2. 河南新仰韶生物科技有限公司, 三门峡 472400
2. Henan Xinyangshao Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Sanmenxia 472400, China
益生菌作为一类安全、绿色的微生态制剂,在维持动物生长与肠道健康方面发挥重要作用[1-3]。尤其是2010年饲料端禁抗后,益生菌逐渐受到业界的关注,因其作为饲用抗生素的替代品之一,具有广阔的应用前景[3-5]。其中,枯草芽孢杆菌是农业农村部批准添加的饲用芽孢杆菌之一,属于典型的革兰氏阳性菌,它的菌落形状呈粗糙状、无荚膜,最适生长的温度约为37 ℃[6-7]。在不同的温度、酸碱条件下,枯草芽孢杆菌的稳定性较好,也不易对药物产生耐药性[8-10]。枯草芽孢杆菌进入动物肠道后,可以增殖并消耗大量游离氧,使肠道形成一个利于厌氧有益菌增殖的内环境,抑制好氧致病菌的生长,进而调节肠道的微生态菌群结构[11-13]。枯草芽孢杆菌可以分泌多种生物活性因子,比如蛋白酶和纤维素酶等,从而改善对饲粮营养物质的消化利用率[14-16]。产蛋后期蛋鸡的产蛋率和蛋品质逐渐下降,如何通过营养手段改善蛋鸡生产性能已成为了研究热点。因此,本研究在饲粮中添加一定比例的枯草芽孢杆菌,研究其对产蛋后期蛋鸡生产性能、蛋品质、肠道形态结构及盲肠微生物的影响,为枯草芽孢杆菌在蛋鸡产蛋后期的应用提供基础数据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验设计与饲养管理试验选取60周龄产蛋率相近的海兰褐蛋鸡240只,随机分为2组(基础产蛋率分别为89.63%和89.28%),每组8个重复,每个重复15只鸡。预试期10 d,正试期60 d。对照组饲喂基础饲粮,试验组在基础饲粮中添加0.03%的枯草芽孢杆菌(由河南某生物科技有限公司提供,活菌数2×106 CFU/g),试验组枯草芽孢杆菌的添加水平参考本实验室的前期试验结果。基础饲粮为玉米-豆粕型饲粮,营养水平参考NRC(1994),基础饲粮组成及营养水平见表 1。在试验期间,蛋鸡自由采食、饮水,采用3层阶梯式笼养方法,每笼饲养3只鸡,通过人工补光和自然光照,设定每天的光照时间为16 h。每日定时饲喂3次(08:00、14:00、18:30),确保料槽的饲料均匀,每日18:00人工收蛋。
|
|
表 1 基础饲粮组成及营养水平(风干基础) Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of the basal diet (air-dry basis) |
以重复为单位,试验期间记录每周采食量、每天产蛋数和产蛋重,计算总产蛋率、料蛋比、平均日产蛋重和平均日采食量。试验第60天采集蛋样,每个重复随机抽取10枚,测定平均蛋重、蛋形指数、哈氏单位、蛋白高度、蛋壳强度和蛋壳厚度等指标。所用仪器为游标卡尺、蛋品质分析仪(QCH,英国)、螺旋测微仪和强度测定仪(In-spec-2200,美国)。
1.3 肠道形态结构测定试验结束后,每组随机选取6只鸡,快速解剖后取十二指肠、空肠及回肠中段2 cm,使用4%多聚甲醛进行固定。设置不同乙醇浓度对肠道样品脱水,之后使用二甲苯清洗,制作石蜡切片,观察肠道形态结构。通过Case Viewer软件测量肠绒毛高度(villus height,VH)、隐窝深度(crypt depth,CD),计算绒毛高度/隐窝深度(VH/CD)。
1.4 盲肠微生物测定试验鸡屠宰后,迅速收集试验鸡(每组6只)的盲肠食糜,先置于液氮中,后迅速转移至-80 ℃冰箱保存。使用D5625-02 DNA检测试剂盒(Omega Bio-Tek Inc.,美国)提取盲肠食糜的微生物基因组DNA,进行DNA纯度和浓度的质检,合格后置于-20 ℃环境下保存。将目的DNA送至上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司,测序平台为Illumina MiSeq。将同源性基因序列聚类为操作分类单元(OTU),使用QIIME 1.9.0计算微生物的α多样性(Shannon指数、Simpson指数、Chao指数和Ace指数)。
1.5 数据处理数据采用Excel 2010初步整理后,使用SAS 9.1.3软件进行t检验分析,数据以平均值和均值标准误(SEM)表示,P < 0.05表示差异显著。
2 结果 2.1 枯草芽孢杆菌对产蛋后期蛋鸡生产性能的影响由表 2可知,饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌对产蛋后期蛋鸡产蛋率、平均日产蛋重、料蛋比和平均日采食量均无显著影响(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 2 枯草芽孢杆菌对产蛋后期蛋鸡生产性能的影响 Table 2 Effects of Bacillus subtilis on performance of laying hens during late laying stage |
由表 3可知,与对照组相比,饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌显著提高产蛋后期蛋鸡蛋白高度和哈氏单位(P < 0.05)。饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌对产蛋后期蛋鸡平均蛋重、蛋形指数、蛋壳强度、蛋壳相对重和蛋黄相对重均无显著影响(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 3 枯草芽孢杆菌对产蛋后期蛋鸡蛋品质的影响 Table 3 Effects of Bacillus subtilis on egg quality of laying hens during late laying stage |
由表 4可知,与对照组相比,饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌显著提高了产蛋后期蛋鸡空肠和回肠的绒毛高度(P < 0.05)。饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌对产蛋后期蛋鸡十二指肠、空肠和回肠的隐窝深度和VH/CD均无显著影响(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 4 枯草芽孢杆菌对产蛋后期蛋鸡肠道形态结构的影响 Table 4 Effects of Bacillus subtilis on intestinal morphology of laying hens during late laying stage |
由表 5可知,与对照组相比,饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌显著提高了产蛋后期蛋鸡盲肠微生物Chao指数(P < 0.05)。饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌对产蛋后期蛋鸡微生物Shannon指数、Simpson和Ace指数均无显著影响(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 5 枯草芽孢杆菌对产蛋后期蛋鸡盲肠微生物多样性的影响蛋鸡盲肠内容物菌群多样性 Table 5 Effects of Bacillus subtilis on cecal microbial diversity of laying hens during late laying stage |
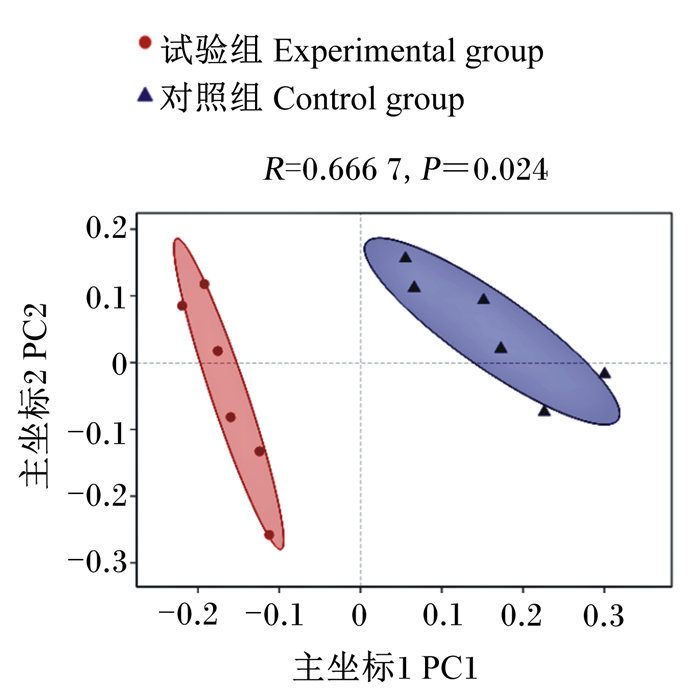
如图 1所示,通过主坐标轴分析(PCoA),发现试验组与对照组微生物结构存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。
|
图 1 基于OTU水平的PCoA Fig. 1 PCoA based on OTU level |
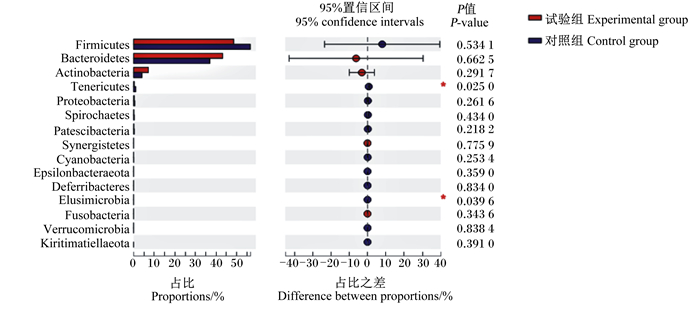
由图 2可知,在门水平上,主要菌门为厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes),2组之间无显著差异(P>0.05)。与对照组相比,试验组软壁菌门(Tenericutes)和迷踪菌门(Elusimicrobia)的相对丰度显著降低(P < 0.05)。
|
Firmicutes:厚壁菌门;Bacteroidetes:拟杆菌门;Actinobacteria:放线菌门;Tenericutes:软壁菌门;Proteobacteria:变形菌门;Spirochaetes:螺旋体菌门;Patescibacteria:芽孢杆菌门;Synergistetes:互养菌门;Cyanobacteria:蓝藻菌门;Epsilonbacteraeota:ε-变形菌门;Deferribacteres:脱铁杆菌门;Elusimicrobia:迷踪菌门;Fusobacteria:梭杆菌门;Verrucomicrobia:疣微菌门;Kiritimatiellaeota:基里氏菌门。 图 2 盲肠微生物在门水平上的差异 Fig. 2 Difference of cecal microbiota on phylum level |
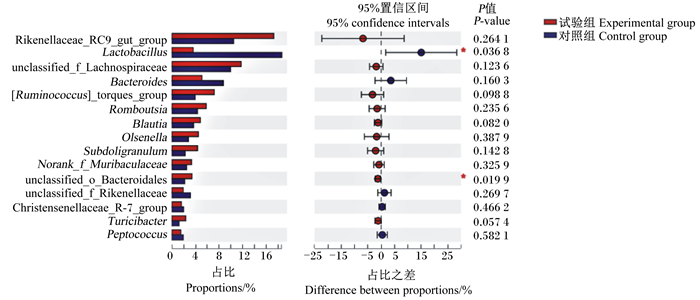
由图 3可知,在属水平上,主要菌属为理研菌科RC9肠道群(Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group)、未分类毛螺菌科(unclassified Lachnospiraceae)、乳酸杆菌属(Lactobacillus)及拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)。与对照组相比,试验组乳酸杆菌属的相对丰度显著降低(P < 0.05),未分类的拟杆菌科(unclassified Bacteroidales)的相对丰度显著提高(P < 0.05)。
|
Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group:理研菌科RC9肠道群;Lactobacillus:乳酸杆菌属;unclassified Lachnospiraceae:未分类毛螺菌科;Bacteroides:拟杆菌属;[Ruminococcus]_torques_group:瘤胃球菌属扭链群;Romboutsia:罗姆布茨菌属;Blautia:布劳特氏菌属;Olsenella:奥尔森氏菌属;Subdoligranulum:罕见小球菌属;Norank Muribaculaceae:未知的Muribaculaceae;unclassified Bacteroidales:未分类的拟杆菌科;unclassified Rikenellaceae:未分类的瘤胃菌科;Christensenellaceae_R-7_group:克里斯滕森菌科R7群;Turicibacter:杆菌属;Peptococcus:肽球菌属。 图 3 盲肠微生物在属水平上的差异 Fig. 3 Difference of cecal microbiota on genus level |
关于枯草芽孢杆菌对蛋鸡生产性能和蛋品质的影响,不同试验的结果并不完全一致。徐海燕等[17]研究结果表明,饲粮添加5×105 CFU/g的枯草芽孢杆菌提高了产蛋后期蛋鸡的产蛋率和蛋壳质量,降低了料蛋比。Ribeiro等[18]研究结果表明,饲粮添加8×105 CFU/g的枯草芽孢杆菌提高了蛋鸡的蛋重和蛋品质指标,但对产蛋率和料蛋比无显著影响。王翔宇[19]也研究了饲粮添加1×1010 CFU/g枯草芽孢杆菌对60周龄蛋鸡生产性能的影响,未发现生产性能的显著变化。在本试验中,基础饲粮添加了0.03%的枯草芽孢杆菌(2×106 CFU/g)时,没有检测到产蛋率的变化,但是提高了鸡蛋的蛋白高度和哈氏单位,表明饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌改善了产蛋后期蛋鸡的蛋品质。造成以上试验结果不同的原因,可能与试验之间枯草芽孢杆菌的添加剂量或菌种来源不同有关。
肠道形态结构是衡量动物肠道发育状态的重要指标之一[20-21]。健康的肠道形态是营养物质高效吸收的基础,主要包括绒毛高度、隐窝深度和VH/CD等[22-23]。一般来说,绒毛高度反映了肠上皮细胞的成熟率,其数值与营养物质的吸收效率呈正相关[24]。肠道隐窝的细胞则具有向绒毛顶端迁移的能力,隐窝变浅反映了细胞分化的速度加快,间接表明肠道细胞更新效率的提高[25]。对于家禽而言,由于消化系统的特殊性,它们的十二指肠较短,营养物质的吸收主要集中在空肠和回肠[26]。在本试验中,饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌提高了蛋鸡空肠和回肠的绒毛高度,显示枯草芽孢杆菌的添加有利于改善产蛋后期蛋鸡的肠道形态。
肠道微生物菌群的多样性可以发挥对肠道内环境的调节作用[27]。本试验中,PCoA的结果表明,饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌可以影响蛋鸡盲肠的微生物区系,发现其优势菌门是厚壁菌门和拟杆菌门,占全部微生物群落的85%以上,这与之前的研究结果[28-29]一致。在检测微生物属水平上的差异时,发现枯草芽孢杆菌降低了乳酸杆菌属的相对丰度,这与一些文献报道结果[30-31]不一致。易中华等[30]研究表明,饲粮中添加枯草芽孢杆菌有助于促进肉鸡盲肠乳酸菌的生长,竞争性的排斥大肠杆菌等病原菌的增长。乳酸菌属是蛋鸡的有益菌之一,其与肠道健康的关系密切,可以调节肠道的酸碱环境,同时抑制有害菌的增殖,促进动物的正常生长。Kridtayopas等[31]研究发现,饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌和益生元可以缓解高密度肉鸡肠道菌群失调的程度,增加肠道内芽孢杆菌属和乳酸菌属等有益微生物的数量,同时抑制大肠杆菌的生长。然而,本试验中,饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌抑制了乳酸菌属微生物的数量,相关机制有待于进一步的研究。
4 结论饲粮添加0.03%的枯草芽孢杆菌提高了产蛋后期蛋鸡空肠和回肠绒毛高度,改善了蛋品质,影响了盲肠微生物组成,但对生产性能无显著影响。
| [1] |
LI L, XU C L, JI C, et al. Effects of a dried Bacillus subtilis culture on egg quality[J]. Poultry Science, 2006, 85(2): 364-368. DOI:10.1093/ps/85.2.364 |
| [2] |
CHEN J F, XU M M, KANG K L, et al. The effects and combinational effects of Bacillus subtilis and montmorillonite on the intestinal health status in laying hens[J]. Poultry Science, 2020, 99(3): 1311-1319. DOI:10.1016/j.psj.2019.11.016 |
| [3] |
HOSSAIN M M, BEGUM M, KIM I H. Effect of Bacillus subtilis, Clostridium butyricum and Lactobacillus acidophilus endospores on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, meat quality, relative organ weight, microbial shedding and excreta noxious gas emission in broilers[J]. Veterinarni Medicina, 2015, 60(2): 77-86. |
| [4] |
LIU X, PENG C Y, QU X Y, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis C-3102 on production, hatching performance, egg quality, serum antioxidant capacity and immune response of laying breeders[J]. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2019, 103(1): 182-190. DOI:10.1111/jpn.13022 |
| [5] |
MAZANKO M S, GORLOV I F, PRAZDNOVA E V, et al. Bacillus probiotic supplementations improve laying performance, egg quality, hatching of laying hens, and sperm quality of roosters[J]. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins, 2018, 10(2): 367-373. DOI:10.1007/s12602-017-9369-4 |
| [6] |
FORTE C, MOSCATI L, ACUTI G, et al. Effects of dietary Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bacillus subtilis on laying performance, egg quality, blood biochemistry and immune response of organic laying hens[J]. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2016, 100(5): 977-987. DOI:10.1111/jpn.12408 |
| [7] |
SOBCZAK A, KOZLOWSKI K. The effect of a probiotic preparation containing Bacillus subtilis ATCC PTA-6737 on egg production and physiological parameters of laying hens[J]. Annals of Animal Science, 2015, 15(3): 711-723. DOI:10.1515/aoas-2015-0040 |
| [8] |
NEIJAT M, SHIRLEY R B, BARTON J, et al. Effect of dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis DSM29784 on hen performance, egg quality indices, and apparent retention of dietary components in laying hens from 19 to 48 weeks of age[J]. Poultry Science, 2019, 98(11): 5622-5635. DOI:10.3382/ps/pez324 |
| [9] |
KHADIEVA G F, LUTFULLIN M T, MOCHALOVA N K, et al. New Bacillus subtilis strains as promising probiotics[J]. Microbiology, 2018, 87(4): 463-471. DOI:10.1134/S0026261718040112 |
| [10] |
陈继发, 曲湘勇. 蒙脱石和枯草芽孢杆菌对蛋鸡血浆生化指标、小肠刷状缘酶活性及黏蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2020, 56(9): 192-197. CHEN J F, QU X Y. Effects of montmorillonite and Bacillus subtilis on plasma biochemical indices, small intestinal brush-margin enzyme activity and mucin expression of laying hens[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2020, 56(9): 192-197 (in Chinese). |
| [11] |
HOSSEINDOUST A, MOHAMMADI M, YAO Z P, et al. Dietary Bacillus subtilis B2A strain in laying hens challenged with Salmonella gallinarum: effects on egg production, egg quality, blood haptoglobin and targeted intestinal Salmonella shedding[J]. Journal of Applied Animal Research, 2018, 46(1): 512-517. DOI:10.1080/09712119.2017.1351369 |
| [12] |
SHI H, ZHANG W L, KIM I H. Effects of dietary Bacillus subtilis RX7 and B2A supplementation on productive performance, egg quality, blood profiles, and excreta Salmonella counts in laying hens[J]. Canadian Journal of Animal Science, 2020, 100(3): 411-417. DOI:10.1139/cjas-2019-0064 |
| [13] |
陈继发, 朱瑾, 曲湘勇. 枯草芽孢杆菌的作用机制及其在家禽生产中的应用[J]. 经济动物学报, 2019, 23(1): 44-50, 56. CHEN J F, ZHU J, QU X Y. Functional mechanisms of Bacillus subtilis and its application in poultry production[J]. Journal of Economic Animal, 2019, 23(1): 44-50, 56 (in Chinese). |
| [14] |
裴跃明, 邵强, 吴桂龙, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌制剂对产蛋后期蛋鸡生产性能、蛋品质、免疫及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2016, 52(7): 61-65, 70. PEI Y M, SHAO Q, WU G L, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on laying performance, egg quality, immunity and intestinal microflora of hens during the postpeak period[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2016, 52(7): 61-65, 70 (in Chinese). |
| [15] |
周晓辉, 李威, 刘浩. 枯草芽孢杆菌微生态制剂在禽畜养殖中的作用[J]. 河北科技大学学报, 2016, 37(5): 503-508. ZHOU X H, LI W, LIU H. Effect of Bacillus subtilis microecological probiotics on livestock breeding[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2016, 37(5): 503-508 (in Chinese). |
| [16] |
张安荣, 刘娇, 陈志敏, 等. 饲粮添加枯草芽孢杆菌对肉仔鸡生长性能、血清生化指标和胫骨指标的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(9): 4123-4131. ZHANG A R, LIU J, CHEN Z M, et al. Effect of dietary Bacillus subtilis on growth performance, serum biochemical indices and tibia index of broilers[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(9): 4123-4131 (in Chinese). |
| [17] |
徐海燕, 曹银生, 崔诗法, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌的分离鉴定及对蛋鸡生产性能的影响[J]. 青岛农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 29(1): 31-35, 40. XU H Y, CAO Y S, CUI S F, et al. Isolation and identification of a Bacillus subtilis strain and effects on performance of layers[J]. Journal of Qingdao Agricultural University(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 29(1): 31-35, 40 (in Chinese). |
| [18] |
RIBEIRO V Jr, ALBINO L F T, ROSTAGNO H S, et al. Effects of the dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis levels on performance, egg quality and excreta moisture of layers[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2014, 195: 142-146. DOI:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2014.06.001 |
| [19] |
王翔宇. 枯草芽孢杆菌对蛋鸡生产性能及蛋品质的影响[D]. 硕士学位论文. 长春: 吉林大学, 2015. WANG X Y. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on production performance and egg quality of laying hens[D]. Master's Thesis. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015. (in Chinese) |
| [20] |
曲湘勇, 陈继发, 匡佑华, 等. 饲粮添加蒙脱石和枯草芽孢杆菌对产蛋鸡盲肠菌群和肠道通透性的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(4): 1887-1896. QU X Y, CHEN J F, KUANG Y H, et al. Effects of dietary montmorillonite and Bacillus subtilis on cecal microflora and intestinal permeability of laying hens[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(4): 1887-1896 (in Chinese). |
| [21] |
ALIAKBARPOUR H R, CHAMANI M, RAHIMI G, et al. The Bacillus subtilis and lactic acid bacteria probiotics influences intestinal mucin gene expression, histomorphology and growth performance in broilers[J]. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2012, 25(9): 1285-1293. DOI:10.5713/ajas.2012.12110 |
| [22] |
黄玉岚, 霍小东, 姚宏明, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌WEI-62体外益生评价及其对仔猪生长性能、肠道形态和肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2020, 56(11): 140-145. HUANG Y L, HUO X D, YAO H M, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis WEI-62 on growth performance, intestinal morphology and intestinal flora of piglets[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2020, 56(11): 140-145 (in Chinese). |
| [23] |
GUO J R, DONG X F, LIU S, et al. Effects of long-term Bacillus subtilis CGMCC 1.921 supplementation on performance, egg quality, and fecal and cecal microbiota of laying hens[J]. Poultry Science, 2017, 96(5): 1280-1289. |
| [24] |
JAYARAMAN S, DAS P P, SAINI P C, et al. Use of Bacillus subtilis PB6 as a potential antibiotic growth promoter replacement in improving performance of broiler birds[J]. Poultry Science, 2017, 96(8): 2614-2622. |
| [25] |
闻治国, 吴学壮, 齐志国, 等. 橡胶籽油对脂多糖刺激蛋鸡产蛋性能、肠道形态和免疫功能的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2020, 56(12): 145-152. WEN Z G, WU X Z, QI Z G, et al. Effect of rubber seed oil on laying performance, intestinal morphological structure, and immune function in LPS-induced laying hens[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2020, 56(12): 145-152 (in Chinese). |
| [26] |
CHEN J F, KUANG Y H, QU X Y, et al. The effects and combinational effects of Bacillus subtilis and montmorillonite supplementation on performance, egg quality, oxidation status, and immune response in laying hens[J]. Livestock Science, 2019, 227: 114-119. |
| [27] |
GAO Z H, WU H H, SHI L, et al. Study of Bacillus subtilis on growth performance, nutrition metabolism and intestinal microflora of 1 to 42 d broiler chickens[J]. Animal Nutrition, 2017, 3(2): 109-113. |
| [28] |
AHIR V B, KORINGA P G, BHATT V D, et al. Metagenomic analysis of poultry gut microbes[J]. Indian Journal of Poultry Science, 2010, 45(2): 111-114. |
| [29] |
OAKLEY B B, LILLEHOJ H S, KOGUT M H, et al. The chicken gastrointestinal microbiome[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2014, 360(2): 100-112. |
| [30] |
易中华, 胥传来, 计成, 等. 果寡糖和枯草芽孢杆菌对肉鸡肠道菌群数量及生产性能的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2005, 41(12): 11-14. YI Z H, XU C L, JI C, et al. Effects of fructo-oligosaccharides and Bacillus subtilis on performance and intestinal microflora in broilers[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2005, 41(12): 11-14 (in Chinese). |
| [31] |
KRIDTAYOPAS C, RAKANGTONG C, BUNCHASAK C, et al. Effect of prebiotic and synbiotic supplementation in diet on growth performance, small intestinal morphology, stress, and bacterial population under high stocking density condition of broiler chickens[J]. Poultry Science, 2019, 98(10): 4595-4605. |




