2. 中国热带农业科学院热带作物品种资源研究所, 儋州 571737
2. Institute of Tropical Crop Variety Resources, Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences, Danzhou 571737, China
氧化应激被认为是体内所释放的氧化自由基超过机体本身的抗氧化水平,引发机体发生不同的生理或病理现象。当仔猪发生氧化应激时会破坏自由基代谢和抗氧化系统[1],从而发生严重的氧化应激反应,由此使机体免疫系统损坏,引发炎症反应[2],同时还与肠道健康有关,可导致肠黏膜屏障功能受损[3]。Li等[4]研究表明,敌草快(Diquat)诱导的仔猪氧化应激会显著降低回肠黏膜结构的绒毛高度/隐窝深度(V/C),导致肠绒毛形态发育不完整。Zheng等[5]研究发现,仔猪腹腔注射Diquat显著提高血清中皮质醇和丙二醛(MDA)的含量,造成仔猪抗氧化能力下降,导致营养物质的吸收减少。因此,寻找一种缓解仔猪肠道氧化应激的饲料添加剂对于仔猪的生产具有实际意义。
白藜芦醇(Res)是一种植物多酚,属于植物抗毒素类的二苯乙烯家族[6],在体内外均表现出强大的抗氧化活性[7-8]。因其具备广泛的生物活性而备受关注,其中还包括抗炎、抗癌、抗衰老、保护心血管和调控脂肪沉积等作用[9-13]。Meng等[14]研究发现,Res能够通过上调核因子E2相关因子2(Nrf2)蛋白表达水平,下调Kelch样环氧氯丙烷相关蛋白1(Keap1)蛋白表达水平,从而激活Nrf2信号通路;并上调Nrf2调节的抗氧化防御系统相关基因表达,包括过氧化氢酶(CAT)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物1型酶(GPX1)和血红素加氧酶1(HO1),提高了母猪妊娠期胎盘的抗氧化能力。另有研究表明,Res可以调节断奶仔猪肠道微生物群,抑制Toll样受体4(TLR4)信号通路,减轻肠道炎症,增强肠道免疫功能[15]。目前,对于Res的研究主要集中在其对动物的生产性能、脂质合成和缓解肠道炎症等方面的影响,然而其对肠黏膜的保护作用以及具体机制鲜有报道。因此,本试验拟通过建立Diquat诱导的断奶仔猪氧化应激模型,比较Res对氧化应激仔猪肠道黏膜结构、抗氧化能力、紧密连接蛋白及炎性因子mRNA表达的影响,明确其对肠黏膜的保护作用,以期为仔猪绿色饲料添加剂的研发提供数据支撑。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验材料Res购于上海某生物科技有限公司,纯度为98%;Diquat溶液购于Sigma公司;荧光定量PCR试剂盒、逆转录试剂盒与RNAiso Plus购于南京诺唯赞生物有限公司;抗氧化试剂盒购于南京建成生物工程研究所。
1.2 试验设计及饲粮选择健康状况良好、胎次相近的28日龄三元杂交(杜×长×大)断奶仔猪30头,随机分为5组,对照组饲喂基础饲粮,试验组在基础饲粮中分别添加0、10、30、90 mg/kg Res,每组6个重复,每个重复1头仔猪。试验期21 d。于试验第15天清晨给试验组(Diquat组、Diquat+10 mg/kg Res组、Diquat+30 mg/kg Res组、Diquat+90 mg/kg Res组)仔猪按照10 mg/kg BW的剂量腹腔注射Diquat建立氧化应激模型,对照组只注射相同剂量灭菌生理盐水为参照,诱导产生氧化应激后再继续饲喂7 d,屠宰采集肠道样品。基础饲粮参考NRC(2012)营养需要配制,其组成及营养水平见表 1。
|
|
表 1 基础饲粮组成及营养水平(风干基础) Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of the basal diet (air-dry basis) |
本试验在中国热带农业科学院热带作物品种资源研究所畜牧基地开展,整个动物饲养试验开展期间所有仔猪自由采食和饮水。每天饲喂3次,以仔猪吃饱后料槽内有余料为度。每天打扫保持圈舍清洁,定期消毒。
1.4 样品采集饲养试验结束前12 h停止对仔猪喂食。试验第22天清晨所有仔猪颈静脉放血处死,屠宰后打开腹腔,取出回肠,立即放入盛有冰块的冰盒中,取回肠中段5~10 cm,用冰浴的生理盐水洗净外壁及内容物,滤纸吸干,剪开肠管,用载玻片轻轻刮取肠黏膜,取约0.5 g肠黏膜用锡箔纸成粒状,每个样品包4~5粒放入2 mL离心管中,编号,放入液氮中暂时保存,采样结束后样品保存于-80 ℃。另取约5 cm回肠中段,用生理盐水洗去内容物后放入4%多聚甲醛固定液固定肠管。
1.5 回肠黏膜形态测定将已固定的组织样修整、冲洗、脱水、透明、浸蜡、包埋、修块、切片、展片[16]后进行苏木精-伊红(HE)染色,光镜下测定小肠绒毛长度、宽度、隐窝深度和V/C,每张切片选取5个视野拍照,并选取3个走向完整的肠绒毛进行测量取均值。
1.6 抗氧化能力测定肠黏膜谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性、MDA含量采用南京建成生物工程研究所提供的试剂盒测定,检测过程按照试剂盒的操作说明完成。
1.7 肠黏膜紧密连接蛋白与细胞因子mRNA相对表达量测定采用实时荧光定量PCR检测肠黏膜闭锁小带蛋白-1(ZO-1)、闭锁蛋白(Occludin)和跨膜蛋白(Claudin)、白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)和白细胞介素-10(IL-10)的mRNA相对表达量。RNAiso Plus试剂盒提取回肠黏膜组织总RNA,利用超微量分光光度计测定仪检测RNA浓度,吸光度在OD260/OD280=1.8~2.2表示RNA纯度较高;采用琼脂糖凝胶电泳鉴定RNA品质,电泳后可见28s、18s和5s的小分子条带则说明RNA完整性较好,之后保存于-80 ℃备用。HiScript Ⅲ RT SuperMix for qPCR试剂盒说明进行cDNA的合成,得到的cDNA于-20 ℃保存备用。以反转录的cDNA为模板扩增基因,进行实时荧光定量PCR(Vazyme Biotech)检测。反应程序为:95 ℃ 30 s→95 ℃ 10 s→60 ℃ 30 s(40个循环);熔解曲线95 ℃ 15 s→60 ℃ 60 s→95 ℃ 15 s。甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶(GAPDH)为内参,采用2-ΔΔCt法计算各组基因的mRNA相对表达量。利用Premier 5.0软件设计引物,引物序列见表 2[16-17]。
|
|
表 2 引物序列 Table 2 Primer sequences |
数据采用SPSS 17.0软件进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)和Duncan氏法进行多重比较,以P < 0.05作为差异显著性判断标准。
2 结果与分析 2.1 Res对氧化应激仔猪回肠黏膜形态的影响由图 1可知,对照组回肠绒毛结构完整,排列整齐(图 1-A),Diquat组肠绒毛结构出现脱落或松散的现象(图 1-B),经过Diquat+Res(10 mg/kg)处理后绒毛结构仍有脱落(图 1-C),Diquat+30 mg/kg Res组和Diquat+90 mg/kg Res组肠黏膜结构发育趋于整齐且密集,形状规则(图 1-D、图 1-E)。
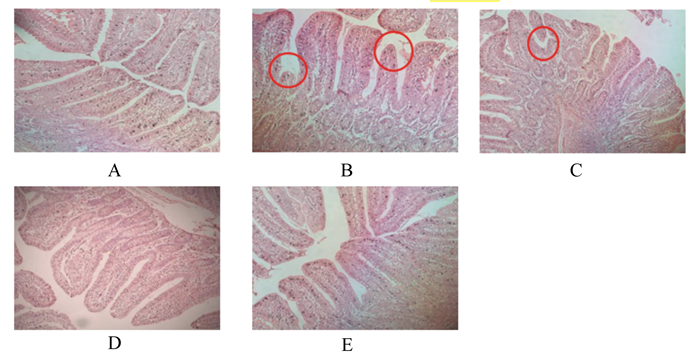
|
A:对照组control group;B:Diquat组Diquat group;C:Diquat+10 mg/kg Res组Diquat+10 mg/kg Res group;D:Diquat+30 mg/kg Res组Diquat+30 mg/kg Res group;E:Diquat+90 mg/kg Res组Diquat+90 mg/kg Res group。 图 1 各组回肠黏膜形态 Fig. 1 Morphology of ileum mucosa in each group (200×) |
由表 3可知,与对照组相比,Diquat组绒毛高度和V/C显著降低(P<0.05),隐窝深度显著升高(P<0.05)。氧化应激状态下,Diquat+30 mg/kg Res组和Diquat+90 mg/kg Res组绒毛高度均显著高于Diquat组(P<0.05),隐窝深度显著低于Diquat组(P<0.05)。
|
|
表 3 Res对氧化应激仔猪回肠黏膜形态的影响 Table 3 Effects of Res on ileal mucosal morphology in oxidative stress piglets (n=6) |
由表 4可知,与对照组相比,Diquat组肠黏膜MDA含量显著升高(P<0.05),GSH-Px和SOD活性显著下降(P<0.05)。与Diqaut组相比,Diquat+30 mg/kg Res组或Diquat+90 mg/kg Res组中肠黏膜GSH-Px和SOD活性显著提高(P<0.05),MDA含量显著降低(P<0.05),且Diquat+90 mg/kg Res组中抗氧化酶活性与对照组无显著差异(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 4 Res对氧化应激仔猪回肠黏膜抗氧化能力的影响 Table 4 Effects of Res on antioxidant ability of ileal mucosa in oxidative stress piglets |
由表 5可知,与对照组相比,Diquat组中肠黏膜ZO-1、Occludin和Claudin的mRNA相对表达量均显著降低(P<0.05)。与Diquat组相比,肠黏膜ZO-1、Occludin和Claudin的mRNA相对表达量均显著提高(P<0.05),且Diquat+10 mg/kg Res组、Diquat+30 mg/kg Res组和Diquat+90 mg/kg Res组间无显著差异(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 5 Res对氧化应激仔猪回肠黏膜紧密连接蛋白mRNA相对表达量的影响 Table 5 Effects of Res on relative expression levels of tight junction protein mRNA of ileal mucosa in oxidative stress piglets |
由表 6可知,与对照组相比,Diquat组肠黏膜IL-1β、TNF-α和IL-6的mRNA相对表达量显著降低(P<0.05),IL-10的mRNA表达量显著升高(P<0.05)。饲粮中添加30和90 mg/kg Res能显著降低氧化应激仔猪肠黏膜细胞因子IL-1β、TNF-α和IL-6的mRNA相对表达量(P<0.05),显著提高IL-10的mRNA相对表达量(P<0.05)。
|
|
表 6 Res对氧化应激仔猪回肠黏膜细胞因子mRNA相对表达量的影响 Table 6 Effects of Res on relative expression levels of inflammatory factor mRNA of ileal mucosa in oxidative stress piglets |
肠道的绒毛结构往往能反映出肠道健康情况,肠道形态损伤影响营养物质的吸收,增加肠道的通透性,从而降低肠道对疾病的抵抗力[18]。Wen等[19]研究表明,氧化应激损害断奶仔猪十二指肠、空肠和回肠的形态发育,缩短绒毛高度,降低V/C,并显著增加十二指肠的隐窝深度。有研究发现,在断奶仔猪的饲粮中补充Res增加了空肠绒毛高度,并有减少空肠凋亡细胞数量的趋势[20]。Chen等[21]研究发现,在饲粮中添加300 mg/kg Res可显著增加断奶仔猪空肠的绒毛高度和V/C。在本试验中,添加Res可以有效地提高氧化应激仔猪回肠的绒毛高度和V/C,降低隐窝深度,其中以添加量30、90 mg/kg Res效果较为显著,说明Res在一定程度上可以改善仔猪的回肠黏膜形态,缓解肠道应激,有利于促进机体对营养物质的消化吸收。
3.2 Res对氧化应激仔猪回肠黏膜抗氧化能力的影响细胞内活性氧(ROS)是机体在代谢过程中产生的一系列活性氧簇。机体的抗氧化系统维持着ROS产生与清除的动态平衡,同时核因子E2相关因子2 /Kelch样环氧氯丙烷相关蛋白1(Nrf2/Keap1)和核因子-κB/核因子-κB抑制蛋白(NF-κB/IκB)也广泛参与氧化应激反应[22]。GSH-Px、CAT和总超氧化物歧化酶(T-SOD)等抗氧化酶都具有很强的清除自由基的能力[23]。此外,MDA含量是衡量氧化应激水平的标志[24]。Meng等[14]研究表明,在母猪妊娠期和哺乳期补充Res降低了胎盘和乳汁中H2O2和MDA含量,增加其胎盘和乳汁的抗氧化状态,从而增加断奶仔猪的抗氧化能力,同时增加了胎盘中Keap1-Nrf2通路和沉默信息调节因子2相关酶1(Sirt1)抗氧化基因表达。Cao等[25]研究发现,在Diquat应激仔猪饲粮中添加Res减少了空肠线粒体ROS的产生。本试验研究结果表明,在氧化应激状态下添加不同水平Res均显著降低了回肠黏膜MDA含量,其中以30和90 mg/kg剂量的效果最为理想。此外,随着Res剂量的增加,肠黏膜GSH-Px和SOD的mRNA相对表达量得到显著升高,且以Diquat+90 mg/kg Res组的效果最为显著;这与胡瑶莲等[26]结果相似,说明适量的Res可以增强氧化应激仔猪的抗氧化能力。
3.3 Res对氧化应激仔猪回肠黏膜紧密连接蛋白mRNA相对表达量的影响黏附连接(AJ)和紧密连接(TJ)是肠道黏膜屏障的关键组成部分,在肠道稳态中起关键作用,ZO-1、Occludin和Claudins是TJ的重要成分,钙黏附蛋白E(E-cadherin)是AJ的主要成分[27]。ZO-1、Occludin、Claudins和E-cadherin的表达量降低会导致肠道通透性增加。研究表明,当仔猪受到氧化应激时会下调紧密连接蛋白的表达[25]。同时Liu等[28]研究发现,Diquat降低了ZO-1、Occludin和Claudin-1的mRNA表达以及ZO-1和Occludin的蛋白质表达,表明肠上皮屏障的紧密连接蛋白受到了氧化应激的破坏。多酚通过多种信号途径调节TJ表达,比如可通过丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)、Nrf2或血红素加氧酶-1(HO-1)信号通路来改善屏障功能[29-31]。Res是多酚类化合物,Zhuang等[32]研究发现,Res通磷脂肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶(PI3K/Akt)介导的Nrf2信号通路上调H2O2诱导的氧化应激下TJ蛋白的表达来减轻肠屏障的功能障碍,提高猪小肠上皮(IPEC-J2)细胞活力,降低凋亡率。本试验研究结果表明,Diquat组仔猪回肠黏膜ZO-1、Occludin和Claudin的mRNA相对表达量均显著降低,但在氧化应激状态下补充90 mg/kg Res可以有效地增加ZO-1、Occludin和Claudin的mRNA相对表达量,其中以Claudin的mRNA相对表达量的增加最为明显。该结果与Cao等[33]的研究结果相似,在注射Diquat的仔猪饲粮中添加100 mg/kg的Res显著提高回肠黏膜Occludin、Claudin-1和ZO-1的蛋白表达水平,说明饲粮中添加Res可以有效促进紧密连接蛋白表达,降低肠道通透性,缓解仔猪回肠黏膜氧化应激损伤,达到保护仔猪肠道健康的作用。
3.4 Res对氧化应激仔猪回肠黏膜炎性因子mRNA相对表达量的影响Res常被用于治疗炎症,如结肠炎[34]、乳腺炎[35]等。NF-κB是氧化应激和炎症相关组织损伤中氧化还原敏感的转录因子,在小鼠巨噬细胞中[36],发现Res通过分别降低和增加ac-NF-κB和IκB-α水平来调节炎症反应。在小鼠糖尿病模型中,Wang等[37]研究结果显示,Res显著增加Nrf2下游抗氧化基因NADPH醌脱氢酶-1(NQO-1)、HO-1的mRNA表达,且显著降低了IL-1β和TNF-α的蛋白表达水平,这说明它可能通过上调Nrf2和下游抗氧化剂的表达控制炎症发生。IL-1β、TNF-α属于炎症关键细胞因子,两者会导致肠黏膜紧密连接蛋白表达和分布发生变化,引起肠道通透性增加[38]。Cheng等[39]在小鼠热应激模型中发现Res可以使TNF-α含量降低,TLR4和细胞因子mRNA表达下调,通过抑制氧化应激和炎症来保护肠功能。本试验研究结果表明,当断奶仔猪受到氧化应激时,肠道黏膜炎症因子IL-1β和TNF-α的mRNA相对表达量显著增加,可能参与了Jun激酶(JNK)或NF-κB介导的信号转导通路的激活;结合IL-6表达丰度的增加和IL-10的mRNA表达量的降低,推测Res可能通过IL-6刺激T细胞增殖、IL-10抑制炎症因子进而实现抑制肠道炎症的发生。此外,与Diquat组相比,Diquat+30 mg/kg Res组或Diquat+90 mg/kg Res组肠黏膜IL-1β、TNF-α和IL-6的mRNA相对表达量均显著降低,而IL-10的mRNA相对表达量则显著升高,且与对照组无显著差异,与Gan等[15]在断奶仔猪添加300 mg/kg Res能降低空肠中IL-1β和TNF-α mRNA表达水平、提高IL-10的mRNA表达水平结果一致。这说明Res对于肠道炎症具有一定的抑制作用,但其具体的信号机制还需再进行深一步探讨。
4 结论当断奶仔猪遭受氧化应激时,其回肠黏膜形态结构遭到破坏,紧密连接蛋白表达显著降低,抗氧化及抗炎性能均显著降低。添加Res可以有效改善回肠黏膜形态,显著增强仔猪抗氧化能力,并抑制肠道炎症的发生,其中添加90 mg/kg Res效果较好。
| [1] |
YIN J, WU W W, XIAO H, et al. Development of an antioxidant system after early weaning in piglets[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2014, 92(2): 612-619. DOI:10.2527/jas.2013-6986 |
| [2] |
STOKES C R, BAILEY M, HAVERSON K, et al. Postnatal development of intestinal immune system in piglets:implications for the process of weaning[J]. Animal Research, 2004, 53(4): 325-334. DOI:10.1051/animres:2004020 |
| [3] |
WIJTTEN P J A, VAN DER MEULEN J, VERSTEGEN M W A. Intestinal barrier function and absorption in pigs after weaning:a review[J]. British Journal of Nutrition, 2011, 105(7): 967-981. DOI:10.1017/S0007114510005660 |
| [4] |
LI M, YUAN D X, LIU Y H, et al. Dietary puerarin supplementation alleviates oxidative stress in the small intestines of Diquat-challenged piglets[J]. Animals, 2020, 10(4): 631. DOI:10.3390/ani10040631 |
| [5] |
ZHENG P, YU B, HE J, et al. Arginine metabolism and its protective effects on intestinal health and functions in weaned piglets under oxidative stress induced by Diquat[J]. British Journal of Nutrition, 2017, 117(11): 1495-1502. DOI:10.1017/S0007114517001519 |
| [6] |
PANDEY K B, RIZVI S I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2009, 2: 897484. |
| [7] |
ZHANG C, WANG L, ZHAO X H, et al. Dietary resveratrol supplementation prevents transport-stress-impaired meat quality of broilers through maintaining muscle energy metabolism and antioxidant status[J]. Poultry Science, 2017, 96(7): 2219-2225. DOI:10.3382/ps/pex004 |
| [8] |
WANG X, LIU M, ZHU M J, et al. Resveratrol protects the integrity of alveolar epithelial barrier via SIRT1/PTEN/p-Akt pathway in methamphetamine-induced chronic lung injury[J]. Cell Proliferation, 2020, 53(3): e12773. |
| [9] |
ZHOU Z X, MOU S F, CHEN X Q, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of resveratrol prevents inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB in animal models of acute pharyngitis[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports, 2018, 17(1): 1269-1274. |
| [10] |
RAUF A, IMRAN M, BUTT M S, et al. Resveratrol as an anti-cancer agent:a review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2018, 58(9): 1428-1447. DOI:10.1080/10408398.2016.1263597 |
| [11] |
BHULLAR K S, HUBBARD B P. Lifespan and healthspan extension by resveratrol[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA):Molecular Basis of Disease, 2015, 1852(6): 1209-1218. DOI:10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.01.012 |
| [12] |
BREUSS J M, ATANASOV A M, UHRIN P. Resveratrol and its effects on the vascular system[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(7): 1523. DOI:10.3390/ijms20071523 |
| [13] |
MOMCHILOVA A, PETKOVA D, STANEVA G, et al. Resveratrol alters the lipid composition, metabolism and peroxide level in senescent rat hepatocytes[J]. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 2014, 207: 74-80. DOI:10.1016/j.cbi.2013.10.016 |
| [14] |
MENG Q W, GUO T, LI G Q, et al. Dietary resveratrol improves antioxidant status of sows and piglets and regulates antioxidant gene expression in placenta by Keap1-Nrf2 pathway and Sirt[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 2018, 9: 34. DOI:10.1186/s40104-018-0248-y |
| [15] |
GAN Z D, WEI W Y, LI Y, et al. Curcumin and resveratrol regulate intestinal bacteria and alleviate intestinal inflammation in weaned piglets[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(7): 1220. DOI:10.3390/molecules24071220 |
| [16] |
荀文娟, 周汉林, 侯冠彧, 等. 姜黄素对早期断奶仔猪回肠黏膜形态、紧密连接蛋白和炎性因子基因表达以及血清免疫球蛋白水平的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2016, 28(3): 826-833. XUN W J, ZHOU H L, HOU G Y, et al. Effects of curcumin on ileal mucosa morphology, tight junction protein and inflammatory factor gene expression and serum immunoglobulin levels in early weaned piglets[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2016, 28(3): 826-833 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2016.03.023 |
| [17] |
赵春萍.姜黄素对大肠杆菌攻毒仔猪生长性能及肠粘膜屏障功能的影响[D].硕士学位论文.海口: 海南大学, 2015: 26-34. ZHAO C P.Effects of curcumin on growth performance and intestinal mucosal barrier function of piglets challenged by E.coli[D]. Master's Thesis.Haikou: Hainan University, 2015: 26-34.(in Chinese) |
| [18] |
王海超.甜菜碱对仔猪生长和肠道功能的影响及机制研究[D].博士学位论文.杭州: 浙江大学, 2019: 19-54. WANG H C.Study on the effect and mechanism of betaine on growth and intestinal function of piglets[D]. Ph.D.Thesis.Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019: 19-54.(in Chinese) |
| [19] |
WEN C Y, GUO Q P, WANG W L, et al. Taurine alleviates intestinal injury by mediating tight junction barriers in Diquat-challenged piglet models[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2020, 11: 449. DOI:10.3389/fphys.2020.00449 |
| [20] |
ZHANG H, CHEN Y A, CHEN Y P, et al. Comparison of the protective effects of resveratrol and pterostilbene against intestinal damage and redox imbalance in weanling piglets[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 2020, 11: 52. DOI:10.1186/s40104-020-00460-3 |
| [21] |
CHEN X L, ZENG Z Y, HUANG Z Q, et al. Effects of dietary resveratrol supplementation on immunity, antioxidative capacity and intestinal barrier function in weaning piglets[J]. Animal Biotechnology, 2019, 24: 1-6. |
| [22] |
文超越.氧化应激对猪肌肉组织的损伤以及牛磺酸的缓解作用机制[D].博士学位论文.长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2019: 11-14. WEN C Y.The damage of oxidative stress to pig muscle tissue and the mitigation mechanism of taurine[D]. Ph.D.Thesis.Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2019: 11-14.(in Chinese) |
| [23] |
ZHANG H, CHEN Y P, LI Y, et al. Medium-chain TAG attenuate hepatic oxidative damage in intra-uterine growth-retarded weanling piglets by improving the metabolic efficiency of the glutathione redox cycle[J]. British Journal of Nutrition, 2014, 112(6): 876-885. DOI:10.1017/S000711451400155X |
| [24] |
CELI P. The role of oxidative stress in small ruminants' health and production[J]. Revista Brasileira De Zootecnia, 2010, 39(Suppl.1): 348-363. |
| [25] |
CAO S T, WU H, WANG C C, et al. Diquat-induced oxidative stress increases intestinal permeability, impairs mitochondrial function, and triggers mitophagy in piglets[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2018, 96(5): 1795-1805. DOI:10.1093/jas/sky104 |
| [26] |
胡瑶莲, 张恒志, 陈代文, 等. 白藜芦醇对生长育肥猪抗氧化能力、空肠黏膜免疫及结肠菌群的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(1): 459-468. HU Y L, ZHANG H Z, CHEN D W, et al. Effects of resveratrol on antioxidant capacity, jejunal mucosal immunity and colonic flora in growing-finishing pigs[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(1): 459-468 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2019.01.054 |
| [27] |
YANG G, XUE Y S, ZHANG H Y, et al. Favourable effects of grape seed extract on intestinal epithelial differentiation and barrier function in IL-10-deficient mice[J]. British Journal of Nutrition, 2015, 114(1): 15-23. DOI:10.1017/S0007114515001415 |
| [28] |
LIU J B, ZHANG Y, LI Y, et al. L-tryptophan enhances intestinal integrity in Diquat-challenged piglets associated with improvement of redox status and mitochondrial function[J]. Animals, 2019, 9(5): 266. DOI:10.3390/ani9050266 |
| [29] |
YANG G, BIBI S, DU M, et al. Regulation of the intestinal tight junction by natural polyphenols:a mechanistic perspective[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2017, 57(18): 3830-3839. DOI:10.1080/10408398.2016.1152230 |
| [30] |
SHIN D Y, LU J N, KIM G Y, et al. Anti-invasive activities of anthocyanins through modulation of tight junctions and suppression of matrix metalloproteinase activities in HCT-116 human colon carcinoma cells[J]. Oncology Reports, 2011, 25(2): 567-572. |
| [31] |
WANG N, HAN Q, WANG G, et al. Resveratrol protects oxidative stress-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by upregulating heme oxygenase-1 expression[J]. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 2016, 61(9): 2522-2534. DOI:10.1007/s10620-016-4184-4 |
| [32] |
ZHUANG Y, WU H R, WANG X X, et al. Resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress-induced intestinal barrier injury through pI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2 signaling pathway[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2019, 1-14. |
| [33] |
CAO S T, SHEN Z J, WANG C C, et al. Resveratrol improves intestinal barrier function, alleviates mitochondrial dysfunction and induces mitophagy in Diquat challenged piglets[J]. Food & Function, 2019, 10(1): 344-355. |
| [34] |
MARTÍN A R, VILLEGA I, SÁNCHEZ-HIDALGO M, et al. The effects of resveratrol, a phytoalexin derived from red wines, on chronic inflammation induced in an experimentally induced colitis model[J]. British Journal of Pharmacology, 2010, 147(8): 873-885. |
| [35] |
张旭.白藜芦醇对LPS诱导小鼠乳腺炎的作用及机制研究[D].硕士学位论文.长春: 吉林大学, 2019: 6-54. ZHANG X.Study on the effect and mechanism of resveratrol on LPS-induced mastitis in mice[D]. Master's Thesis.Changchun: Jilin University, 2019: 6-54.(in Chinese) |
| [36] |
LEE E H, KIM S S, SEO S R. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) inhibits inflammatory signaling via expression of regulator of calcineurin activity 1 (RCAN1):anti-inflammatory mechanism of PDTC through RCAN1 induction[J]. Biochemical Pharmacology, 2017, 143: 107-117. DOI:10.1016/j.bcp.2017.07.011 |
| [37] |
WANG X X, FANG H, XU G, et al. Resveratrol prevents cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetic mice by upregulating Nrf2 expression and transcriptional level[J]. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity:Targets and Therapy, 2020, 13: 1061-1075. DOI:10.2147/DMSO.S243560 |
| [38] |
FRAZIER T H, DIBAISE J K, MCCLAIN C J. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, obesity-induced inflammation, and liver injury[J]. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, 2011, 35(5S): 14S-20S. |
| [39] |
CHENG K, SONG Z H, LI S M, et al. Effects of resveratrol on intestinal oxidative status and inflammation in heat-stressed rats[J]. Journal of Thermal Biology, 2019, 85: 102415. DOI:10.1016/j.jtherbio.2019.102415 |




