD随着DCP在玉米-豆粕型饲粮中添加水平的增加而呈二次函数增加(P < 0.05)。在添加DCP后,玉米-豆粕型饲粮中总粪磷排泄量极显著高于小麦-豆粕型饲粮(P < 0.01),而小麦-豆粕型饲粮中的全肠道可消化磷含量及磷的ATTD极显著高于玉米-豆粕型饲粮(P < 0.01)。但饲粮类型和磷水平的互作效应对总粪磷排泄量、全肠道可消化磷含量及磷的ATTD的影响不显著(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 3 饲粮添加磷酸氢钙对生长猪磷消化率的影响(试验1) Table 3 Effects of dietary dicalcium phosphate on the digestibility of phosphorus of growing pigs (experiment 1) |
全肠道可消化磷与总磷摄入量之间显著线性相关是使用线性回归法测定磷的真消化率的前提条件,本试验结果满足上述条件。根据回归方程的公式,以mg/kg为单位计算磷的排泄量,由此得出的线性回归方程。由表 5可知,生长猪采食添加DCP的玉米-豆粕型饲粮和小麦-豆粕型饲粮后,得到的回归方程分别为Y=0.823 3X-2 035.54和Y=0.828 8X-1 840.51。其中Y表示可消化磷含量,X代表饲粮总磷摄入量。生长猪对玉米-豆粕型饲粮和小麦-豆粕型饲粮DCP中磷的TTTD分为82.33%和82.88%,二者差异不显著(P>0.05)。其相应的内源性磷损失分别为2 036和1 841 mg/kg干物质摄入量,其回归方程相应的决定系数(R2)分别为0.948 1和0.936 4,回归方程拟合良好。
|
|
表 4 饲粮添加磷酸二氢钙对生长猪磷消化率的影响(试验二) Table 4 Effects of dietary monocalcium phosphate on the digestibility of phosphorus for growing pigs (experiment 2) |
由表 4可知,玉米-豆粕型饲粮和小麦-豆粕型饲粮中,随着MCP添加水平的增加,总粪磷排泄量、全肠道可消化磷含量及磷的ATTD均呈线性增加(P < 0.01)。在玉米-豆粕型饲粮和小麦-豆粕型饲粮中添加MCP后,小麦-豆粕型饲粮中总粪磷排泄量极显著低于玉米-豆粕型饲粮(P < 0.01),但小麦-豆粕型饲粮中全肠道可消化磷含量及磷的ATTD极显著高于玉米-豆粕型饲粮(P < 0.01)。但饲粮类型和磷水平的交互作用对总粪磷排泄量、全肠道可消化磷含量及磷的ATTD均无显著影响(P>0.05)。
由表 5可知,通过线性回归法,生长猪采食添加MCP的玉米-豆粕型饲粮和小麦-豆粕型饲粮后,得到的回归方程分别Y=0.858 8X-2 062.44和Y=0.846 2X-1 874.62,生长猪基础饲粮组成对MCP中磷的TTTD分别为85.88%和84.62%,二者无显著差异(P>0.05)。内源性磷损失分别为2 062和1 875 mg/kg干物质摄入量,其回归方程相应的R2分别为0.913 1和0.922 8,回归方程拟合良好。
|
|
表 5 生长猪基础饲粮类型对无机磷中磷真消化率的影响 Table 5 Effect of dietary type on the true digestibility of phosphorus in inorganic phosphorus for growing pigs |
在本试验条件下,在无DCP和MCP添加的玉米-豆粕型和小麦-豆粕型饲粮中生长猪对磷的ATTD分别为16.91%~18.27%和28.99%~30.43%,与刘正群等[17]报道磷的ATTD均基本相近。通过在玉米-豆粕型和小麦-豆粕型2种类型饲粮中添加可消化磷含量较高的DCP,可显著提高总粪磷排泄量及全肠道可消化磷含量,磷的ATTD也相应增加,这与Wu等[7]、刘正群等[17]及Seynaeve等[18]研究结果一致。通过在上述2种类型饲粮中添加富含可消化磷的MCP时,也均可显著提高总粪磷排泄量、全肠道可消化磷含量及生长猪对磷的ATTD,这与Stein等[19]研究结果一致。且Beers等[20]研究也发现,在仔猪饲粮中添加MCP也可显著提高仔猪对磷的ATTD。在总磷含量相近的2种类型饲粮中,生长猪对小麦-豆粕型饲粮中磷的ATTD显著高于玉米-豆粕型饲粮中磷的ATTD,这可能与小麦中的可消化磷含量高于玉米中的可消化磷含量相关[21]。故在畜牧业生产中,为减少环境的中磷排放,可以考虑用小麦部分替代玉米作为能量饲料。
3.2 基础饲粮组成对生长猪磷的TTTD的影响目前饲料原料中磷真消化率的评定方法主要包括同位素稀释技术、差量法及线性回归法等[22]。在各种测定方法中,由Fan等[5]和Shen等[6]提出的线性回归法被认为是测定饲料原料中磷的真消化率和动物内源磷排泄量的可靠方法,且使用较为广泛。线性回归法测定结果是否准确主要在于动物内源磷排泄量和待测饲料原料中磷的真消化率不受饲粮磷水平影响的前提假设是否成立[5],本试验满足上述条件。
目前,关于生长猪对饲粮中无机磷源中磷真消化率的报道较少,Petersen等[4]通过饲喂无磷饲粮法测得生长猪对常用的无机磷源中磷的TTTD。本试验通过在玉米-豆粕型和小麦-豆粕型饲粮中添加不同水平的DCP及MCP作为无机磷源,通过使用线性回归法,测得了生长猪对添加无机磷源中磷的TTTD。其结果显示,添加DCP作为无机磷源的玉米-豆粕型以及小麦-豆粕型饲粮中磷的TTTD分别为82.33%和82.88%,添加MCP作为无机磷源的2种饲粮中磷的TTTD分别为85.88%和84.62%,2种基础饲粮对2种无机磷源中磷TTTD均无显著差距。由线性回归方程可知,生长猪对添加MCP的饲粮组磷的TTTD高于添加DCP饲粮组磷的TTTD,该结果与Jongbloed等[2]、Eeckhout等[3]和Petersen等[4]研究结果一致。但本试验通过线性回归法测定的生长猪对DCP和MCP中磷的TTTD值均低于Petersen等[4]通过无磷饲粮法测得的磷的TTTD,究其原因,可能在于本试验饲粮中总磷的来源除添加的无机磷源外,还由玉米-豆粕型和小麦-豆粕型2种基础饲粮提供。
4 结论生长猪基础饲粮组成对DCP和MCP中磷的TTTD无显著影响。因此,使用DCP和MCP中磷的TTTD用于配制生长猪饲粮时无需考虑基础饲粮中碳水化合物和植酸酶活性对DCP和MCP中磷消化率的影响。
| [1] |
WEREMKOD, FANDREJEWSKIH, ZEBROWSKAT, 等. Bioavailability of phosphorus in feeds of plant origin for pigs[J].
WEREMKOD, FANDREJEWSKIH, ZEBROWSKAT, 等. Bioavailability of phosphorus in feeds of plant origin for pigs[J]. Asian Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 1997 , 10 (6) :551 –566.
( 0) 0)
|
| [2] |
JONGBLOED A W, EVERTS H, KEMME P A.Phosphorus availability and requirements in pigs[M]//Heinemann.Recent advances in animal nutrition.London, UK:Butterworth, 1991:65-80.
( 0) 0)
|
| [3] |
EECKHOUTW, DEPAEPE M. The digestibility of three calcium phosphates for pigs as measured by difference and by slope-ratio assay[J].
EECKHOUTW, DEPAEPE M. The digestibility of three calcium phosphates for pigs as measured by difference and by slope-ratio assay[J]. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 1997 , 77 .
( 0) 0)
|
| [4] |
PETERSENG I, STEINH H. Novel procedure for estimating endogenous losses and measurement of apparent and true digestibility of phosphorus by growing pigs[J].
PETERSENG I, STEINH H. Novel procedure for estimating endogenous losses and measurement of apparent and true digestibility of phosphorus by growing pigs[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2006 , 84 (8) :2126 –2132.
( 0) 0)
|
| [5] |
FANM Z, ARCHBOLDT, SAUERW C, 等. Novel methodology allows simultaneous measurement of true phosphorus digestibility and the gastrointestinal endogenous phosphorus outputs in studies with pigs[J].
FANM Z, ARCHBOLDT, SAUERW C, 等. Novel methodology allows simultaneous measurement of true phosphorus digestibility and the gastrointestinal endogenous phosphorus outputs in studies with pigs[J]. The Journal of Nutrition, 2001 , 131 (9) :2388 –2396.
( 0) 0)
|
| [6] |
SHENY R, FANM Z, AJAKAIYEA, 等. Use of the regression analysis technique to determine the true phosphorus digestibility and the endogenous phosphorus output associated with corn in growing pigs[J].
SHENY R, FANM Z, AJAKAIYEA, 等. Use of the regression analysis technique to determine the true phosphorus digestibility and the endogenous phosphorus output associated with corn in growing pigs[J]. The Journal of Nutrition, 2002 , 132 (6) :1199 –1206.
( 0) 0)
|
| [7] |
WUX, RUANZ, ZHANGY G, 等. True digestibility of phosphorus in different resources of feed ingredients in growing pigs[J].
WUX, RUANZ, ZHANGY G, 等. True digestibility of phosphorus in different resources of feed ingredients in growing pigs[J]. Asian Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2008 , 21 (1) :107 –119.
( 0) 0)
|
| [8] |
LIUJ B, YANGY K, HEJ, 等. Comparison of two diet types in the estimation of true digestibility of phosphorus in soybean and canola meals for growing pigs by the regression method[J].
LIUJ B, YANGY K, HEJ, 等. Comparison of two diet types in the estimation of true digestibility of phosphorus in soybean and canola meals for growing pigs by the regression method[J]. Livestock Science, 2014 , 167 :269 –275.
( 0) 0)
|
| [9] |
LIUJ, BOLLINGERD W, LEDOUXD R, 等. Effects of dietary calcium:phosphorus ratios on apparent absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the small intestine, cecum, and colon of pigs[J].
LIUJ, BOLLINGERD W, LEDOUXD R, 等. Effects of dietary calcium:phosphorus ratios on apparent absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the small intestine, cecum, and colon of pigs[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2000 , 78 (1) :106 –109.
( 0) 0)
|
| [10] |
JOHNSONS L, WILLIAMSS B, SOUTHERNL L, 等. Effect of phytase addition and dietary calcium and phosphorus levels on plasma metabolites and ileal and total-tract nutrient digestibility in pigs[J].
JOHNSONS L, WILLIAMSS B, SOUTHERNL L, 等. Effect of phytase addition and dietary calcium and phosphorus levels on plasma metabolites and ileal and total-tract nutrient digestibility in pigs[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2004 , 82 (3) :705 –714.
( 0) 0)
|
| [11] |
AKINMUSIREA S, ADEOLAO. True digestibility of phosphorus in canola and soybean meals for growing pigs:influence of microbial phytase[J].
AKINMUSIREA S, ADEOLAO. True digestibility of phosphorus in canola and soybean meals for growing pigs:influence of microbial phytase[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2009 , 87 (3) :977 –983.
( 0) 0)
|
| [12] |
KEMMEP A, RADCLIFFEJ S, JONGBLOEDA W, 等. Factors affecting phosphorus and calcium digestibility in diets for growing-finishing pigs[J].
KEMMEP A, RADCLIFFEJ S, JONGBLOEDA W, 等. Factors affecting phosphorus and calcium digestibility in diets for growing-finishing pigs[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 1997 , 75 (8) :2139 –2146.
( 0) 0)
|
| [13] |
METZLERB U, MOSENTHINR. A review of interactions between dietary fiber and the gastrointestinal microbiota and their consequences on intestinal phosphorus metabolism in growing pigs[J].
METZLERB U, MOSENTHINR. A review of interactions between dietary fiber and the gastrointestinal microbiota and their consequences on intestinal phosphorus metabolism in growing pigs[J]. Asian Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2008 , 21 (4) :603 –615.
( 0) 0)
|
| [14] |
NORTEYT N, PATIENCEJ F, SIMMINSP H, 等. Effects of individual or combined xylanase and phytase supplementation on energy, amino acid, and phosphorus digestibility and growth performance of grower pigs fed wheat-based diets containing wheat millrun[J].
NORTEYT N, PATIENCEJ F, SIMMINSP H, 等. Effects of individual or combined xylanase and phytase supplementation on energy, amino acid, and phosphorus digestibility and growth performance of grower pigs fed wheat-based diets containing wheat millrun[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2007 , 85 (6) :1432 –1443.
( 0) 0)
|
| [15] |
张丽英.
饲料分析及饲料质量检测技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2003 .
( 0) 0)
|
| [16] |
FENTONT W, FENTONM. An improved procedure for the determination of chromic oxide in feed and feces[J].
FENTONT W, FENTONM. An improved procedure for the determination of chromic oxide in feed and feces[J]. Canadian Journal of Animal Science, 1979 , 59 (3) :631 –634.
( 0) 0)
|
| [17] |
刘正群, 刘静波, 吕帅兵, 等. 饲粮类型和磷水平对生长猪后肠磷消化率的影响[J].
刘正群, 刘静波, 吕帅兵, 等. 饲粮类型和磷水平对生长猪后肠磷消化率的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2015 , 27 (8) :2509 –2516.
( 0) 0)
|
| [18] |
SEYNAEVEM, JANSSENSG, HESTAM, 等. Effects of dietary Ca/P ratio, P level and microbial phytase supplementation on nutrient digestibilities in growing pigs:precaecal, post-ileal and total tract disappearances of OM, P and Ca[J].
SEYNAEVEM, JANSSENSG, HESTAM, 等. Effects of dietary Ca/P ratio, P level and microbial phytase supplementation on nutrient digestibilities in growing pigs:precaecal, post-ileal and total tract disappearances of OM, P and Ca[J]. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2000 , 83 (1) :36 –48.
( 0) 0)
|
| [19] |
STEINH H, KADZEREC T, KIMS W, 等. Influence of dietary phosphorus concentration on the digestibility of phosphorus in monocalcium phosphate by growing pigs[J].
STEINH H, KADZEREC T, KIMS W, 等. Influence of dietary phosphorus concentration on the digestibility of phosphorus in monocalcium phosphate by growing pigs[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2008 , 86 (8) :1861 –1867.
( 0) 0)
|
| [20] |
BEERSS, JONGBLOEDA W. Effect of supplementary Aspergillus niger phytase in diets for piglets on their performance and apparent digestibility of phosphorus[J].
BEERSS, JONGBLOEDA W. Effect of supplementary Aspergillus niger phytase in diets for piglets on their performance and apparent digestibility of phosphorus[J]. Animal Production, 1992 , 55 (3) :425 –430.
( 0) 0)
|
| [21] |
冯占雨, 乔家运. 在肥育猪和母猪饲粮中利用小麦替代玉米的应用研究[J].
冯占雨, 乔家运. 在肥育猪和母猪饲粮中利用小麦替代玉米的应用研究[J]. 养猪, 2012 (4) :13 –16.
( 0) 0)
|
| [22] |
罗赞, 贺建华. 猪用饲料原料有效磷评定方法的研究[J].
罗赞, 贺建华. 猪用饲料原料有效磷评定方法的研究[J]. 饲料工业, 2008 , 29 (5) :53 –58.
( 0) 0)
|




