2. 哈尔滨医科大学大庆校区, 大庆 163000
2. Daqing Campus of Harbin Medical University, Daqing 163000, China
胰岛素样生长因子(insulin-like growth factors, IGF)对卵巢作用主要是扩大促性腺激素(gonadotropins, Gn)的效应,并在卵泡中期卵泡刺激素(follicle-stimulating hormone, FSH)含量低时,卵泡仍能自行生长发育中起重要作用[1]。IGF刺激卵巢细胞有丝分裂和类固醇生成及抑制凋亡[2]。血液中的IGF家族的IGF-1、胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白-1(insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1, IGFBP-1) 主要由肝脏合成并分泌[3],其表达受多种营养条件调控,与动物所处生理状态也密切相关,血液中IGFBP-1主要功能是抑制IGF-1的活性,在血液中,胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白1~6(insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 to -6, IGFBP-1~IGFBP-6) 可以延长血液中的IGF-1的半衰期[4-5]。IGFBP-1对IGF-1的调节可以在伤口愈合中起到重要作用[6]。IGF家族还与糖尿病、甲亢、免疫系统、癌症等疾病的发生有关[7-11]。植物雌激素主要有3类:异黄酮类(isoflavones)、木酚素类(lignans)和黄豆素类(coumestans),存在于豆类物质、植物及其种子中,其中异黄酮类含量较高。GEN是大豆异黄酮中活性较强的成分,与人体自身的雌激素在分子结构上相似,可与雌激素受体相结合,产生雌激素样作用。
国内学者关于大豆异黄酮对动物卵巢的影响报道较多。将大豆异黄酮加入产蛋后期蛋鸡饲粮中,50 mg/kg时能够显著提高产蛋率,且其对蛋鸡的蛋品质及繁殖器官无副作用[12-13];卢建等[14]在饲粮中添加50、100、200 mg/kg大豆黄酮能够提高皋黄鸡的受精率及入孵化率,同时也未发现副作用的发生。曹满湖等[15]发现大豆异黄酮可能通过提高血清雌二醇(E2)与β-内啡肽水平,来改善卵巢的功能。关于GEN对雌性动物卵巢的试验研究报道较少,Jourdehi等[16]就GEN及雌马酚(equol, EQ)对雌性欧洲鳇(Huso huso)进行干预,结果显示GEN与EQ均可以提升卵母细胞直径,提升血清E2的水平,表明GEN及EQ添加在饲粮中,对渔业的发展有帮助。综合国内外的研究表明,目前GEN的作用研究大多集中在去卵巢骨质疏松治疗、绝经期的雌激素替代治疗、多囊卵巢综合症的治疗等方面,就GEN对青年雌性大鼠的卵巢内功能基因及生育能力的影响较少。
本课题组前期研究发现GEN的雌激素样作用能够调节青年期、成年期、围绝经期的雌性大鼠卵巢功能。通过动物试验证实GEN在15、30、60 mg/kg的剂量下,对小鼠的卵巢及其他重要脏器无显著影响[17]。在此基础上,进一步研究GEN对雌性大鼠卵巢功能的调节作用,本试验选择了体内Gn及IGF作为研究目标,研究GEN对它们的影响,为进一步研究GEN对卵巢功能的调节作用及生殖能力的影响提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验试剂、基础饲粮和主要仪器GEN(99.82%)购自上海融禾医药科技发展有限公司,己烯雌酚(DES)(99.4%)购自西安天正药用辅料有限公司,花生油购自山东鲁花集团有限公司。为了排除饲粮中可能含有的GEN对试验的影响,突出GEN的作用效果,采用基础饲粮饲养,基础饲粮组成见表 1[18-19]。
|
|
表 1 基础饲粮组成(风干基础) Table 1 Composition of the basal diet (air-dry basis) |
TRIzol Reagent (Thermo公司)、SYBR Green PCR试剂盒(Thermo公司)、逆转录PCR试剂盒(Thermo公司)、酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)试剂盒(上海研谨生物科技有限公司)。
主要仪器有:TG-16M低温冷冻离心机(上海卢湘仪离心机仪器有限公司)、K-30旋涡振荡器(青浦泸西仪器厂)、PRO-200电动匀浆机(FLUKO公司)、Nanodrop-2000超微量分光光度计(Thermo公司)、ABI-7300 real-time PCR检测仪(ABI公司); 酶标仪(BioTec公司)。
1.2 试验设计选取49日龄雌性SD大鼠40只,体重为(200±20) g,许可证号:SCXK(黑)203-001。按照体重随机分为5组,每组8只,每组单笼饲养。5组分别为阴性对照(NC)组、GEN低(L)、中(M)、高剂量(H)组及阳性对照(PC)组。NC组灌胃花生油(其他组灌胃试剂以此为溶剂);L、M、H组分别灌胃15、30、60 mg/(kg BW·d)GEN,PC组灌胃DES 0.5 mg/(kg BW·d)。每天给予14 h光照、10黑暗的周期性光照,动物室温度(20±2) ℃,相对湿度(45±10)%,自由饮水,自由采食。试验期30 d。
1.3 样品采集试验期结束后,对所有大鼠进行阴道涂片观察,挑选出处于动情间期大鼠(挑选出动情间期大鼠进行后续试验,其余继续观察至动情间期再继续试验,完成在10 d内即2个动情周期的挑选),禁食不禁水12 h后,采用乙醚麻醉,并于腹主动脉采集血液,分离血清,采集卵巢组织,液氮速冻后-80 ℃保存。
1.4 血清FSH、黄体生成素(luteinizing hormone, LH)、IGF-1、IGFBP-1含量的测定采用ELISA法检测血清中FSH、LH、IGF-1、IGFBP-1含量,按照试剂盒说明书操作。
1.5 卵巢IGF-1、IGFBP-1 mRNA表达水平的测定 1.5.1 引物采用NCBI primer designing tool设计实时定量PCR扩增引物,引物由上海生工生物技术有限公司合成,引物信息见表 2。
|
|
表 2 实时定量PCR引物信息 Table 2 Information of primers for real-time qPCR |
按Trizol试剂盒说明书提取总RNA;Nanodrop 2000超微量分光光度计测定总RNA的吸光度(OD)值,分析总RNA的纯度和浓度。
1.5.3 cDNA合成25 μL反应体系:RNA-Primer Mix 12 μL, 5×RT Reaction Buffer 5 μL, 25 mmol/L dNTP 1 μL, 25 U/μL RNase Inhibitor 1 μL, 200 U/μL M-MLV Rtase 1 μL, Oligo(dt)18 1 μL, ddH2O (DNase-free) 4 μL。
反应程序:37 ℃ 60 min;85 ℃ 5 min;4 ℃ 5 min;得到的cDNA置于-20 ℃保存。
1.5.4 实时定量PCR25 μL反应体系:cDNA模板2 μL,SYBRGreen Mix 12.5 μL,上游引物(0.1 mmol/μL)0.5 μL,下游引物(0.1 mmol/μL)0.5 μL,ddH2O 9.5 μL。
反应程序:95 ℃ 10 min; 95 ℃ 15 s, 60 ℃ 45 s, 40个循环; 95 ℃ 15 s; 60 ℃ 1 min; 95 ℃ 15 s; 60 ℃ 15 s。
1.6 数据统计分析数据采用SPSS 19.0软件中t检验程序进行分析,采用GraphPad Prism 5.0软件作图。P<0.05为差异显著,P<0.01为差异极显著。
2 结果 2.1 GEN对雌性大鼠血清FSH、LH、IGF-1和IGFBP-1含量的影响表 3结果显示,与NC组比较,试验组血清中FSH与LH含量均表现上升趋势,但差异不显著(P>0.05),PC组血清中FSH与LH含量也升高。与NC组比较,M、H组血清中IGF-1含量降低,但差异不显著(P>0.05);PC组血清中IGF-1含量显著降低(P<0.05)。与NC组比较,试验组血清中IGFBP-1含量升高,L、H组显著升高(P<0.05),M组极显著升高(P<0.01);PC组血清中IGFBP-1含量显著升高(P<0.05)。
|
|
表 3 GEN对雌性大鼠血清卵泡刺激素、黄体生成素、胰岛素样生长因子-1、胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白-1含量的影响 Table 3 Effects of GEN on serum FSH, LH, IGF-1 and IGFBP-1 contents of female rats (n=8) |
图 1结果显示,熔解曲线中呈现单一峰,引物的特异性较好。
|
图 1 β肌动蛋白(a)、胰岛素样生长因子-1(b)、胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白-1 mRNA的实时定量PCR产物(c)的熔解曲线 Figure 1 The melt curves of real-time qPCR products of β-actin (a), IGF-1 (b) and IGFBP-1 mRNAs (c) |
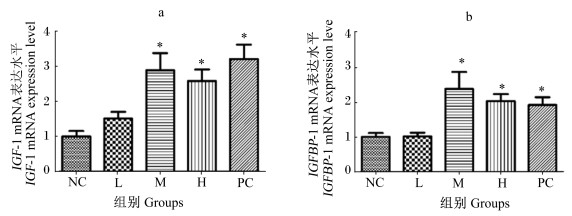
图 2结果显示,与NC组比较,试验组卵巢组织中IGF-1、IGFBP-1 mRNA表达水平均提高,其中M、H组显著升高(P<0.05);PC组卵巢组织中IGF-1、IGFBP-1 mRNA表达水平显著升高(P<0.05)。
|
*表示与NC组差异显著(P<0.05)。 *indicated significantly different from NC group (P < 0.05). 图 2 GEN对雌性大鼠卵巢组织中IGF-1(a)、IGFBP-1 mRNA表达水平(b)的影响 Figure 2 Effects of GEN on expression levels of IGF-1 (a) and IGFBP-1 mRNAs (b) in ovary tissue of female rats (n=8) |
IGFBP-1对IGF-1活性的调节是复杂的,在空腹状态下,由于胰岛素的低抑制效应以及皮质醇和胰高血糖素对肝脏IGFBP-1 mRNA转录的刺激作用,血液IGFBP-1含量较高。因为IGFBP-1对IGF-1的亲和力超过IGF-1对于IGF-1受体的亲和力,高IGFBP-1含量可以抑制IGF-1结合IGF-1受体,从而降低IGF-1对外周代谢的胰岛素样活性[20]。空腹检测较高IGFBP-1含量与前列腺癌的相关性较低,而较高的IGF-1却是相反的[21]。有文献表示,IGFBP-1可以不与IGF-1结合,直接与细胞膜上受体蛋白作用,刺激中国仓鼠卵巢细胞迁移[22]。硬骨鱼卵母细胞发育及成熟过程中,人重组IGF-1能刺激真鲷(Pagrus major)、纹犬牙石首鱼(Cynoscion nebulosus)卵巢中的生发泡破裂,促进其卵母细胞成熟[23-24]。多囊卵巢综合征妇女的卵巢中,IGF-1与胰岛素、LH协同作用,通过旁分泌、自分泌和内分泌协同作用增加雄激素的产生,IGFBP-1 mRNA的表达水平降低,引发高雄激素血症,抑制卵泡成熟和雌激素的合成[25-26]。IGFBP-1 mRNA在各组织中的表达情况存在差异,在卵巢中的表达弱于肝脏[27]。IGF-1 mRNA在正常卵巢的小窦卵泡和闭锁卵泡膜细胞上表达水平较低,在优势卵泡中则不表达,而IGFBP-1 mRNA仅出现于优势卵泡的颗粒细胞上。研究表明,IGF-1在培养的颗粒细胞中的分泌和作用中可以以自分泌或旁分泌方式起作用,以增强Gn在卵巢组织中的作用[28],而Gn是调节脊椎动物性腺发育、促进性激素生成和分泌的糖蛋白激素,如垂体前叶分泌的LH和FSH,两者协同作用,可刺激卵巢或睾丸中生殖细胞的发育及性激素的生成及分泌。
4 结论GEN能够提高雌性大鼠血清FSH、LH含量、降低血清IGF-1含量、提高血清IGFBP-1含量,同时提高卵巢中IGFBP-1、IGF-1 mRNA的表达水平,这些指标协同作用于卵巢,能够促进卵泡的成熟,调节卵巢功能。
| [1] |
蒋彦. 卵巢内调节因子与多囊卵巢综合征[J]. 中国妇幼健康研究, 2003, 14(2): 104-107. |
| [2] |
AMATO G, AIZZO A, TUCKER A, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 reduction in follicular fluid in spontaneous and stimulated cycles[J]. Fertility and Sterility, 1998, 70(1): 141-144. DOI:10.1016/S0015-0282(98)00115-0 |
| [3] |
ARANY E, AFFORD S, STRAIN A J, et al. Differential cellular synthesis of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1(IGFBP-1) and IGFBP-3 within human liver[J]. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 1995, 79(6): 1871-1876. |
| [4] |
BINKERT C, LANDWEHR J, MARY J L, et al. Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of a cDNA encoding a novel insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP-2)[J]. EMBO Journal, 1989, 8(9): 2497-2502. |
| [5] |
SHIMASAKI S, SHIMONAKA M, ZHANG H P, et al. Identification of five different insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) from adult rat serum and molecular cloning of a novel igfbp-5 in rat and human[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1991, 266(16): 10646-10653. |
| [6] |
SKOTTNER A, KANJE M, JENNISCHE E, et al. Tissue repair and IGF-Ⅰ[J]. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica Supplement, 1988, 347: 110-112. |
| [7] |
ABBAS A, GRANT P J, KEARNEY M T. Role of IGF-1 in glucose regulation and cardiovascular disease[J]. Expert Review of Cardiovascular Therapy, 2008, 6(8): 1135-1149. DOI:10.1586/14779072.6.8.1135 |
| [8] |
EZZAT V A, DUNCAN E R, WHEATCROFT S B, et al. The role of IGF-Ⅰ and its binding proteins in the development of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease[J]. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 2008, 10(3): 198-211. DOI:10.1111/dom.2008.10.issue-3 |
| [9] |
LEE C, RAFFAGHELLO L, LONGO V D. Starvation, detoxification, and multidrug resistance in cancer therapy[J]. Drug Resistance Updates, 2012, 15(1/2): 114-122. |
| [10] |
RAJPATHAK S N, GUNTER M J, WYLIE-ROSETT J, et al. The role of insulin-like growth factor-Ⅰ and its binding proteins in glucose homeostasis and type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, 2009, 25(1): 3-12. DOI:10.1002/dmrr.v25:1 |
| [11] |
SMITH T J. Insulin-like growth factor-Ⅰ regulation of immune function:a potential therapeutic target in autoimmune diseases?[J]. Pharmacological Reviews, 2010, 62(2): 199-236. DOI:10.1124/pr.109.002469 |
| [12] |
顾欢, 施寿荣, 童海兵, 等. 大豆黄酮对产蛋后期蛋鸡生产性能、血液指标和经济效益的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2013, 25(2): 390-396. |
| [13] |
蔡娟, 顾欢, 常玲玲, 等. 大豆黄酮在蛋鸡饲料中的安全性评价:生产性能、蛋品质和繁殖器官发育[J]. 动物营养学报, 2013, 25(3): 635-642. |
| [14] |
卢建, 王克华, 曲亮, 等. 大豆黄酮对45~58周龄如皋黄鸡蛋鸡生产性能、繁殖器官发育和种蛋孵化率的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2014, 26(11): 3420-3425. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2014.11.031 |
| [15] |
曹满湖, 罗理成, 孙佳静, 等. 大豆异黄酮对产蛋后期蛋鸡卵巢机能的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2016, 28(8): 2458-2464. |
| [16] |
JOURDEHI A Y, SUDAGAR M, BAHMANI M, et al. Comparative study of dietary soy phytoestrogens genistein and equol effects on growth parameters and ovarian development in farmed female beluga sturgeon, Huso huso[J]. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014, 40(1): 117-128. DOI:10.1007/s10695-013-9829-z |
| [17] |
张明玉, 迟晓星, 丁啸宇, 等. 金雀异黄素对围绝经期模型小鼠卵巢组织及其安全性的影响[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2016, 28(3): 51-55. |
| [18] |
陈容. 金雀异黄素对多囊卵巢综合征大鼠的调节作用研究[D]. 硕士学位论文. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10223-1013207898.htm
|
| [19] |
舒翔. 染料木素和槲皮素对幼鼠卵巢发育及肿瘤发生发展的影响[D]. 硕士学位论文. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2012. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10403-1015506002.htm
|
| [20] |
WHEATCROFT S B, KEARNEY M T. IGF-dependent and IGF-independent actions of IGF-binding protein-1 and-2:implications for metabolic homeostasis[J]. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2009, 20(4): 153-162. |
| [21] |
ALLEN N E, APPLEBY P N, KAAKS R, et al. Lifestyle determinants of serum insulin-like growth-factor Ⅰ(IGF-Ⅰ), C-peptide and hormone binding protein levels in British women[J]. Cancer Causes & Control, 2003, 14(1): 65-74. |
| [22] |
JONES J I, GOCKERMAN A, BUSBY W H JR, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 stimulates cell migration and binds to the α5β 1 integrin by means of its Arg-Gly-Asp sequence[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1993, 90(22): 10553-10557. DOI:10.1073/pnas.90.22.10553 |
| [23] |
KAGAWA H, KOBAYASHI M, HASEQAWA Y, et al. Insulin and insulin-like growth factors Ⅰ and Ⅱ induce final maturation of oocytes of red seabream, Pagrus major, in vitro[J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 1994, 95(2): 293-300. DOI:10.1006/gcen.1994.1126 |
| [24] |
THOMAS P, PINTER J, DAS S. Upregulation of the maturation-inducing steroid membrane receptor in spotted seatrout ovaries by gonadotropin during oocyte maturation and its physiological significance[J]. Biology of Reproduction, 2001, 64(1): 21-29. DOI:10.1095/biolreprod64.1.21 |
| [25] |
AQUINO C P, HERNÁNDEZ V M, HICKS G J J, et al. The role of insulin-like growth factor in polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Ginecología Y Obstetricia De México, 1999, 67: 267-271. |
| [26] |
宋娟娟, 吴效科, 侯丽辉. 卵巢功能障碍与多囊卵巢综合征[C]//2006哈尔滨多囊卵巢综合征国际论坛论文集. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江中医药大学, 2006: 363-367.
|
| [27] |
LEE P D K, GIUDICE L C, CONOVER C A, et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1:recent findings and new directions[J]. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 1997, 216(3): 319-357. DOI:10.3181/00379727-216-44182 |
| [28] |
HAMMOND J M, HSU C J, KLINDT J, et al. Gonadotropins increase concentrations of immunoreactive insulin-like growth factor-Ⅰ in porcine follicular fluid in vivo[J]. Biology of Reproduction, 1988, 38(2): 304-308. DOI:10.1095/biolreprod38.2.304 |




