2. 浙江农林大学动物科技学院, 杭州 311300;
3. 青岛润博特生物科技有限公司, 青岛 266324
2. College of Animal Science and Technology, Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University, Hangzhou 311300, China;
3. Qingdao Runbiotech Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Qingdao 266324, China
近年来,肉鸡规模化养殖水平不断提高,在集约化养殖模式下,过高的饲养密度及免疫功能减弱等问题,导致肉鸡的生长性能下降[1]。为了解决这些问题,抗生素被应用于肉鸡养殖业中,然而抗生素的大量使用会导致细菌耐药谱增多、耐药菌株的出现等问题,严重危害肉鸡的健康。于是,世界各国开始禁止抗生素在养殖业中的应用,2019年7月,我国农业农村部明确指出除中草药外的促生长药物饲料添加剂在2020年全面退出。然而,抗生素的全面退出会导致养殖业中家禽的发病率上升、死淘率升高、肠道受损、生产成本增加等一系列问题,进而导致养殖效益下降[2-3]。因此,抗生素替代物成为家禽养殖业发展研究的重点之一[4-7]。水解单宁酸是从植物中提取的多酚类化合物,可水解为没食子酸和葡萄糖[8],因其具有抗氧化、抗炎症等广泛的生物学功能而受到人们的关注。研究表明,饲粮中添加单宁酸可提高畜禽的生长性能,改善肠道微生态环境[8-10]。然而,目前关于水解单宁酸直接应用于饲料,评价其替代抗生素对肉鸡影响的报道还不够充分,对肉鸡生长性能及肠道健康的影响还需要进一步研究。因此,本试验旨在研究饲粮中添加水解单宁酸对肉鸡生长性能及肠道健康的影响,为水解单宁酸在肉鸡养殖生产中的应用提供科学依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验材料水解单宁酸由青岛某生物科技有限公司提供,从五倍子中提取,为黄褐色颗粒,原料组成为:水解单宁酸、棕榈油、纤维素,其中水解单宁酸含量为30.60%。
1.2 试验设计试验采用单因素完全随机设计,选取42 000只1日龄、体况相近的健康爱拔益加(AA)肉仔鸡,随机分为3组,每组4个重复,每个重复3 500只鸡。预试期10 d,正试期32 d。预试期各组统一饲喂基础饲粮,基础饲粮中不添加任何抗生素,为颗粒料。正试期对照组饲喂基础饲粮,试验组分别饲喂在基础饲粮中添加200和400 mg/kg水解单宁酸的试验饲粮。基础饲粮组成及营养水平见表 1[11]。肉仔鸡采用笼养,全程自由饮水和采食,按照鸡场常规管理程序进行免疫接种。
|
|
表 1 基础饲粮组成及营养水平(风干基础) Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of basal diets (air-dry basis) |
每天准确记录鸡只的采食量,试验开始和结束时对鸡只进行空腹称重,记录始重、末重,计算平均日增重(ADG)、平均日采食量(ADFI)及料重比(F/G);每天记录疾病和死亡情况,计算死淘率。
1.3.2 欧洲效益指数(EPI)欧洲效益指数计算公式如下:

|
于42日龄时,每个重复随机选取4只鸡,屠宰后立即打开腹腔,分清各肠段位置进行结扎,在各肠段前1/4处剪开一小口,用PHB-2型便携式pH计测定十二指肠、空肠、回肠内容物的pH。
1.3.4 肠道酶活性肉鸡屠宰后分别取十二指肠、空肠、回肠内容物于液氮中暂时保存,然后转移至-80 ℃超低温冰箱保存备用。准确称量肠道内容物样品,按照肠道内容物∶匀浆介质=1 ∶ 9(m/V)进行制样,匀浆在冰水浴条件下进行,将所得悬浮液以2 500 r/min离心10 min,取上清液用于测定十二指肠、空肠、回肠内容物的胰蛋白酶、淀粉酶和脂肪酶活性,试剂盒均购自南京建成生物工程研究所,方法参见说明书。
1.3.5 肠道黏膜形态肉鸡屠宰后分别取十二指肠、空肠、回肠组织样品各2~3 cm于4%甲醛固定液中固定后,流水冲洗48 h,制成石蜡切片,然后采用苏木精-伊红(HE)进行染色。使用Nikon Eclipse 80i显微照相系统观察各肠段形态,用Motic images 2000.1.3软件在线测量十二指肠、空肠、回肠的隐窝深度和绒毛高度,并计算绒毛高度/隐窝深度。
1.3.6 盲肠乳酸杆菌及大肠杆菌数量肉鸡屠宰后立即打开腹腔,取适量盲肠内容物放于灭菌的冻存管中,采用平板计数法检测乳酸杆菌和大肠杆菌的数量。称取适量内容物样品,按照样品∶灭菌生理盐水=1 ∶ 9(m/V)配制成10-1倍稀释液,再将该稀释液进行稀释,配制成10-2倍稀释液,再依次进行10-3~10-7倍稀释。将稀释液接种于MRS培养基中,37 ℃有氧培养36 h后进行乳酸杆菌计数;将稀释液接种于麦康凯培养基中,37 ℃有氧培养20 h后进行大肠杆菌计数。每个菌种选择3个梯度,每个稀释梯度重复3次,盲肠内容物微生物数量用每克肠道内容物中含菌落总数的对数[lg(CFU/g)]表示。
1.4 数据统计试验数据使用SAS 9.2软件进行统计,采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)进行组间差异分析,用Duncan氏法进行多重比较,P < 0.05为差异显著,P < 0.01为差异极显著,结果均以“平均值±标准差(mean±SD)”表示。
2 结果 2.1 水解单宁酸对肉鸡生长性能的影响由表 2可知,与对照组相比,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸对肉鸡的末重、平均日增重、平均日采食量、死淘率及欧洲效益指数均无显著影响(P>0.05);但400 mg/kg水解单宁酸组的料重比显著降低(P < 0.05)。此外,饲粮中添加200和400 mg/kg的水解单宁酸使肉鸡的死淘率由4.99%分别降低至4.12%和4.07%,分别降低了17.43%和18.44%;欧洲效益指数由394.10分别提高至397.86和400.77,分别提高了0.95%和1.69%。
|
|
表 2 水解单宁酸对肉鸡生长性能的影响 Table 2 Effects of hydrolyzed tannic acid on growth performance of broilers |
由表 3可知,与对照组相比,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸极显著降低肉鸡的十二指肠pH(P < 0.01);2个试验组的空肠和回肠pH均有所降低,但差异不显著(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 3 水解单宁酸对肉鸡肠道pH的影响 Table 3 Effects of hydrolyzed tannic acid on intestinal pH of broilers |
由表 4可知,与对照组相比,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸极显著提高肉鸡的十二指肠、空肠胰蛋白酶活性(P < 0.01);饲粮中添加400 mg/kg水解单宁酸极显著提高十二指肠淀粉酶活性(P < 0.01),显著提高空肠淀粉酶活性(P < 0.05);饲粮中添加200 mg/kg水解单宁酸显著提高空肠脂肪酶活性(P < 0.05)。
|
|
表 4 水解单宁酸对肉鸡肠道消化酶活性的影响 Table 4 Effects of hydrolyzed tannic acid on intestinal digestive enzyme activities of broilers |
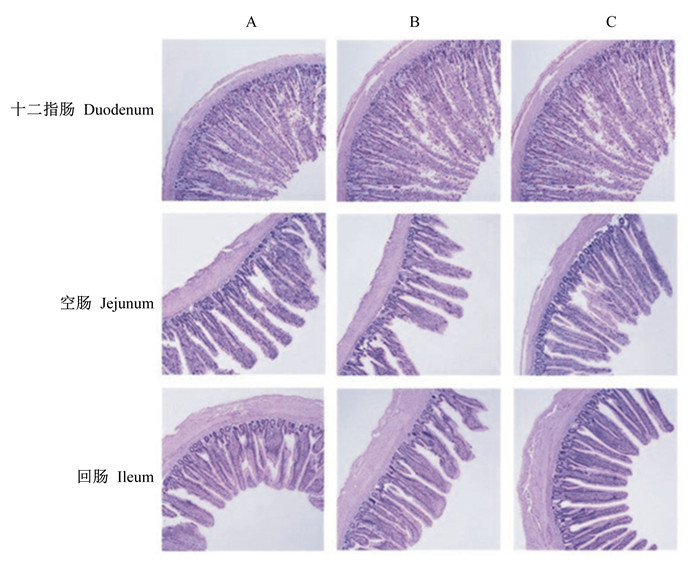
由图 1可知,各组肉鸡的十二指肠绒毛呈现出宽叶片状,绒毛密度高,而空肠和回肠绒毛多呈现出短柱状,排列疏松。与对照组相比,2个试验组肉鸡的十二指肠、空肠和回肠绒毛高度较高,肠绒毛发育较好。
|
A:对照组;B:200 mg/kg水解单宁酸组;C:400 mg/kg水解单宁酸组。 A: Control group; B: 200 mg/kg hydrolyzed tannic acid group; C: 400 mg/kg hydrolyzed tannic acid group. 图 1 肉鸡肠道黏膜组织结构图 Fig. 1 Intestinal mucosa tissue structure graphs of broilers (40×) |
由表 5可知,与对照组相比,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸极显著提高肉鸡的十二指肠绒毛高度和绒毛高度/隐窝深度(P < 0.01);饲粮中添加水解单宁酸极显著提高空肠绒毛高度和绒毛高度/隐窝深度(P < 0.01);饲粮中添加400 mg/kg水解单宁酸显著降低空肠隐窝深度(P < 0.05)。
|
|
表 5 水解单宁酸对肉鸡肠道形态结构的影响 Table 5 Effects of hydrolyzed tannic acid on intestinal morphology of broilers |
由表 6可知,与对照组相比,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸可显著提高肉鸡的盲肠乳酸杆菌数量(P < 0.05);2个试验组的大肠杆菌数量均有降低,但差异不显著(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 6 水解单宁酸对肉鸡盲肠乳酸杆菌和大肠杆菌数量的影响 Table 6 Effects of hydrolyzed tannic acid on the number of Lactobacillus and Escherichia Coli in cecum of broilers |
缩合单宁酸是一种抗营养因子,在家禽上的研究较多。研究表明,饲粮中过多添加单宁酸可使动物的采食量下降[12],然而又有研究发现,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸可作为生长促进剂提高饲粮利用率并促进畜禽的生长[13-14]。安文亭等[15]研究发现,肉鸡中后期饲粮中添加1 500 mg/kg水解单宁酸可提高肉鸡的采食量,降低料重比。本试验中,并未发现水解单宁酸对肉鸡的采食量有影响,但可降低料重比。吴雅清[16]研究发现,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸可提高黄羽肉鸡的平均成活率,其中添加水平为600 g/t时平均成活率最高,为98.33%,与本试验结果基本一致。本试验研究结果表明,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸可降低肉鸡的料重比,提高成活率及欧洲效益指数。这可能与以下2个方面有关:一方面可能是水解单宁酸通过收敛作用减弱肠道蠕动,延长饲粮在消化道内的通过时间,从而促进小肠的消化吸收,进一步提高肉鸡的生长性能;另一方面可能是水解单宁酸的抗炎等作用在一定程度上可提高肉鸡的免疫力,进而提高成活率。
在动物体消化系统中肠道pH发挥着不可替代的作用,适宜的肠道pH可促进动物对食物的消化和吸收[17]。然而关于水解单宁酸对畜禽肠道pH影响的报道较少。李茜等[18]研究发现,当肉鸡采食含有水解单宁酸的饲粮时,肠道pH降低,肠道内环境得到改善,促进肠道发育。本研究发现,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸极显著降低十二指肠pH。这可能与水解单宁酸本身含有三羟基苯甲酸、没食子酸等D-葡萄糖为核心的酚醛酸聚酯类化合物有关,在碱性肠液与单宁酸水解酶的作用下可得到酸和葡萄糖,呈弱酸性,降低肠道pH,促进水解单宁酸与消化酶结合,进一步促进肠道发育。
肠道消化酶的活性与动物体内物质代谢存在着密切关系。当水解单宁酸与消化酶结合后,可以提高消化酶活性,进而提高饲料转化率[18]。Majumda等[19]研究发现,与对照组相比,饲粮中添加200和300 mg/d单宁酸时,成年鸡的肠道胰蛋白酶、淀粉酶、脂肪酶活性显著提高。本研究结果表明,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸可极显著提高肉鸡的十二指肠和空肠胰蛋白酶活性,400 mg/kg水解单宁酸可显著提高空肠淀粉酶活性,200 mg/kg水解单宁酸可显著提高空肠脂肪酶活性,这与Mole等[20]的报道结果不一致。推测可能是由于试验饲养环境不同,单宁酸的来源、纯度及提取工艺有差异等因素造成的,关于水解单宁酸对肠道酶活性影响的具体机制需要进一步研究。
小肠是动物消化和吸收的主要器官,肠道上皮结构完整性是反映动物肠道健康和消化能力的重要因素[21],肠道形态的改变影响机体对营养物质的消化、吸收和转运[22-23],进而影响动物的生长性能。小肠的养分消化率和吸收能力与肠道绒毛高度、隐窝深度、绒毛高度/隐窝深度有关[24],肠道绒毛高度变长、隐窝深度变浅说明小肠的吸收能力增强;绒毛高度/隐窝深度越大表明肠道上皮表面积越大,完整性越好,吸收能力越强[25]。Liu等[26]研究发现,在肉鸡热应激状况下,饲粮中添加板栗单宁可显著提高肉鸡的空肠绒毛高度,而隐窝深度无显著变化。本试验研究表明,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸可极显著提高肉鸡的十二指肠和空肠绒毛高度、绒毛高度/隐窝深度,降低隐窝深度,而并未发现水解单宁酸对回肠的作用,这与Bilić-Šobot等[27]的研究结果基本一致。这可能是由于水解单宁酸具有类似植物多酚维护肠道健康的作用,可以减少毒素对肠道形态的损害,促进肠道发育,进一步促进小肠对营养物质的吸收利用,进而提高肉鸡的生长性能。因此,水解单宁酸有利于保护肠道形态完整,提高肉鸡对营养物质的消化吸收。
肠道微生物在动物消化吸收过程中起着至关重要的作用。水解单宁酸的抑菌能力取决于其分子质量的大小,对不同类型的细菌存在不同的效果[28]。报道发现,单宁酸可通过收敛、抗氧化、抗菌等作用相互协同共同改变畜禽内部生理环境,且有很强的生物和药理活性,可增强机体的免疫活性,维护肠道健康,对于动物十分有益[29-32]。侯海锋等[10]研究发现,水解单宁酸会改变蛋鸡肠道微生物菌群结构,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸可显著降低肠道大肠杆菌定植数量,其中0.10%和0.15%添加水平可显著增加肠道乳酸杆菌数量。魏昆鹏等[33]研究发现,灌服0.1 mg/mL水解单宁酸可降低家禽肠道大肠杆菌数量,增加乳酸菌和双歧杆菌数量。Jamroz等[34]研究发现,较高剂量的单宁酸可显著降低28日龄肉鸡的肠道大肠杆菌数量。本试验研究表明,饲粮中添加水解单宁酸可显著提高肉鸡的盲肠乳酸杆菌数量,大肠杆菌数量呈下降趋势。这可能是由于水解单宁酸通过引起细胞壁形态变化,增加膜通透性,进而影响细胞代谢功能,促进乳酸杆菌的增殖。此外,益生菌可能通过利用水解单宁酸降低肠道pH的特性,抑制有害菌的繁殖。关于水解单宁酸对肠道微生物菌群的影响,具体等待进一步的研究。
4 结论饲粮中添加水解单宁酸可降低肉鸡的料重比和死淘率,提高欧洲效益指数、肠道消化酶活性和乳酸杆菌数量,促进肠道发育并保护肉鸡肠道健康。在本试验条件下,肉鸡饲粮中添加400 mg/kg水解单宁酸效果最佳。
| [1] |
郭晓宇, 韩俊英, 闫素梅, 等. 维生素A对肉鸡生长性能、免疫及抗氧化功能的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(8): 3582-3589. GUO X Y, HAN J Y, YAN S M, et al. Effects of vitamin A on growth performance, immunity and antioxidant function of broilers[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(8): 3582-3589 (in Chinese). |
| [2] |
张文婷, 汪琛, 张腾飞, 等. 无抗养殖趋势下的家禽细菌病防控[J]. 中国家禽, 2019, 41(22): 1-4. ZHANG W T, WANG C, ZHANG T F, et al. Prevention and control of poultry bacteriological diseases under the trend of antibiotic-free breeding[J]. China Poultry, 2019, 41(22): 1-4 (in Chinese). |
| [3] |
郝海红, 程古月, 戴梦红, 等. 对动物饲料中禁用抗菌促生长剂的反思[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(3): 595-604. HAO H H, CHENG G Y, DAI M H, et al. Rethinking the withdrawal of antimicrobial growth promotants in animal feed[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(3): 595-604 (in Chinese). |
| [4] |
凌彩金, 周巧仪, 刘淑媚. 日粮中添加茶叶对肉鸡生长性能和抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2018, 38(11): 2175-2180. LING C J, ZHOU Q Y, LIU S M. Effect of tea leaves on growth performance and antioxidant property of broilers[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2018, 38(11): 2175-2180 (in Chinese). |
| [5] |
曹乾大. 我国细菌耐药性问题及抗生素替代品的研发方向[J]. 猪业科学, 2016, 33(4): 36-38. CAO Q D. The problem of bacterial resistance and the development direction of antibiotic substitutes in China[J]. Swine Industry Science, 2016, 33(4): 36-38 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5358.2016.04.016 |
| [6] |
杨欣, 杨小军, 李绍钰, 等. 我国白羽肉鸡一般饲料添加剂研究进展[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(10): 4592-4601. YANG X, YANG X J, LI S Y, et al. Research advances in common feed additives of white feather broilers in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(10): 4592-4601 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.10.012 |
| [7] |
黄晓霞, 谭树华. 生猪无抗养殖替代物研究现状与前景[J]. 猪业科学, 2019, 36(4): 72-75. HUANG X X, TANG S H. Research status and prospects of non-resistant pig breeding substitutes[J]. Swine Industry Science, 2019, 36(4): 72-75 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5358.2019.04.022 |
| [8] |
刘汉锁, 龙沈飞, 尚庆辉, 等. 水解单宁酸的作用机制及其在畜禽生产中的应用进展[J]. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(9): 3991-3999. LIU H S, LONG S F, SHANG Q H, et al. Mechanism of action hydrolyzed tannic acid and its application in livestock and poultry production[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(9): 3991-3999 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267X.2019.09.010 |
| [9] |
何子煜, 张佩华. 单宁酸的生理功能及其在畜禽生产中的研究进展[J]. 湖南饲料, 2018(1): 40-42. HE Z Y, ZHANG P H. The physiological function of tannin and its research progress in livestock and poultry production[J]. Hunan Feed, 2018(1): 40-42 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7539.2018.01.017 |
| [10] |
侯海锋, 高宗旺, 李茜. 水解单宁酸对蛋鸡生产性能及肠道健康的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2017(12): 21-23. HOU H F, GAO Z W, LI X. Effects of hydrolyzed tannin acid on laying performance and intestinal health of layers[J]. China Feed, 2017(12): 21-23 (in Chinese). |
| [11] |
NRC. Nutrient requirements of poultry[S]. 9th ed. Washington, D.C. : National Academy Press, 1994.
|
| [12] |
崔朝霞, 张书杰, 刘志伟. 饲料原料中常见的抗营养因子及其消除方法[J]. 河南畜牧兽医(综合版), 2007, 28(10): 27-28. CUI Z X, ZHANG S J, LIU Z W. Common anti-nutritional factors in feed ingredients and its elimination methods[J]. Henan Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine (Comprehensive Version), 2007, 28(10): 27-28 (in Chinese). |
| [13] |
CENGIZ Ö, KÖKSAL B H, TATLI O, et al. Effect of dietary tannic acid supplementation in corn- or barley-based diets on growth performance, intestinal viscosity, litter quality, and incidence and severity of footpad dermatitis in broiler chickens[J]. Livestock Science, 2017, 202: 52-57. DOI:10.1016/j.livsci.2017.05.016 |
| [14] |
SCHIAVONE A, GUO K, TASSONE S, et al. Effects of a natural extract of chestnut wood on digestibility, performance traits, and nitrogen balance of broiler chicks[J]. Poultry Science, 2008, 87(3): 521-527. DOI:10.3382/ps.2007-00113 |
| [15] |
安文亭, 刘树栋, 郭佳伟, 等. 单宁酸对肉鸡饲料养分消化率及消化酶活性影响[C]//中国畜牧兽医学会动物营养学分会第七届中国饲料营养学术研讨会论文集. 郑州: 中国畜牧兽医学会动物营养学分会, 2014: 1. AN W T, LIU S D, GUO J W, et al. Effect of tannic acid on the nutrient digestibility and digestive enzyme activity of broiler feed[C]//Proceedings of the Seventh National Symposium on Feed Nutrition of Animal Nutrition Branch of Chinese Society of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine. Zhengzhou: Animal Nutrition Branch of Chinese Society of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2014: 1. (in Chinese) |
| [16] |
吴雅清. 不同水解单宁酸的添加量对黄羽肉鸡生产性能的影响[J]. 畜禽业, 2017, 28(6): 4-5. WU Y Q. Effect of different hydrolyzed tannins on the performance of yellow feather broilers[J]. Livestock and Poultry Industry, 2017, 28(6): 4-5 (in Chinese). |
| [17] |
黄俊文, 林映才, 冯定远, 等. 纳豆菌、甘露寡糖对仔猪肠道pH、微生物区系及肠黏膜形态的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2005, 36(10): 1021-1027. HUANG J W, LIN Y C, FENG D Y, et al. Effect of natto and MOS on intestinal pH, colonic microflora population and intestinal membrane shape of early weaning piglet[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 2005, 36(10): 1021-1027 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0366-6964.2005.10.008 |
| [18] |
李茜, 侯海锋, 刘彦慈, 等. 水解单宁酸对蛋鸡肠道健康的影响[J]. 饲料工业, 2016, 37(19): 12-15. LI Q, HOU H F, LIU Y C, et al. Effects of hydrolyzed tannin acid on intestinal health of layers[J]. Feed Industry, 2016, 37(19): 12-15 (in Chinese). |
| [19] |
MAJUMDA S, MOUDGAL R P. Effect of tannic acid on activities of certain digestive enzymes and alkaline phosphatase in intestine and glucose absorption in adult chickens[J]. Journal of Applied Animal Research, 1994, 6(2): 105-112. DOI:10.1080/09712119.1994.9706032 |
| [20] |
MOLE S, WATERMAN P G. Stimulatory effects of tannins and cholic acid on tryptic hydrolysis of proteins: ecological implications[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 1985, 11(9): 1323-1332. DOI:10.1007/BF01024119 |
| [21] |
SHAMOTO K, YAMAUCHI K. Recovery responses of chick intestinal villus morphology to different refeeding procedures[J]. Poultry Science, 2000, 79(5): 718-723. DOI:10.1093/ps/79.5.718 |
| [22] |
邢帅兵, 陈代文, 余冰, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌对断奶仔猪生长性能和肠道形态、黏膜免疫及菌群数量的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(5): 2066-2073. XING B S, CHEN D W, YU B, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on growth performance, intestinal morphology, mucosal immune and microflora number of weaned piglets[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(5): 2066-2073 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.05.015 |
| [23] |
王前光, 李闯, 黄璇, 等. 葡萄糖氧化酶对1~6周龄临武鸭生长性能、血清生化和抗氧化指标、肠道形态结构和微生物多样性的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(8): 3605-3614. WANG Q G, LI C, HUANG X, et al. Effects of glucose oxidase on growth performance, serum biochemical and antioxidant indexes, intestinal morphology and microbial diversity of 1 to 6-week-old Linwu ducks[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(8): 3605-3614 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.08.019 |
| [24] |
MONTAGNE L, PLUSKE J R, HAMPSON D J. A review of interactions between dietary fibre and the intestinal mucosa, and their consequences on digestive health in young non-ruminant animals[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2003, 108(1/2/3/4): 95-117. |
| [25] |
郭雪峰, 边连全, 付亮亮, 等. 酸化剂对早期断奶仔猪胃肠道pH和肠黏膜形态结构的影响[J]. 养猪, 2006(5): 4-6. GUO X F, BIAN L Q, FU L L, et al. Effects of acidulants on the pH of the gastrointestinal tract and the morphological structure of intestinal mucosa in early weaned piglets[J]. Swine Production, 2006(5): 4-6 (in Chinese). |
| [26] |
LIU H W, LI K, ZHAO J S, et al. Effects of chestnut tannins on intestinal morphology, barrier function, pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, microflora and antioxidant capacity in heat-stressed broilers[J]. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2018, 102(3): 717-726. DOI:10.1111/jpn.12839 |
| [27] |
BILIĆ-ŠOBOT D, KUBALE V, ŠKRLEP M, et al. Effect of hydrolysable tannins on intestinal morphology, proliferation and apoptosis in entire male pigs[J]. Archives of Animal Nutrition, 2016, 70(5): 378-388. DOI:10.1080/1745039X.2016.1206735 |
| [28] |
杨镒峰, 魏海军. 单宁对反刍动物影响的研究进展[J]. 特产研究, 2010, 32(1): 60-64. YANG Y F, WEI H J. Review of effects of tannins on ruminants[J]. Special Wild Economic Animal and Plant Research, 2010, 32(1): 60-64 (in Chinese). |
| [29] |
ZOTTE A D, COSSU M E. Dietary inclusion of tannin extract from red quebracho trees (Schinopsis spp.) in the rabbit meat production[J]. Italian Journal of Animal Science, 2009, 8(Suppl.2): 784-786. |
| [30] |
MARÍN-MARTINEZ R, VELOZ-GARCÍA R, VELOZ-RODRÍGUEZ R, et al. Antimutagenic and antioxidant activities of quebracho phenolics (Schinopsis balansae) recovered from tannery wastewaters[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 100(1): 434-439. DOI:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.05.029 |
| [31] |
MANSOORI B, MODIRSANEI M. The effect of tannic acid and polyethylene glycol on the absorption capacity of chicken intestine for D-xylose and β-carotene[J]. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2012, 96(1): 47-51. DOI:10.1111/j.1439-0396.2010.01120.x |
| [32] |
MAERTENS L, ŠTRUKLEC M. Preliminary results with a tannin extract on the performance and mortality of growing rabbits in an enteropathy infected environment[J]. World Rabbit Science, 2006, 14(3): 189-192. |
| [33] |
魏昆鹏, 朱子洁. 水解单宁酸对家禽肠道健康的促进作用[J]. 中国动物保健, 2016, 18(7): 30-31. WEI K P, ZHU Z J. The promoting effect of hydrolyzed tannins on poultry intestinal health[J]. China Animal Health, 2016, 18(7): 30-31 (in Chinese). |
| [34] |
JAMROZ D, WILICZKIEWICZ A, SKORUPIŃSKA J, et al. Effect of sweet chestnut tannin (SCT) on the performance, microbial status of intestine and histological characteristics of intestine wall in chickens[J]. British Poultry Science, 2009, 50(6): 687-699. |




