2. 湖南师范大学生命科学学院, 省部共建淡水鱼类发育生物学国家重点实验室, 长沙 410081;
3. 深圳市澳华集团股份有限公司, 深圳 518067
2. State Key Laboratory of Developmental Biology of Freshwater Fish, College of Life Sciences, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410081, China;
3. Shenzhen Alpha Group Co., Ltd., Shenzhen 518067, China
豆粕因蛋白质含量高且氨基酸组成较为均衡而成为水产饲料中重要的蛋白质源,但随着国内水产行业的迅速发展,豆粕需求量逐年增长,而我国大豆主要依靠进口,加之近年来中美贸易关系紧张,导致大豆价格持续走高,因此寻找成本低廉且对养殖动物无负面影响的替代蛋白质源显得尤为重要。玉米干酒糟及其可溶物(DDGS)是玉米产出燃料乙醇后,再通过低温干燥处理形成的含有可溶固形物的干酒糟。玉米DDGS中蛋白质、纤维素、维生素和脂肪含量较高,且价格低廉,来源广泛[1-2]。玉米DDGS在畜禽生产中已有广泛的研究和应用,有研究表明饲粮中添加适量玉米DDGS对动物的生长无不利影响,但在肉鸡饲粮中添加水平过高可能会导致鸡胸肉产量下降[3]。有研究显示,玉米DDGS中含有玉米黄质及叶黄素,动物摄入后会对肌肉、皮肤或其副产物颜色产生影响[4-5],例如,在蛋鸡饲粮中添加玉米DDGS会对蛋黄的颜色产生显著影响。
关于玉米DDGS对水产动物影响的研究多集中在生长和免疫方面,饲料中适量添加玉米DDGS对水产动物的生长性能无负面影响且能在一定程度上提高机体免疫力[6-7],但对体色、肉色和肠道菌群结构的研究未见报道。
斑点叉尾

以鱼粉、豆粕为主要蛋白质源,并分别添加0(对照组)、3%(D1组)、6%(D2组)和12%(D3组)的玉米DDGS(主要成分为蛋白质、脂肪、粗纤维及有效磷),配制4种试验饲料,其组成及营养水平见表 1。饲料制备前先将饲料原料粉碎,过60目筛,按配比从小到大逐级定量均匀混合,再将其投入V型搅拌机充分混合25 min;随后将豆油与混好的饲料干粉充分混匀,再喷入适量的水混合均匀,将混合均匀的饲料用单螺杆挤压式饲料膨化机(安德里茨EX1250,中国,调制温度100 ℃,出模温度120 ℃左右)制成粒径为3.0 mm的膨化饲料,阴凉处风干后储存备用。
|
|
表 1 试验饲料组成及营养水平(风干基础) Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of experimental diets (air-dry basis) |
养殖试验在湖南省娄底市车田江水库试验基地中进行,试验鱼统一购于种苗公司,并在网箱(9 m×9 m×2 m)中暂养1个月,暂养期间投喂对照组饲料,分组前饥饿24 h。挑选规格一致、体格健康、初始体重(50.0±0.2)g的斑点叉尾
试验开始前和结束后记录每个网箱斑点叉尾
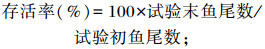
|
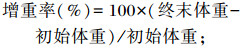
|

|
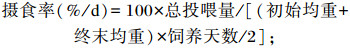
|
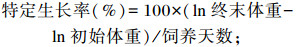
|
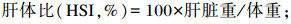
|
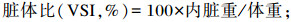
|
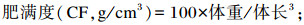
|
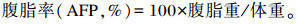
|
养殖试验结束后,从每个网箱中随机取6尾鱼,参考梁高杨等[9]的方法,用色差仪(NR110)测定腹部与侧线附近皮肤的亮度(L*)、红度(a*)、黄度(b*)值以及背部肌肉的L*、a*、b*值。具体测样点如图 1所示。
|
图 1 体色测样点(图片来自百度网站) Fig. 1 Body color test points (picture from Baidu website) |
养殖试验结束后,从每个网箱中随机取5尾鱼,使用经0.2%的肝素钠润洗后的注射器自尾静脉取血,储存于4 ℃冰箱,2 h后使用离心机3 000 r/min离心10 min,吸取血清并保存于-80 ℃冰箱中待测。血清碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase, AKP)活性以及低密度脂蛋白(low-density lipoprotein, LDL)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol, TC)、甘油三酯(triglyceride, TG)、总胆汁酸(total bile acid, TBA)含量采用南京建成生物工程研究所生产的试剂盒进行测定,免疫球蛋白M(immunoglobulin M,IgM)、补体3(complement 3,C3)和补体4(complement 4,C4)含量采用浙江伊利康生物技术有限公司生产的试剂盒进行测定。
1.3.4 肠道菌群结构养殖试验结束后,从每个网箱中随机取3尾鱼,用于肠道菌群结构检测样品采集。将解剖盘与器材用75%酒精消毒后,在酒精灯旁取出鱼体肠道后放入无菌离心管,于-80 ℃冰箱保存,用于后续肠道菌群结构分析。使用天根总DNA提取试剂盒进行斑点叉尾 肠道菌群DNA提取。选取对照组、D2组、D3组DNA送北京诺和致源生物科技有限公司进行肠道菌群测序,后续利用诺和致源售后平台工具(https://magic.novogene.com)进行数据分析统计。
肠道菌群DNA提取。选取对照组、D2组、D3组DNA送北京诺和致源生物科技有限公司进行肠道菌群测序,后续利用诺和致源售后平台工具(https://magic.novogene.com)进行数据分析统计。
试验数据通过SPSS 25.0软件采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)程序进行方差分析,并采用Duncan氏法进行组间多重比较。显著水平为P<0.05,结果用平均值±标准误表示。
2 结果 2.1 饲料中添加不同水平玉米DDGS对斑点叉尾
由表 2可知,饲料中添加不同水平玉米DDGS替代部分豆粕对斑点叉尾
|
|
表 2 饲料中添加不同水平玉米DDGS对斑点叉尾 |

由表 3可知,饲料中添加不同水平玉米DDGS替代部分豆粕对斑点叉尾

|
|
表 3 饲料中添加不同水平玉米DDGS对斑点叉尾 |
|
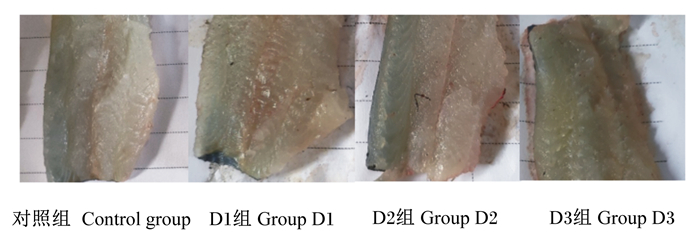
图 2 斑点叉尾 |

由表 4可知,饲料中添加不同水平玉米DDGS替代部分豆粕对斑点叉尾
|
|
表 4 饲料中添加不同水平DDGS对斑点叉尾 |

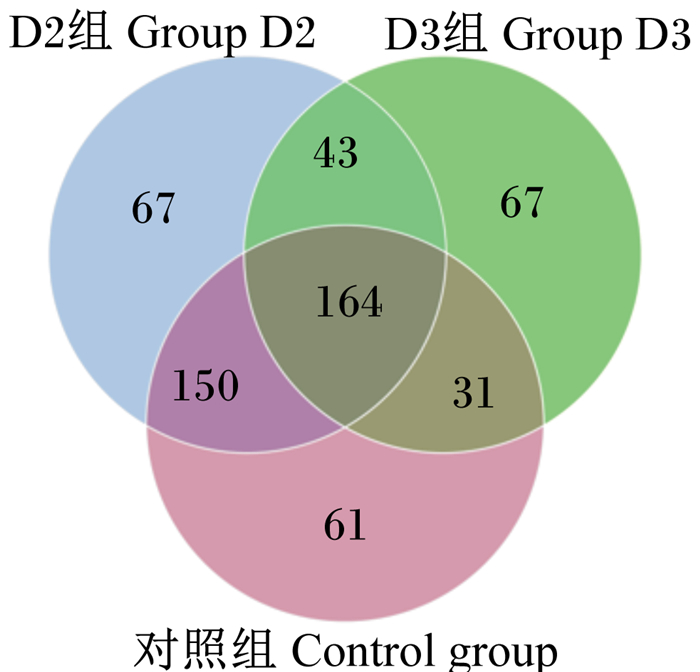
根据生长性能、血清生化指标和体色、肉色差异,对对照组、D2组和D3组肠道菌群进行测序。由图 3可知,对照组操作分类单元(OTU)数目为406个,D2组OTU数目为424个,D3组OTU数目为305个,3组共有的OTU数目为164个,对照组与D2组共有OTU数目为150个,对照组与D3组共有OTU数目为31个,D2组与D3组共有OTU数目为43个,对照组特有OTU数目为61个,D2组、D3组特有OTU数目均为67个。
|
图 3 OTU韦恩图 Fig. 3 OTU Venn chart |
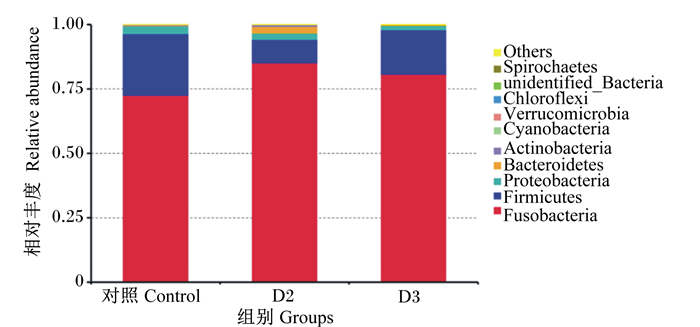
通过对斑点叉尾
|
Fusobacteria:梭杆菌门;Firmicutes:厚壁菌门;Proteobacteria:变形菌门;Bacteroidetes:拟杆菌门;Actinobacteria:放线菌门;Cyanobacteria:蓝细菌门;Verrucomicrobia:疣微菌门;Chloroflexi:绿弯菌门;unidentified_Bacteria:未鉴定细菌;Spirochaetes:螺旋体门;Others:其他。 图 4 门水平物种相对丰度 Fig. 4 Relative abundance of species on phylum level |
|
|
表 5 门水平排名前5的物种相对丰度 Table 5 Relative abundance of top 5 species on phylum level |
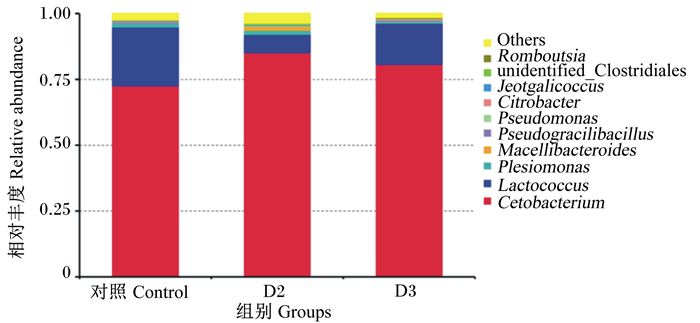
由图 5可知,斑点叉尾
|
Cetobacterium:鲸杆菌属;Lactococcus:乳球菌属;Plesiomonas:邻单胞菌属;Macellibacteroides:屠场杆状菌属;Pseudogracilibacillus:假纤细芽胞杆菌属;Pseudomonas:假单胞菌属;Citrobacter:柠檬酸杆菌属;Jeotgalicoccus:咸海鲜球菌属;unidentified_Clostridiales:梭菌目未鉴定属;Romboutsia:罗姆布茨菌属;Others:其他。 图 5 属水平物种相对丰度 Fig. 5 Relative abundance of species on genus level |
|
|
表 6 属水平排名前3的物种相对丰度 Table 6 Relative abundance of top 3 species on genus level |

研究表明,细鳞鲳(Piaractus mesopotamicus)幼鱼饲料中添加玉米DDGS可提高饲料效率,对增重率和形体指标无显著影响[10]。本研究结果表明,饲料中添加不同水平玉米DDGS替代部分豆粕对斑点叉尾



鱼类的皮肤和肌肉颜色的变化取决于摄取的类胡萝卜素,鱼类和其他动物一样,自生不能合成类胡萝卜素[15]。玉米DDGS中含有的玉米黄质和叶黄素会影响斑点叉尾


血清中LDL、TC、TG和TBA含量是评价动物肝胆健康及脂质吸收代谢的重要指标,LDL作为胆固醇的载体,其含量与血清中TC含量呈正相关。本试验结果显示,随着饲料中玉米DDGS添加水平的升高,血清中LDL、TC、TG含量均不同程度下降,血清TBA含量各组间无显著差异,与黄文庆等[18]的研究结果相似。在亚麻籽饲料中添加玉米DDGS会显著降低肉鸡血清TG和TC含量[19],说明饲料中添加玉米DDGS能改善脂质吸收代谢且不会对肝脏功能造成负面影响。Shelby等[20]使用玉米DDGS部分替代饲料中豆粕后对尼罗罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus L.)血清免疫指标并无显著影响,本研究中血清IgM和C4含量的结果与其一致。AKP作为生物体内重要的磷酸酶,能够反映机体肝脏功能是否有损伤[21]。在正常情况下血清中AKP的活性保持在相对较低且稳定的状态下,只有当肝脏受到损伤时其活性才会升高[22]。本研究中,饲料中玉米DDGS添加水平为6%时血清AKP活性显著低于对照组,添加水平为12%时与对照组差异不显著,因此推测斑点叉尾

硬骨鱼类与水生环境直接接触,因此水环境中复杂而动态的微生物群落可能对其健康产生影响[23]。肠道黏膜表面是肠道菌群与宿主相互作用的主要部位,正常微生物群落在肠道黏膜表面的定植对肠道的消化吸收和机体免疫调节功能具有积极作用,而微生物群落失衡对鱼体则会产生不利影响[24]。与水环境相比,消化道是一个营养更丰富的生态系统,因此更有利于大多数细菌的生长,但并不是所有进入鱼类消化道的食物中的细菌都会寄生在肠道内[25]。存在于消化道中的微生物以寄主的食物为食,寄主的食物被它们和寄主自身产生的酶消化,而寄主产生的食糜决定了消化道中微生物的丰度和质量组成[26],因此饲料的组成成分会对其肠道菌群结构产生一定影响。本试验研究结果显示,斑点叉尾


在本试验中,当饲料中玉米DDGS添加水平达到6%时,斑点叉尾



综上所述,饲料中添加12%的玉米DDGS替代部分豆粕不会对斑点叉尾
| [1] |
IRAM A, CEKMECELIOGLU D, DEMIRCI A. Distillers' dried grains with solubles (DDGS) and its potential as fermentation feedstock[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(14): 6115-6128. DOI:10.1007/s00253-020-10682-0 |
| [2] |
罗威才. 美国玉米DDGS的营养价值及其在蛋鸭饲粮中的应用研究[D]. 硕士学位论文. 厦门: 集美大学, 2017. LUO W C. Nutritional value of corn DDGS from America and its application in diet of laying ducks[D]. Master's Thesis. Xiamen: Jimei University, 2017. (in Chinese) |
| [3] |
REIS V A, REIS R A, DA ROS DE ARAÚJO T L, et al. Performance, beef quality and expression of lipogenic genes in young bulls fed low-fat dried distillers grains[J]. Meat Science, 2020, 160: 107962. DOI:10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.107962 |
| [4] |
NIEMIEC J, RIEDEL J, SZULC T, et al. Feeding corn distillers's dried grains with solubles (DDGS) and its effect on egg quality and performance of laying hens[J]. Annals of Animal Science, 2013, 13(1): 97-107. DOI:10.2478/v10220-012-0062-y |
| [5] |
LI M H, ROBINSON E H, OBERLE D F, et al. Effects of various corn distillers by-products on growth, feed efficiency, and body composition of channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus[J]. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2010, 16(2): 188-193. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2095.2009.00650.x |
| [6] |
OVERLAND M, KROGDAHL Å, SHURSON G, et al. Evaluation of distiller's dried grains with solubles (DDGS) and high protein distiller's dried grains (HPDDG) in diets for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)[J]. Aquaculture, 2013, 416/417: 201-208. DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.09.016 |
| [7] |
DIÓGENES A F, BASTO A, ESTEVÃO-RODRIGUES T T, et al. Soybean meal replacement by corn distillers dried grains with solubles (DDGS) and exogenous non-starch polysaccharidases supplementation in diets for gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) juveniles[J]. Aquaculture, 2019, 500: 435-442. DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.10.035 |
| [8] |
LIANG G Y, LI X Q, YANG H, et al. Dietary oxidized oils decreased growth, antioxidative capacity, and negatively affected skin color of channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus[J]. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 2019, 50(3): 692-706. DOI:10.1111/jwas.12556 |
| [9] |
梁高杨, 李小勤, 高启平, 等. 氧化油脂对斑点叉尾鮰生长、体色和抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 水生生物学报, 2019, 43(1): 60-68. LIANG G Y, LI X Q, GAO Q P, et al. Effect of oxidized oils on growth, body color and antioxidant capacity of channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2019, 43(1): 60-68 (in Chinese). |
| [10] |
OLIVEIRA K R B, SEGURA J G, OLIVEIRA B A, et al. Distillers' dried grains with soluble in diets for pacu, Piaractus mesopotamicus juveniles: growth performance, feed utilization, economic viability, and phosphorus release[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2020, 262: 114393. DOI:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2020.114393 |
| [11] |
钟广贤. 玉米DDGS对草鱼、鲤鱼生长性能及体成分的影响[D]. 硕士学位论文. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2013. ZHONG G X. The effects of corn DDGS on growth performance and body composition in grass carp and carp[D]. Master's Thesis. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2013. (in Chinese) |
| [12] |
何晓庆, 曹俊明, 黄燕华, 等. 玉米DDGS替代豆粕对奥尼罗非鱼生长性能的影响[J]. 饲料工业, 2009, 30(22): 26-29. HE X Q, CAO J M, HUANG Y H, et al. Effects of corn DDGS instead of soybean meal on the growth performance in hybrid tilapia Oreochromis niloticus×O.aureus[J]. Feed Industry, 2009, 30(22): 26-29 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-991X.2009.22.008 |
| [13] |
KAUSHIK S J, COVÈS D, DUTTO G, et al. Almost total replacement of fish meal by plant protein sources in the diet of a marine teleost, the European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax[J]. Aquaculture, 2004, 230(1/2/3/4): 391-404. |
| [14] |
BENEDITO-PALOS L, NAVARRO J C, SITJÀ-BOBADILLA A, et al. High levels of vegetable oils in plant protein-rich diets fed to gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.): growth performance, muscle fatty acid profiles and histological alterations of target tissues[J]. British Journal of Nutrition, 2008, 100(5): 992-1003. DOI:10.1017/S0007114508966071 |
| [15] |
URBAN J, ŠTYS D, SERGEJEVOVÁ M, et al. Expertomica Fishgui: comparison of fish skin colour[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 2013, 29(1): 172-180. DOI:10.1111/jai.12011 |
| [16] |
LI M H, ROBINSON E H, OBERLE D F, et al. Effects of various dietary carotenoid pigments on fillet appearance and pigment absorption in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus[J]. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 2007, 38(4): 557-563. DOI:10.1111/j.1749-7345.2007.00130.x |
| [17] |
LI M H, OBERLE D F, LUCAS P M. Evaluation of corn distillers dried grains with solubles and brewers yeast in diets for channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus (Rafinesque)[J]. Aquaculture Research, 2011, 42(10): 1424-1430. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2109.2010.02734.x |
| [18] |
黄文庆, 王国霞, 罗志锋, 等. 玉米DDGS替代豆粕对草鱼幼鱼生长性能、血清生化指标和免疫指标的影响[J]. 饲料工业, 2012, 33(16): 33-36. HUANG W Q, WANG G X, LUO Z F, et al. Effects of soya bean meal replaced by DDGS on growth performance, serum biochemical indexand immune index of Ctenopharyngodon idella[J]. Feed Industry, 2012, 33(16): 33-36 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-991X.2012.16.009 |
| [19] |
MIR N A, TYAGI P K, BISWAS A K, et al. Effect of feeding broken rice and distillers's dried grains with solubles in a flaxseed-based diet on the growth performance, production efficiency, carcass characteristics, sensory evaluation of meat, and serum biochemistry of broiler chickens[J]. Turkish Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, 2017, 41(5): 583-589. |
| [20] |
SHELBY R A, LIM C, AKSOY M Y, et al. Effect of distillers dried grains with solubles-incorporated diets on growth, immune function and disease resistance in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.)[J]. Aquaculture Research, 2008, 39(12): 1351-1353. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.02000.x |
| [21] |
RODGERSON D O, MCBRIDE J H. Fundamentals of clinical chemistry: Norbert W.Tietz (editor) third edition W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, PA., 19105, 1987, 1, 044 pp.$44.95[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta, 1987, 166(2/3): 339-340. |
| [22] |
何勤, 贾睿, 曹丽萍, 等. 氧化应激对鲤抗氧化状态和免疫功能的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2021, 45(1): 33-43. HE Q, JIA R, CAO L P, et al. Antioxidative and immune response in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) under oxidative stress[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2021, 45(1): 33-43 (in Chinese). |
| [23] |
GOMEZ D, SUNYER J O, SALINAS I. The mucosal immune system of fish: the evolution of tolerating commensals while fighting pathogens[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2013, 35(6): 1729-1739. |
| [24] |
PÉREZ T, BALCÁZAR J L, RUIZ-ZARZUELA I, et al. Host-microbiota interactions within the fish intestinal ecosystem[J]. Mucosal Immunology, 2010, 3(4): 355-360. DOI:10.1038/mi.2010.12 |
| [25] |
WANG Y B, LI J R, LIN J D. Probiotics in aquaculture: challenges and outlook[J]. Aquaculture, 2008, 281(1/2/3/4): 1-4. |
| [26] |
GANGULY S, PRASAD A. Microflora in fish digestive tract plays significant role in digestion and metabolism[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 2011, 22(1): 11-16. |
| [27] |
HANSEN G H, OLAFSEN J A. Bacterial interactions in early life stages of marine cold water fish[J]. Microbial Ecology, 1999, 38(1): 1-26. DOI:10.1007/s002489900158 |
| [28] |
何娇娇, 王萍, 冯建, 等. 发酵豆粕对大黄鱼生长、肠道结构及肠道微生物菌群的研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 2018, 42(5): 919-928. HE J J, WANG P, FENG J, et al. Effects of fermented soybean meal on the growth and intestinal histology and microbiota of jucenile large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2018, 42(5): 919-928 (in Chinese). |
| [29] |
QI X Z, XUE M Y, YANG S B, et al. Ammonia exposure alters the expression of immune-related and antioxidant enzymes-related genes and the gut microbial community of crucian carp (Carassius auratus)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2017, 70: 485-492. |
| [30] |
WANG L, WANG J, LU K L, et al. Total replacement of fish meal with soybean meal in diets for bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus): effects on growth performance and gut microbial composition[J]. Aquaculture, 2020, 524: 735236. DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735236 |
| [31] |
COWEY C B. Amino acid requirements of fish: a critical appraisal of present values[J]. Aquaculture, 1994, 124(1/2/3/4): 1-11. |
| [32] |
LI P, MAI K, TRUSHENSKI J, et al. New developments in fish amino acid nutrition: towards functional and environmentally oriented aquafeeds[J]. Amino Acids, 2009, 37(1): 43-53. DOI:10.1007/s00726-008-0171-1 |
| [33] |
ZHAO L P, ZHANG F, DING X Y, et al. Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes[J]. Science, 2018, 359(6380): 1151-1156. DOI:10.1126/science.aao5774 |
| [34] |
VENDRELL D, BALCÁZAR J L, RUIZ-ZARZUELA I, et al. Lactococcus garvieae in fish: a review[J]. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 2006, 29(4): 177-198. DOI:10.1016/j.cimid.2006.06.003 |
| [35] |
ELDAR A, GHITTINO C, ASANTA L, et al. Enterococcus seriolicida is a junior synonym of Lactococcus garvieae, a causative agent of septicemia and meningoencephalitis in fish[J]. Current Microbiology, 1996, 32(2): 85-88. DOI:10.1007/s002849900015 |




