2. 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(湛江), 湛江 524025
2. Guangdong Laboratory of Southern Marine Science and Engineering (Zhanjiang), Zhanjiang 524025, China
目前已知上皮细胞黏附结构存在4种连接方式,其中细胞间紧密连接(tight junction,TJ)是广泛存在于上皮及内皮细胞中的不通透连接,由闭锁蛋白(Occludin)、跨膜蛋白(Claudin)、紧密连接黏附分子(JAMs)和闭锁小带蛋白(ZO)及与其相连接的细胞骨架蛋白组成,负责调节离子和其他溶质的细胞旁运动,对上皮和内皮屏障的形成和功能起到至关重要的作用[1-2]。构成紧密连接的主要骨架蛋白Claudin是一个庞大的膜蛋白家族,目前哺乳动物中已发现27个家族成员[3],Claudin的异常表达会导致组织的渗透屏障功能受损,细胞的极性完全消失,细胞间的黏附能力下降,进而导致内分泌紊乱[4]。哺乳动物的Occludin在进化上具有一定的保守性,N末端在紧密连接超微结构和屏障功能起重要作用,上调Occludin的表达可以增强肠道黏膜屏障的稳定性,敲除Occludin则会增加肠道紧密连接的通透性[5]。ZO是紧密连接支持结构的基础,闭锁小带蛋白-1(ZO-1)与肌动蛋白微丝相连,一同参与细胞骨架的构成,并且ZO-1作为膜相关鸟苷酸激酶家族中的一员,可以游离于细胞膜和细胞核之间,在信号传导中发挥重要作用[6]。紧密连接结构一旦损伤,细胞膜通透性就会增加,外界的有毒物质或者微生物代谢产物等便会渗透进入机体,造成损害。
鱼类摄取营养物质,获得健康生长和发育,与肠道黏膜屏障完整性密切相关。饲料中添加适量的氨基酸和维生素可以显著上调草鱼(Ctenopharyngodon idella)肠道Occludin、Claudin-3、Claudin-15a mRNA的表达,增强黏膜细胞间紧密连接的保护,保护细胞的通透性,维持肠道和鳃丝黏膜屏障[7-11];氨基酸缺乏或过量会通过雷帕霉素靶蛋白(TOR)信号通路下调草鱼肠道紧密连接蛋白Occludin、Claudin、ZO-1 mRNA的表达[12],或者下调草鱼肠道中Claudin-b和Claudin-3 mRNA的表达,破坏肠道黏膜屏障,削弱免疫状态,诱发肠炎[13]。氨基酸是肠道生长发育的重要营养支持,饲料中大约40%的精氨酸(Arg)在小肠内直接被消化吸收,参与氧化供能,促进细胞增殖和黏膜上皮生长分化,维护肠黏膜屏障。本研究团队前期试验表明,适宜的饲料精氨酸水平有助于改善斜带石斑鱼肠道皱襞高度和肌层厚度,促进肠道发育和机体生长[14]。那么,精氨酸是否可通过调控紧密连接蛋白家族成员的表达维护石斑鱼肠道机械屏障完整性呢?
2019年我国海水鱼养殖产量达160.58万t,其中石斑鱼产量仅次于大黄鱼,居于第2位[15]。然而,石斑鱼肠炎频发,严重影响了其健康养殖。珍珠龙胆石斑鱼是由棕点石斑鱼(Epinephelus fuscoguttatus ♀)×鞍带石斑鱼(Epinephelus lanceolatus)杂交而来[16],具备亲本抗逆性强及成长速度快等优点,是我国沿海地区重要的石斑鱼养殖品种。本研究旨在克隆珍珠龙胆石斑鱼ZO-1、Occludin和Claudin-15a的cDNA全长,并通过精氨酸干预评估紧密连接蛋白基因对珍珠龙胆石斑鱼肠道屏障功能的影响,以期在营养途径为石斑鱼肠炎的治疗提供策略。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验用鱼试验使用同一遗传背景的健康珍珠龙胆石斑鱼,体重(11.0±0.5) g,采自东南码头石斑鱼苗厂。用丁香酚(1 ∶ 10 000)麻醉后,冰盘上解剖获得脑、鳃、皮肤、肌肉、肝脏、胃、肠(前、中、后)、头肾、体肾、脾脏和心脏11种器官组织,每个样品取3个重复,迅速放入装有RNA later的EP管中,4 ℃存放过夜后置于-80 ℃冰箱保存,用于基因克隆及组织表达分布试验。
1.2 动物设计和饲料配方通过cDNA末端快速扩增(rapid amplification of cDNA ends,RACE)-PCR技术克隆珍珠龙胆石斑鱼ZO-1、Occludin和Claudin-15a的cDNA全长,运用实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)方法分析其在健康珍珠龙胆石斑鱼脑、鳃、皮肤、肌肉、肝脏、胃、前肠、中肠、后肠、头肾、体肾、脾脏和心脏13种组织中的mRNA相对表达量。
配制3组精氨酸水平分别为1.96%、3.06%和3.74%的等氮等脂试验饲料,试验饲料组成及营养水平见表 1。选择375尾珍珠龙胆石斑鱼,初重为(20.79±0.09) g,随机分为3组,每组5个重复,每个重复25尾鱼。养殖8周后,每个重复随机取3尾鱼,剥离肠道放入无酶冻存管中,立即投入液氮中速冻,随后转移到-80 ℃冰箱中保存,用于分析饲料精氨酸水平对紧密连接蛋白基因mRNA表达的影响。饲料精氨酸水平参考本研究团队前期试验结果[14]。
|
|
表 1 试验饲料组成及营养水平(干物质基础) Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of experimental diets (DM basis) |
使用Trizol(Invitrogen公司,美国)试剂提取石斑鱼组织的总RNA。通过琼脂糖凝胶电泳及紫外分光光度法分别检测确定总RNA的完整性及纯度。以各组织总RNA(1 μg)为模板,Oligo(dT)20为反转录引物,使用Invitrogen公司M-MLV First-Strand Synthesis System操作方案,用不含RNA的DNase处理除去DNA污染物,总反应体系为10 μL:5×Buffer 2 μL、gDNA Eraser 1 μL、总RNA 1 μL、RNA Free dH2O 6 μL。以各组织总RNA为模板并使用PrimeScriptTM RT Reagent Kit (TaKaRa)试剂盒进行反转录,反应体系为20 μL:去除基因组DNA产物10 μL、Primer Script RT Enzyme MixⅠ 1 μL、RT Primer Mix 1 μL、5×Prime Script Buffer 4 μL、RNase Free dH2O 4 μL。反应条件参考试剂盒说明书,合成cDNA第1链。
1.4 ZO-1、Claudin-15a、Occludin基因克隆采用SMARTerTM RACE cDNA扩增试剂盒(Clontech公司,美国)制备RACE-PCR的模板,根据NCBI数据库已知基因的保守区设计扩增引物(表 2),得到ZO-1核心片段为5 106 bp片段,Claudin-15a核心片段为669 bp片段,Occludin核心片段为1 515 bp片段。通过BLAST搜索GenBank的数据库鉴定所得序列为上述基因的部分cDNA序列,根据这些片段设计对应的RACE引物。PCR的步骤如下:94 ℃变性3 min,94 ℃变性20 s,55~60 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸1 s,扩增35个循环,72 ℃下延伸10 min。采用1.5%琼脂糖凝胶对RACE扩增产物进行电泳,以获得目的片段。将目的片段连接至pMD18-T载体,转化到DH-5A活性细胞后,获得阳性克隆,送至上海生工生物工程有限公司进行细菌液体PCR检测。
|
|
表 2 基因克隆引物序列 Table 2 Sequence primers for gene cloning |
ZO-1、Claudin-15a、Occludin的序列由ORF Finder翻译(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gotf.html),利用Signal P4.1(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/)预测信号肽序列。用TMHMM 2.0(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/)预测跨膜结构域;使用ExPASy蛋白质组学工具(http://www.expasy.org/tools/)预测蛋白质结构。使用DNAMAN Package 6.0进行氨基酸多序列比对。用MEGA 7.0采用邻接(neighbor joining,NJ)法构建ZO-1、Claudin-15a、Occludin氨基酸序列的分子系统发育树。
1.6 RT-qPCR分析采用RT-qPCR检测ZO-1、Claudin-15a和Occludin在石斑鱼脑、鳃、皮肤、肌肉、肝脏、胃、肠(前、中、后)、头肾、体肾、脾脏、心脏中以及评价精氨酸对养殖试验获取的肠道中的mRNA表达水平。β-肌动蛋白(β-actin)(GenBank:AY510710.2)作为RT-qPCR的内参基因(表 3)。反应条件如下:1个周期,95 ℃ 30 s,95 ℃ 15 s,58 ℃ 34 s,72 ℃ 20 s,40个循环。通过熔解曲线分析确定只有1种PCR产物。采用2-△△Ct法计算ZO-1、Claudin-15a、Occludin在各组织中的相对表达量。
|
|
表 3 实时荧光定量PCR引物 Table 3 Primer for RT-qPCR |
养殖试验8周结束后,计算各重复鱼体数量并称重。计算存活率(survival rate,SR)和增重率(weight gain rate,WGR):

|
试验数据采用SPSS 22.0软件进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),当有显著差异时,进行Tukey HSD多重性检验,比较组间的差异,数据以平均值±标准误(mean±SE)表示,P < 0.01为差异极显著,P < 0.05为差异显著。
2 结果 2.1 基因克隆和序列分析珍珠龙胆石斑鱼ZO-1的cDNA全长为6 355 bp,包括208 bp的5′-非翻译区(UTR),1 144 bp的3′-UTR;开放阅读框(open reading frame,ORF)为5 106 bp,可编码1 701个氨基酸;预测分析蛋白质分子质量为187.4 ku,等电点(pI)为5.92(图 1)。珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Occludin的cDNA全长为2 222 bp,包括69 bp的5′-UTR,638 bp的3′-UTR;ORF为1 515 bp,可编码504个氨基酸;预测分析蛋白质分子质量为55.8 ku,pI为5.60(图 2)。珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-15a的cDNA全长为1 584 bp,包括387 bp的5′-UTR,528 bp的3′-UTR;ORF为669 bp,可编码222个氨基酸;预测分析蛋白质分子质量为23.8 ku,pI为8.09(图 3)。

|
起始密码子(ATG)、终止密码子(TAA)用加粗字体表示,预测的磷酸化位点用下划线表示。图 2、图 3同。 The start codon (ATG) and stop codon (TAA) were indicated in bold font, and the predicted phosphorylation sites were indicated by underline. The same as Fig. 2 and Fig. 3. 图 1 ZO-1的cDNA序列及预测的氨基酸序列 Fig. 1 cDNA sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of ZO-1 |

|
5个预测的跨膜区域用方框表示。 The 5 predicted transmembrane regions were indicated with boxes. 图 2 Occludin的cDNA序列及预测的氨基酸序列 Fig. 2 cDNA sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of Occludin |

|
4个预测的跨膜区域用方框表示。 The 4 predicted transmembrane regions were indicated with boxes. 图 3 Claudin-15a的cDNA序列及预测的氨基酸序列 Fig. 3 cDNA sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of Claudin-15a |
利用Signal P4.1软件预测ZO-1、Occludin、Claudin-15a均不具有信号肽序列。蛋白质二级跨膜结构预测ZO-1无跨膜区域,Occludin有5个跨膜区域,Claudin-15a有4个跨膜区域。Net Phos 3.1软件预测ZO-1共有208个磷酸化位点(分值大于0.5),丝氨酸(serine)134处,苏氨酸(threonine)44处,酪氨酸(tyrosine)30处;Occludin共有53个磷酸化位点,丝氨酸27处,苏氨酸8处,酪氨酸18处;Claudin-15a共有30个磷酸化位点,丝氨酸10处,苏氨酸12处,酪氨酸8处。完整的cDNA和推测的氨基酸序列已上传NCBI数据库,ZO-1、Occludin、Claudin-15a的GenBank登录号分别为MK809396、MK809395、MK809394。
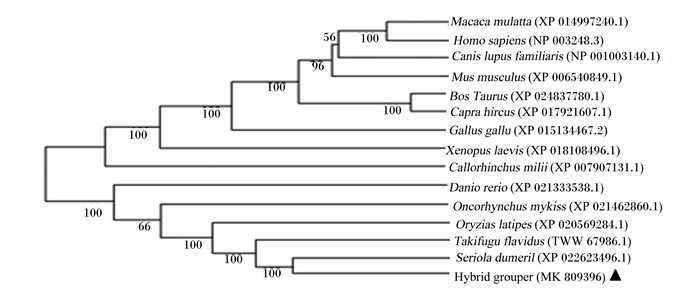
2.2 氨基酸序列比对与系统发育分析根据NCBI的Blastp和DNAMAN Package 6.0软件对珍珠龙胆石斑鱼与其他物种的ZO-1氨基酸序列进行同源比对(图 4)。比对结果显示,珍珠龙胆石斑鱼ZO-1氨基酸序列与硬骨鱼的同源性为87%~94%;与高体鰤(Seriola dumerili)的同源性最高,为94%;与青鳉(Oryzias latipes)的同源性也高达90%;与小鼠(Mus musculus)、猕猴(Macaca mulatta)、非洲爪蟾(Xenopus tropicalis)和鸡(Gallus gallus)的同源性较低,为63%。系统发育树分析表明(图 5),珍珠龙胆石斑鱼与硬骨鱼的亲缘关系较近,其中与高体鰤的亲缘关系最近,与软骨鱼、哺乳类、两栖类和鸟类的亲缘关系较远。

|
Homo sapiens:人;Mus musculus:小鼠;Macaca mulatta:猕猴;Capra hircus:山羊;Canis lupus familiaris:犬;Bos Taurus:牛;Gallus gallu:鸡;Xenopus laevis:非洲爪蟾;Callorhinchus milii:叶吻银鲛;Oncorhynchus mykiss:虹鳟;Takifugu flavidus:菊黄东方鲀;Danio rerio:斑马鱼;Oryzias latipes:青鳉;Seriola dumeril:高体;Hybrid grouper:珍珠龙胆石斑鱼。下图同The same as below。 相同的氨基酸以黑色标示,同源氨基酸以紫色标示。图 6、图 8同。 Identical amino acids were marked in black, and homologous amino acids were marked in purple. The same as Fig. 6 and Fig. 8. 图 4 珍珠龙胆石斑鱼ZO-1氨基酸的序列比对 Fig. 4 Alignment of ZO-1 amino acid sequences of hybrid grouper |
|
图 5 珍珠龙胆石斑鱼ZO-1序列的系统发育树 Fig. 5 Phylogenetic tree based on ZO-1 sequences of hybrid grouper |
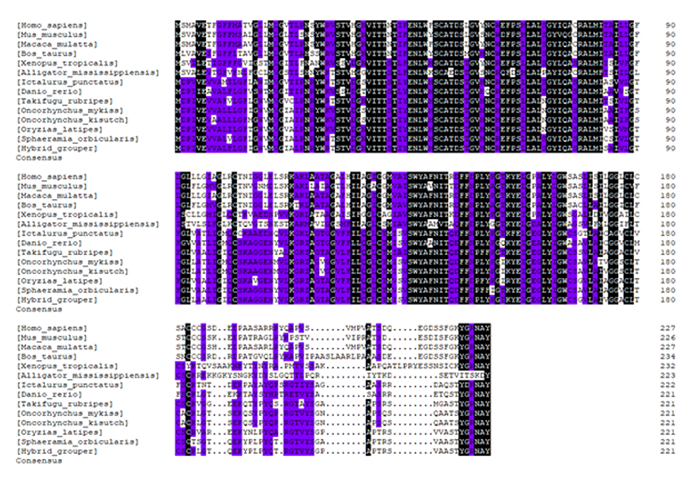
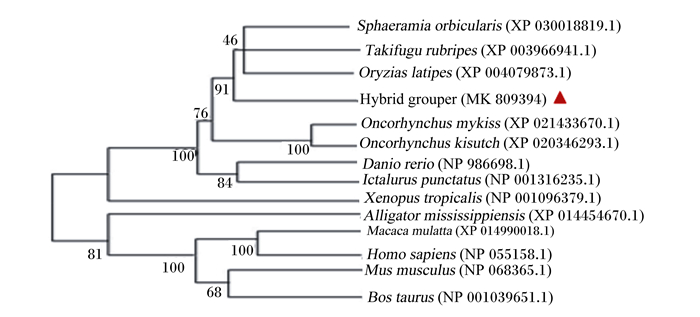
根据NCBI的Blastp和DNAMAN Package 6.0软件对珍珠龙胆石斑鱼与其他物种的Claudin-15a氨基酸序列进行同源比对(图 6)。比对结果显示,珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-15a氨基酸序列与硬骨鱼的同源性为75%~92%;与环纹圆天竺鲷(Sphaeramia orbicularis)相似度最高,为92%;与非洲爪蟾、短吻鳄(Alligator mississippiensis)、猕猴、牛(Bos taurus)、人(Homo sapiens)的同源性分别为58%、53%、54%、53%、54%;而与小鼠的同源性最低,为49%。系统发育树分析表明(图 7),珍珠龙胆石斑鱼独立成一支,再与其他鱼类紧密汇成一支,说明珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-15a与其他鱼类同源性较高;珍珠龙胆石斑鱼与人、猕猴、短吻鳄、非洲爪蟾同源性较低,与牛、小鼠的亲缘关系较远。
|
Alligator mississippiensis短吻鳄;Ictalurus punctatus斑点叉尾;Takifugu rubripes红鳍东方鲀;Oncorhynchus mykiss虹鳟;Oncorhynchus kisutch银鲑;Sphaeramia orbicularis环纹圆天竺鲷。图 7同The same as Fig. 7. 图 6 珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-15a氨基酸序列的比对 Fig. 6 Alignment of Claudin-15a amino acid sequences of hybrid grouper |
|
图 7 珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-15a序列的系统发育树 Fig. 7 Phylogenetic tree based on Claudin-15a sequences of hybrid grouper |
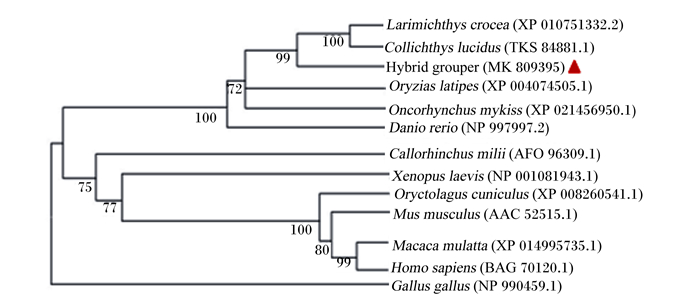
根据NCBI的Blastp和DNAMAN Package 6.0软件对珍珠龙胆石斑鱼与其他物种的Occludin氨基酸序列进行同源比对(图 8)。比对结果显示,珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Occludin氨基酸序列与大黄鱼的同源性最高,为84%;其次是棘头梅童鱼(Collichthys lucidus),为81%;与虹鳟、青鳉、斑马鱼(Danio rerio)、叶吻银鲛(Callorhinchus milii)、非洲爪蟾、穴兔(Oryctolagus cuniculus)、猕猴、人、小鼠的同源性分别为67%、65%、61%、49%、49%、47%、47%、47%、46%;而与鸡的同源性很低,仅有39%。系统发育树分析表明(图 9),珍珠龙胆石斑鱼单独为一枝;与大黄鱼、棘头梅童鱼再汇为一枝,亲缘关系最近,同源性较高;然后与其他鱼类汇为一枝。珍珠龙胆石斑鱼与非洲爪蟾、短吻鳄、鸡以及哺乳动物的同源性较低。

|
Oryctolagus cuniculus穴兔;Collichthys lucidus棘头梅童鱼;Larimichthys crocea大黄鱼。图 9同The same as Fig. 9. 图 8 珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Occludin氨基酸序列的比对 Fig. 8 Alignment of Occludin amino acid sequences of hybrid grouper |
|
图 9 珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Occludin序列的系统发育树 Fig. 9 Phylogenetic tree based on Occludin sequences of hybrid grouper |
由图 10可知,ZO-1、Claudin-15a、Occludin在各组织中均有表达。后肠中ZO-1 mRNA相对表达量极显著高于其他组织(P < 0.05),其次是脾脏、前肠、中肠、皮肤中ZO-1 mRNA相对表达量较高,而脑、鳃、心脏、头肾、胃、肝脏、肌肉、体肾中ZO-1 mRNA相对表达量差异不显著(P>0.05)。前肠、中肠中Claudin-15a mRNA相对表达量显著高于其他各组织(P < 0.05);胃和体肾中Claudin-15a mRNA相对表达量差异不显著(P>0.05),但显著高于脑、鳃、心脏、头肾、脾脏、肝脏、肌肉和皮肤(P < 0.05)。皮肤、前肠中Occludin mRNA相对表达量最高,其次为中肠和后肠,皮肤、前肠、中肠、后肠中Occludin mRNA相对表达量差异不显著(P>0.05);脑、心脏、头肾、脾脏、胃、肝脏、肌肉、体肾中Occludin mRNA相对表达量较低,且显著低于皮肤、前肠、中肠、后肠和鳃(P < 0.05)。
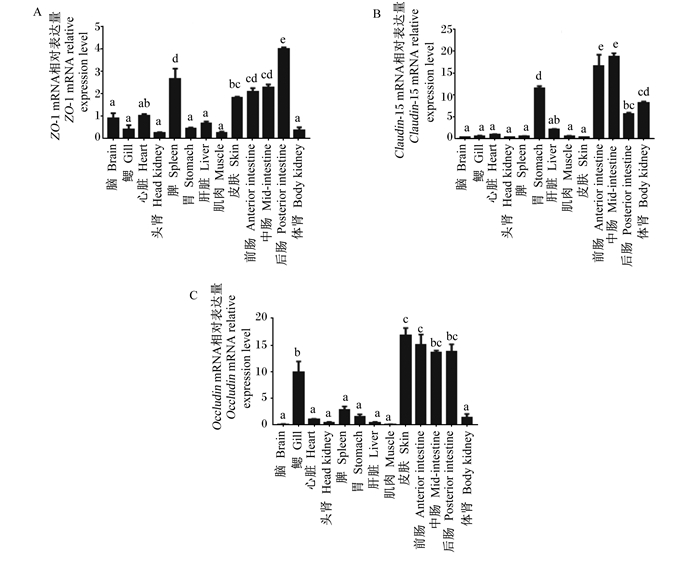
|
数据柱标相同小写字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05),不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。下图同。 Value columns with the same small letter mean no significant difference (P > 0.05), while with different small letters mean significant difference (P < 0.05). The same as below 图 10 各组织中ZO-1(A)、Claudin-15a(B)和Occludin(C)mRNA相对表达量 Fig. 10 mRNA relative expression levels of ZO-1 (A), Claudin-15a (B) and Occludin (C) in various tissues |
由图 11可知,3.06%精氨酸水平组的增重率显著高于1.96%和3.74%精氨酸水平组(P < 0.05),1.96%和3.74%精氨酸水平组之间无显著差异(P>0.05)。各组之间存活率无显著差异(P>0.05)。
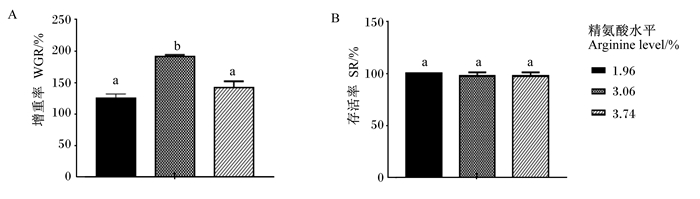
|
图 11 饲料精氨酸水平对珍珠龙胆石斑鱼增重率(A)和存活率(B)的影响 Fig. 11 Effects of dietary arginine levels on weight gain rate (A) and survival rate (B) of hybrid grouper |
由图 12可知,3.06%精氨酸水平组肠道中ZO-1、Occludin、Claudin-15a mRNA相对表达量显著高于1.96%和3.74%精氨酸水平组(P < 0.05)。3.74%精氨酸水平组肠道中ZO-1和Occludin mRNA相对表达量显著高于1.96%精氨酸水平组(P < 0.05),1.96%和3.74%精氨酸水平组之间肠道中Claudin-15a mRNA相对表达量无显著差异(P>0.05)。
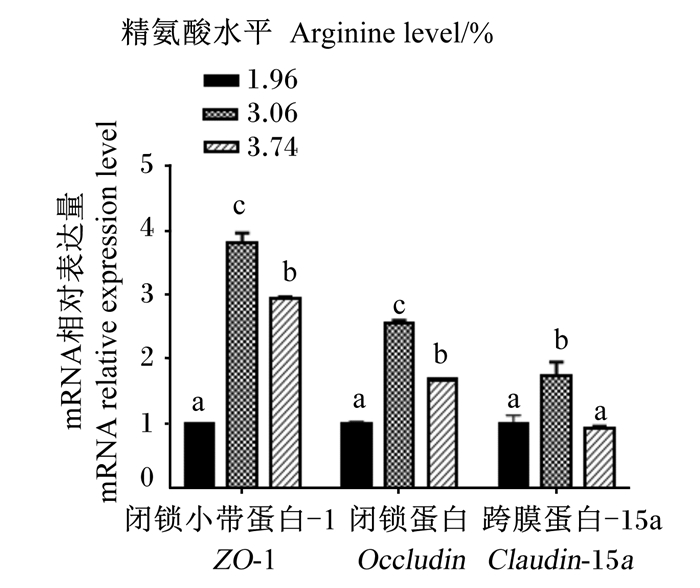
|
图 12 肠道中ZO-1、Occludin、Clauin-15a mRNA相对表达量 Fig. 12 mRNA relative expression levels of ZO-1, Occludin and Clauin-15a in intestine |
机体细胞生长和凋亡之间的不平衡以及紧密连接蛋白的改变容易引起黏膜屏障完整性的破坏,生存环境、饲料营养水平等的变化是导致该事件发生的主要诱因,掌握紧密连接蛋白的表达对调控机体健康至关重要。系统发育树分析显示,珍珠龙胆石斑鱼ZO-1氨基酸序列与其他鱼类比对结果在62%~94%,与高体鰤的亲缘关系最为密切,与非洲爪蟾、人、小鼠和鸡的比对结果在63%~64%,说明ZO-1基因保守性较高。珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Occludin氨基酸序列与其他鱼类比对结果在49%~84%,与大黄鱼的亲缘关系最密切。珍珠龙胆石斑鱼Claudin-15a氨基酸序列与环纹圆天竺鲷比对结果相似度最高,达到92%,亲缘关系最近,与其他硬骨鱼类同源性也在75%以上,说明Claudin-15a基因在鱼类中相似度比较高。
紧密连接蛋白能够通过结合肌动蛋白细胞骨架维持黏膜组织完整性,是影响黏膜物理屏障功能和通透性的重要指标[17-18]。金鱼(Carassius auratus)暴露在低离子水中,鳃组织中钠钾泵(K+-Na+-ATP酶)活性迅速下降,Occludin基因表达短暂上调[19]。核黄素的缺乏会上调草鱼幼鱼鳃部Claudin-12和肌球蛋白轻链激酶的mRNA表达,下调Claudin-c、Claudin-3、Occludin和ZO-1的mRNA表达,破坏紧密连接屏障[20]。上调ZO-1、Occludin、Claudin-b、Claudin-c和Claudin-3c的mRNA表达和下调Claudin-12和Claudin-15的mRNA表达能够提高草鱼肠道细胞间的结构完整性[21]。本试验中,紧密连接相关基因ZO-1、Claudin-15a、Occludin在珍珠龙胆石斑鱼13种组织中均有分布,在肠道(前、中、后肠)组织中相对表达量都较高,提示这3个基因在维护肠道黏膜屏障中起着重要的作用。ZO-1在细胞间紧密连接中起着枢纽的作用,维系着Occludin蛋白和肌动蛋白骨架,在受到外界信号刺激下,完成收缩运动[22],该基因在石斑鱼脾脏中的相对表达量较高。头肾和脾脏作为鱼类免疫器官和黏膜免疫屏障,其结构的完整性是保障免疫功能正常工作的基础[23],推断ZO-1基因有可能参与保护石斑鱼脾脏细胞间的结构完整性,维持鱼体健康。Claudin蛋白作为胃上皮细胞连接相关的重要蛋白,其异常表达可能会导致胃黏膜屏障出现损伤[24-26],这也与本试验中Claudin-15a在胃组织中mRNA相对表达量较高的结果符合,说明Claudin-15a可能参与保护石斑鱼胃黏膜屏障。当前对Claudin-15a基因的研究较少,可能与损伤后的渗透性改变相关[27]。Occludin基因在石斑鱼组织中广泛表达,在皮肤和鳃中mRNA相对表达量较高,这与Chasiotis等[28]发现金鱼鳃和皮肤中Occludin mRNA相对表达量较高的试验结果一致。Occludin蛋白作为紧密连接跨膜蛋白,对保护紧密连接屏障和跨上皮细胞旁通路的通透性有显著贡献[29],在维持虹鳟水盐平衡相关的器官如肠道、皮肤、鳃中mRNA相对表达量高,在头肾和脾脏中mRNA相对表达量较低[30];也可能因为Occludin基因在这2个组织中mRNA相对表达量低,导致维生素C对中期草鱼头肾和脾脏中Occludin基因调控无显著影响[31]。
机体肠道健康与肠道物理屏障和紧密连接蛋白表达相关[32-33]。下调肠道紧密连接蛋白Claudin、ZO-1和Occludin的mRNA表达,会影响肠道形态及屏障功能,导致机体生长发育速度变缓[34-35],上调十二指肠、空肠以及回肠ZO-1和Occludin的mRNA表达,可促进细胞间紧密连接结构的形成,增强仔猪小肠黏膜的屏障功能[36]。本课题组前期研究表明,7个精氨酸水平中,当饲料精氨酸水平为2.95%时,斜带石斑鱼生长和肠道发育情况最好,对肠道细胞的增殖分化和细胞形态具有保护作用,有利于提高石斑鱼皱襞高度,增大肠道吸收面积,通过二元拟合得知3.06%精氨酸水平是该规格石斑鱼最适精氨酸需求量;低或高水平精氨酸导致斜带石斑鱼前、中、后3个肠段的皱襞高度降低,肌层厚度变薄[14, 37]。本试验中,精氨酸缺乏组(1.96%精氨酸水平组)和过量组(3.74%精氨酸水平组)增重率下降,紧密连接蛋白ZO-1、Occludin和Claudin-15a的mRNA相对表达量均较低;当珍珠龙胆石斑鱼摄食含适宜水平精氨酸的饲料后,肠道紧密连接蛋白的mRNA表达显著上调,鱼体增重率显著提高,进一步表明精氨酸可通过上调紧密连接蛋白的mRNA表达,保护肠道黏膜屏障,促进鱼体的健康生长。饲料配方中精氨酸的有效含量可以改善鱼体肠道黏膜健康状态,为后续石斑鱼营养素需求、饲料配制及健康生长的研究提供了基础。
4 结论① 本研究通过同源克隆及RACE-PCR技术克隆获得了珍珠龙胆石斑鱼ZO-1、Claudin-15a、Occludin的cDNA序列长度,提交到NCBI GenBank数据库,登录号分别为MK809396、MK809394、MK809395。
② ZO-1、Occludin和Claudin-15a在杂交石斑鱼13种组织中均有表达,mRNA相对表达量最高的组织分别为后肠、中肠和皮肤。
③ 饲料适宜精氨酸水平可显著上调珍珠龙胆石斑鱼肠道ZO-1、Occludin、Claudin-15a mRNA相对表达量,维护肠道黏膜屏障完整,促进鱼健康生长。
| [1] |
邢晓辉, 李力仙, 郭天林, 等. Occludin蛋白与细胞间紧密连接关系及其临床意义[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2015, 15(8): 1405, 1553-1555. XING X X, LI L X, GUO T L, et al. The tight junction relationship between Occludin protein and cells and its clinical significance[J]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine, 2015, 15(8): 1405 (in Chinese). |
| [2] |
GŪNZEL D, FROMM M. Claudins and other tight junction proteins[J]. Comprehensive Physiology, 2012, 2(3): 1819-1852. |
| [3] |
SCHMIDT H, BRAUBACH P, SCHILPP C, et al. IL-13 impairs tight junctions in airway epithelia[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(13): 3222. DOI:10.3390/ijms20133222 |
| [4] |
娄文静, 刘冬妍. 肠道紧密连接跨膜蛋白研究进展[J]. 实用药物与临床, 2019, 22(11): 1214-1219. LOU W J, LIU D Y. Research progress in intestinal tight junction membrane proteins[J]. Practical Pharmacy and Clinical Remedies, 2019, 22(11): 1214-1219 (in Chinese). |
| [5] |
PUTT K K, PEI R S, WHITE H M, et al. Yogurt inhibits intestinal barrier dysfunction in Caco-2 cells by increasing tight junctions[J]. Food & Function, 2017, 8(1): 406-414. |
| [6] |
孔瑶瑶, 马秀华, 麦康森, 等. 饲料营养素对鱼类肠道紧密连接蛋白闭锁小带蛋白-1影响的研究进展[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(11): 5081-5088. KONG Y Y, MA X H, MAI K S, et al. Research progress of effects of diet nutrients on intestinal tight junction protein zonula occludens-1 of fish[J]. Chinese Journal Of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(11): 5081-5088 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.11.014 |
| [7] |
陈娇娇. 精氨酸对草鱼幼鱼生长、肠道结构调控及机制研究[D]. 硕士学位论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017. CHEN J J. Effects of arginine on growth performance, intestinal morphology regulation and mechanism research of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus)[D]. Master's Thesis. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese) |
| [8] |
FENG L, LI W, LIU Y, et al. Protective role of phenylalanine on the ROS-induced oxidative damage, apoptosis and tight junction damage via Nrf2, TOR and NF-κB signalling molecules in the gill of fish[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2017, 60: 185-196. |
| [9] |
FENG L, GAN L, JIANG W D, et al. Gill structural integrity changes in fish deficient or excessive in dietary isoleucine: towards the modulation of tight junction protein, inflammation, apoptosis and antioxidant defense via NF-κB, TOR and Nrf2 signaling pathways[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2017, 63: 127-138. |
| [10] |
LI S Q, FENG L, JIANG W D, et al. Deficiency of dietary niacin impaired gill immunity and antioxidant capacity, and changes its tight junction proteins via regulating NF-κB, TOR, Nrf2 and MLCK signaling pathways in young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2016, 55: 212-222. |
| [11] |
SHI L, FENG L, JIANG W D, et al. Folic acid deficiency impairs the gill health status associated with the NF-κB, MLCK and Nrf2 signaling pathways in the gills of young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 47(1): 289-301. |
| [12] |
FENG L, LUO J B, JIANG W D, et al. Changes in barrier health status of the gill for grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) during valine deficiency: regulation of tight junction protein transcript, antioxidant status and apoptosis-related gene expression[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 45(2): 239-249. |
| [13] |
JIANG W D, DENG Y P, LIU Y, et al. Dietary leucine regulates the intestinal immune status, immune-related signalling molecules and tight junction transcript abundance in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Aquaculture, 2015, 444: 134-142. DOI:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.04.005 |
| [14] |
迟淑艳, 韩凤禄, 谭北平, 等. 饲料精氨酸水平对斜带石斑鱼幼鱼生长和肠道形态的影响[J]. 水生生物学报, 2016, 40(2): 388-394. CHI S Y, HAN F L, TAN B P, et al. Effects of dietary arginine level on growth performance and intestine morphology of juvenile grouper Epinephelus Coioides[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2016, 40(2): 388-394 (in Chinese). |
| [15] |
农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站, 中国水产学会. 中国渔业统计年鉴-2020[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2020. Fisheries and Fishery Administration Bureau of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, National Fishery Technology Promotion Station, China Society of Fisheries. 2020 China Fishery Statistics Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2020 (in Chinese). |
| [16] |
于欢欢, 李炎璐, 陈超, 等. 棕点石斑鱼(♀)×鞍带石斑鱼(♂)杂交F1仔、稚、幼鱼的摄食与生长特性分析[J]. 中国水产科学, 2015, 22(5): 968-977. YU H H, LI Y L, CHEN C, et al. Feeding habits and growth characteristics of larval, juvenile, and young F1 of Epinephelus fuscoguttatus (♀)×E.lanceolatus (♂)[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2015, 22(5): 968-977 (in Chinese). |
| [17] |
夏邹, 冯江鑫, 蒋俊劼, 等. 饲粮组成及抗生素对断奶仔猪生长性能和肠道健康的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(8): 3594-3604. XIA Z, FENG J, JIANG J Z, et al. Effects of diet composition and antibiotics on growth performance and intestinal health of weaned piglets[J]. Chinese Journal Of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(8): 3594-3604 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.08.018 |
| [18] |
DE MEDINA F S, ROMERO-CALVO I, MASCARAQUE C, et al. Intestinal inflammation and mucosal barrier function[J]. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, 2014, 20(12): 2394-2404. DOI:10.1097/MIB.0000000000000204 |
| [19] |
CHASIOTIS H, EFFENDI J C, KELLY S P. Occludin expression in goldfish held in ion-poor water[J]. Journal of Comparative Physiology B, 2009, 179(2): 145-154. DOI:10.1007/s00360-008-0297-1 |
| [20] |
CHEN L, FENG L, JIANG W D, et al. Dietary riboflavin deficiency decreases immunity and antioxidant capacity, and changes tight junction proteins and related signaling molecules mRNA expression in the gills of young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 45(2): 307-320. |
| [21] |
LI L, FENG L, JIANG W D, et al. Dietary pantothenic acid deficiency and excess depress the growth, intestinal mucosal immune and physical functions by regulating NF-κB, TOR, Nrf2 and MLCK signaling pathways in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 45(2): 399-413. |
| [22] |
李小兰. 色氨酸对肠道屏障功能的作用[D]. 硕士学位论文. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2015. LI X L. The effect of tryptophan on the intestinal barrier function[D]. Master's Thesis. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2015. (in Chinese) |
| [23] |
MAGNADÓTTIR B. Innate immunity of fish (overview)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2006, 20(2): 137-151. |
| [24] |
OSHIMA T, MIWA H. Gastrointestinal mucosal barrier function and diseases[J]. Journal of Gastroenterology, 2016, 51(8): 768-778. DOI:10.1007/s00535-016-1207-z |
| [25] |
TSUKITA S, FURUSE M. The structure and function of claudins, cell adhesion molecules at tight junctions[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2000, 915: 129-135. |
| [26] |
项航. Claudin蛋白在胃癌中的作用及其临床研究进展[J]. 中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志, 2019, 26(8): 910-915. XIANG H. Role of Claudin protein in gastric cancer and its clinical research progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Cancer Biotherapy, 2019, 26(8): 910-915 (in Chinese). |
| [27] |
许凡. 草鱼(Ctenopharyngodon idellus)肠道紧密连接蛋白基因克隆与表达活性分析[D]. 硕士学位论文. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2013. XU F. Cloning and expression activity analysis of the tight junction protein genes of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus)[D]. Master's Thesis. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2013. (in Chinese) |
| [28] |
CHASIOTIS H, KELLY S P. Permeability properties and occludin expression in a primary cultured model gill epithelium from the stenohaline freshwater goldfish[J]. Journal of Comparative Physiology B, 2011, 181(4): 487-500. DOI:10.1007/s00360-010-0535-1 |
| [29] |
FELDMAN G J, MULLIN J M, RYAN M P. Occludin: structure, function and regulation[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2005, 57(6): 883-917. DOI:10.1016/j.addr.2005.01.009 |
| [30] |
CHASIOTIS H, WOOD C M, KELLY S P. Cortisol reduces paracellular permeability and increases occludin abundance in cultured trout gill epithelia[J]. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 2010, 323(2): 232-238. DOI:10.1016/j.mce.2010.02.030 |
| [31] |
徐慧君. 维生素C对生长中期草鱼生产性能、肠道、机体和鳃健康以及肉质的作用及其作用机制[D]. 硕士学位论文. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2016. XU H J. Effects of dietary vitamin C on growth performance, the health status of intestinal, body and gill, and flesh quality of young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) and the mechanisms[D]. Master's Thesis. Ya'an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese) |
| [32] |
HU F, GAO X, SHE R, et al. Effects of antimicrobial peptides on growth performance and small intestinal function in broilers under chronic heat stress[J]. Poultry Science, 2017, 96(4): 798-806. DOI:10.3382/ps/pew379 |
| [33] |
LIU S, FENG L, JIANG W D, et al. Impact of exogenous lipase supplementation on growth, intestinal function, mucosal immune and physical barrier, and related signaling molecules mRNA expression of young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2016, 55: 88-105. |
| [34] |
李娜, 杨华, 吕文涛, 等. 丁酸梭菌早期干预对幼龄番鸭生长性能、肠道黏膜形态及肠屏障功能的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2021, 57(4): 200-206. LI N, YANG H, LYU W T, et al. Effects of early intervention of Clostridium butyricum on growth performance, intestinal mucosal morphology and intestinal barrier function of young muscovy duck[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2021, 57(4): 200-206 (in Chinese). |
| [35] |
王开卓. 棉酚对草鱼肠道结构和免疫屏障的作用及其机制[D]. 博士学位论文. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2019. WANG K Z. Effects of gossypol on the intestinal structure and immune barrier and the related mechanisms in grass carp (Ctenopharymgodon idella)[D]. Master's Thesis. Ya'an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese) |
| [36] |
吴国超, 单安山, 王军军, 等. 谷氨酰胺对妊娠期饲喂精氨酸民猪母猪后代肠道发育及ZO-1、occludin基因表达的影响[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2016, 36(11): 1949-1953. WU G C, SHAN A S, WANG J J, et al. Effect of glutamine on intestinal development and gene expression of ZO-1 and occludin in descendants of Min pig sows which supplemented with arginine during pregnancy[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2016, 36(11): 1949-1953 (in Chinese). |
| [37] |
韩凤禄. 养成期两个生长阶段斜带石斑鱼对精氨酸最适需要量的研究[D]. 硕士学位论文. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2016. HAN F L. Dietary arginine requirements of orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) at grow-out stages. [D]. Master's Thesis. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2016. (in Chinese) |




