幼兔断奶应激是目前养兔业面临的严重问题,断奶前幼兔所需的主要营养物质和免疫蛋白来自于母乳,断奶后幼兔失去母乳的被动免疫且幼兔处于生长阶段,自身的消化机能和免疫系统发育不完善,体内消化酶和胃酸分泌不足,极易引起断奶幼兔腹泻甚至死亡[1]。因此,改善幼兔断奶应激是当前养兔生产中迫在眉睫的问题。酸化剂具有调节胃肠道菌群、提高消化道酶活、改善免疫功能、促进营养物质吸收和调节胃肠道pH等功能[2-6]。国内研究发现,饲粮中添加0.1%复合酸化剂(二甲酸钾和磷酸复合)可显著增加商品肉兔平均日增重,降低料重比,并显著提高养分表观消化率,改善肉兔生长性能[7]。国外研究发现,饲粮中添加2%柠檬酸可显著提高肉兔的末重和平均日采食量,降低料重比,提高饲料转化率,增加体内淋巴细胞数量,增强肉兔免疫能力[8]。不过,复合酸化剂在兔生产中的应用较少,且其对肝脏抗氧化能力及作用机制鲜有报道。同时,复合酸化剂的有效成分不同,其对试验结果的影响也有差异。因此,本试验使用小分子有机酸(甲酸和丙酸)组成的复合酸化剂来探究其对伊拉兔生长性能、免疫和抗氧化功能以及空肠形态的影响,以筛选出较为合适的添加剂量,为酸化剂在伊拉兔中的生产应用提供理论依据和实践指导。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验设计试验选取192只(35±2)日龄健康、体重接近的断奶商品伊拉兔公兔,随机分为4个组,每组6个重复,每个重复8只。对照组饲喂基础饲粮,参照山东省地方标准《肉兔饲养标准》(DB 37/T 1835—2011)营养需要配制,为颗粒料,其组成及营养水平见表 1;抗生素组饲喂在基础饲粮中添加60 mg/kg盐霉素的饲粮;试验组饲喂在基础饲粮中分别添加0.1%(试验Ⅰ组)和0.2%复合酸化剂(试验Ⅱ组)的饲粮。复合酸化剂由漳州某生物科技有限公司提供,其中含29%甲酸、6%丙酸、30%木质磺酸盐以及35%二氧化硅载体。试验期28 d,期间试验兔自由采食,充足饮水,按正常免疫程序进行免疫接种。
|
|
表 1 基础饲粮组成及营养水平(风干基础) Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of the basal diet (air-dry basis) |
试验第27天21:00禁食不禁水,试验第28天09:00开始对试验兔进行空腹称重,记录宰前活重。从各组的每个重复中分别选择1只接近平均体重的试验兔,耳缘静脉采血,颈部放血处死,打开腹腔,将肝脏、空肠取出,取适当大小肝脏组织,-80 ℃保存,取3 cm左右的空肠中段,用生理盐水冲洗干净,于4%多聚甲醛中固定。
1.3 检测指标及方法 1.3.1 生长性能试验期间,每天17:00记录各组试验兔采食量和余料量,计算平均日采食量、平均日增重和料重比;观察每天每只试验兔的腹泻情况,统计腹泻率。计算公式如下:

|
试验兔屠宰后,切开颈部和腹腔,分离并摘取胸腺、脾脏、圆小囊和蚓突,剔除脂肪组织,用滤纸吸干血水后准确称重,计算免疫器官指数。计算公式如下:
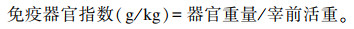
|
试验兔耳缘静脉采血约5 mL,注入不含抗凝剂的真空采血管中,室温静置30 min后,3 000 r/min离心15 min;将上清液收集于EP管中,-20 ℃保存。血清白细胞介素-6(IL-6)、白细胞介素-10(IL-10)、白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)和肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)含量采用酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)试剂盒(南京建成生物工程研究所)进行测定,严格按照试验盒说明书进行操作。
1.3.4 肝脏抗氧化指标试验兔屠宰后,取肝脏组织,于-80 ℃保存。肝脏超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、谷胱甘肽过氧化氢酶(GSH-Px)活性、总抗氧能力(T-AOC)以及丙二醛(MDA)、还原型谷胱甘肽(GSH)、氧化型谷胱甘肽(GSSG)含量和GSH/GSSG值,采用ELISA试剂盒(南京建成生物工程研究所)进行测定,严格按照试验盒说明书进行操作。
1.3.5 空肠形态空肠组织经过固定、脱水、包埋、切片、染色和封片等处理,在光学显微镜观察并测量其绒毛高度、隐窝深度,并计算绒毛高度/隐窝深度(V/C)值。
1.4 数据统计分析试验数据用Excel 2021整理后,采用SPSS 26.0统计软件进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),并采用Duncan氏法进行多重比较检验,结果以“平均值±标准差”表示,以P<0.05为差异显著,0.05<P < 0.10为差异有显著趋势。
2 结果与分析 2.1 复合酸化剂对伊拉兔生长性能的影响由表 2可知,与对照组相比,试验Ⅰ组伊拉兔平均日采食量显著提高(P < 0.05),平均日增重有提高趋势(P=0.076);抗生素组和试验Ⅰ组腹泻率显著降低(P < 0.05)。各组料重比之间均无显著差异(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 2 复合酸化剂对伊拉兔生长性能的影响 Table 2 Effects of compound acidifiers on growth performance of Ira rabbits |
由表 3可知,各组伊拉兔免疫器官指数之间均无显著差异(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 3 复合酸化对伊拉兔免疫器官指数的影响 Table 3 Effects of compound acidifiers on immune organ indices of Ira rabbits |
由表 4可知,与对照组相比,抗生素组和试验Ⅰ组伊拉兔血清IL-6含量显著降低(P < 0.05),抗生素组、试验Ⅰ组和试验Ⅱ组血清TNF-α含量显著降低(P < 0.05)。各组血清IL-1β和IL-10含量之间均无显著差异(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 4 复合酸化剂对伊拉兔血清免疫指标的影响 Table 4 Effects of compound acidifiers on serum immune indices of Ira rabbits |
由表 5可知,与对照组相比,试验Ⅰ组伊拉兔肝脏MDA含量有降低趋势(P=0.084)。各组其他肝脏抗氧化指标之间均无显著差异(P>0.05)。
|
|
表 5 复合酸化剂对伊拉兔肝脏抗氧化指标的影响 Table 5 Effects of compound acidifiers on liver antioxidant indices of Ira rabbits |
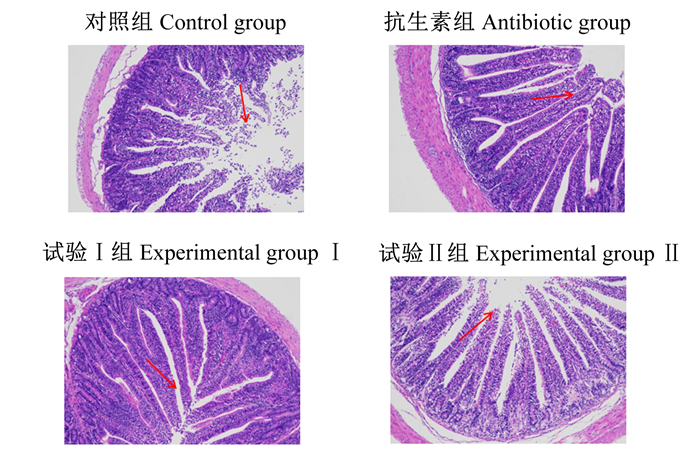
由表 6可知,与对照组相比,抗生素组、试验组Ⅰ组和试验Ⅱ组伊拉兔空肠绒毛高度和V/C值显著提高(P < 0.05)。各组空肠隐窝深度之间均无显著差异(P>0.05)。由图 1可以看出,如红色箭头所指,在100×放大下,对照组空肠肠绒毛顶端微绒毛较多出现脱落和断裂,肠绒毛排列相对不整齐、疏松,肠绒毛相对较短;抗生素组和试验Ⅰ组空肠肠绒毛整体结构完整,肠微绒毛未见明显脱落,肠绒毛排列相对整齐、紧密,肠绒毛相对较长;试验Ⅱ组空肠肠绒毛顶端也出现了部分脱落、断裂,但明显较对照组少,肠绒毛排列相对整齐、紧密,肠绒毛明显比对照组长。
|
|
表 6 复合酸化剂对伊拉兔空肠形态的影响 Table 6 Effects of compound acidifiers on jejunum morphology of Ira rabbits |
|
图 1 伊拉兔空肠组织切片 Fig. 1 Jejunal tissue sections of Ila rabbits (100×) |
断奶幼兔易发生腹泻,从而影响其生长发育。酸化剂可以调节肠道菌群,增强消化酶活性,提高机体免疫力,并促进机体对营养物质的消化吸收,从而改善断奶幼兔的生长性能[9]。本研究结果发现,与对照组相比,饲粮添加0.1%复合酸化剂可以显著提高伊拉兔平均日采食量,且有提高平均日增重的趋势。Luise等[10]研究发现,饲粮添加甲酸可显著提高断奶仔猪平均日增重,有降低平均日采食量和料重比的趋势。费洪标等[11]研究发现,饲粮添加0.1%复合酸化剂可显著提高断奶獭兔平均日增重。这些研究与本试验研究结果基本一致。其主要原因可能是:1)甲酸具有良好的酸化作用,能够调节肠道菌群的平衡,促进动物肠道内营养物质的吸收[12];2)丙酸经畜禽吸收后,可通过糖异生途径转化为葡萄糖,从而促进机体发育[13]。本研究结果还发现,饲粮添加复合酸化剂对伊拉兔料重比无显著影响,这与Debi等[8]的研究结果基本一致;但Long等[14]和Bosi等[15]研究表明,饲粮添加酸化剂可以显著降低料重比,改善饲料报酬。造成这种差异的原因可能与复合酸化剂的组成成分、添加剂量、饲养动物以及饲养环境等不同有关。吴秋玉等[16]研究发现,饲粮添加1%有机酸可显著降低断奶仔猪腹泻率,有效预防仔猪腹泻。本试验结果显示,饲粮添加复合酸化剂可显著降低幼兔腹泻率,其原理可能是酸化剂通过降低肠道pH,改变菌群最适pH,调节肠道菌群平衡,从而降低腹泻率。
3.2 复合酸化剂对伊拉兔免疫功能的影响免疫器官是机体防御系统的重要组成部分,其生长发育状况会影响机体的免疫能力。本试验结果显示,饲粮添加复合酸化剂对伊拉兔免疫器官指数无不良影响,这与冯国亮等[17]的研究结果基本一致;但李万军[18]研究显示,饲粮添加复合酸化剂可显著提高肉鸡免疫器官指数。结果的差异性可能是不同畜禽对酸化剂的利用能力不同,以及复合酸化剂的组成成分对畜禽的影响也不同。
免疫反应和炎症反应是机体的保护性防御反应,正常情况下机体免疫系统处于平衡状态,当免疫失衡时,免疫系统会产生大量炎症反应,并可能诱导疾病产生[19]。炎症因子含量的变化可以间接说明机体炎症反应的强弱,并反映机体的健康状态。Wang等[20]研究发现,饲粮添加复合酸化剂可以显著降低断奶仔猪血清TNF-α含量,显著提高血清免疫球蛋白G(IgG)含量,增强断奶仔猪免疫能力。程远之等[21]研究发现,饲粮添加0.2%乳酸型酸化剂可显著提高断奶仔猪血清IgG和免疫球蛋白M(IgM)含量,并显著提高十二指肠和空肠免疫因子的表达,增强断奶仔猪免疫能力。Kuang等[22]研究发现,饲粮添加复合有机酸可抑制断奶仔猪空肠促炎细胞因子的表达。本试验结果发现,与对照组相比,饲粮添加复合酸化剂可以显著降低伊拉兔血清促炎因子IL-6和TNF-α含量,增强断奶幼兔免疫能力。这与Han等[23]和汪晶晶[24]的研究结果基本一致。酸化剂增强机体免疫能力的原因可能是:1)部分酸化剂如延胡索酸等参与了机体三羧酸循环,能够产生ATP维持机体供能,从而提高免疫力[25];2)部分酸化剂如丙酸等可以通过糖异生等途径合成葡萄糖,保证机体正常营养需求和物质代谢[13];3)有机酸具有杀菌和调节pH的功能,能够促进机体消化吸收营养物质,从而增强机体免疫能力,提高抗病力[26]。
3.3 复合酸化剂对伊拉兔肝脏抗氧化功能的影响抗氧化是机体健康状况的重要指标之一。机体产生过多氧自由基会引起氧化损伤,正常情况下,机体通过维持抗氧化系统的平衡状态来保持氧自由基的平衡。刘新泽等[27]研究表明,饲粮添加0.1%复合酸化剂可以显著提高肉鸡血清T-AOC,显著降低血清MDA含量,增强肉鸡抗氧化能力,改善肉鸡健康状况。秦枫等[28]研究表明,饲粮添加延胡索酸能够提高幼兔血清T-AOC和SOD活性,降低血清MDA含量,增强机体抗氧化能力,维持机体健康。王铭洋等[29]研究表明,饮水型酸化剂可显著降低蛋鸡肝脏MDA含量,显著提高肝脏T-AOC。酸化剂增强机体抗氧化能力的原因可能是:1)部分有机酸参与机体三羧酸循环,为机体供能,从而提高机体清除自由基的能力[25];2)部分有机酸可作为GSH-Px合成的原料,提高机体抗氧化能力[30]。本试验结果显示,饲粮添加复合酸化剂有降低伊拉兔肝脏MDA含量的趋势,这与前人结果基本一致。本试验中,各组其他抗氧化指标之间均无显著差异,其原因可能是复合酸化剂的组成成分不同、饲养动物不同以及饲养环境差异等因素导致。
3.4 复合酸化剂对伊拉兔空肠形态的影响肠道是机体最大的免疫器官,肠道形态尤其是绒毛高度和隐窝深度是机体肠道健康的重要指标。肠道绒毛边缘可分泌多种消化酶,所以绒毛高度越高,机体消化吸收能力越强;隐窝深度代表肠细胞生产率,隐窝越浅,细胞成熟度越高,分泌功能越强[31]。周嘉鑫等[32]研究表明,饲粮中添加0.09%甲酸+0.06%木质磺酸混合制品可显著提高黄羽肉鸡空肠绒毛高度和V/C值,改善肉鸡肠道形态。Chen等[33]研究表明,饲粮添加苯甲酸可显著降低断奶仔猪空肠隐窝深度,提高空肠V/C值,促进肠道营养物质吸收。何博等[34]研究发现,饲粮添加甲酸和二甲酸钾可显著提高肉鸡回肠绒毛高度和V/C值,促进肠细胞增殖,改善肠道形态。以上研究表明,饲粮添加酸化剂可以改善肠道形态,促进肠道发育。本试验结果显示,与对照组相比,饲粮添加复合酸化剂可以显著提高伊拉兔空肠绒毛高度和V/C值,这与前人研究结果基本一致。其原因可能是:1)酸化剂可以降低肠道pH,调节肠道微生物平衡,促进肠道发育[35];2)甲酸对大肠杆菌、沙门氏菌等病原菌具有很强的抑制作用,能降低病原菌的生长与增殖,缓解肠道黏膜炎症反应,增强绒毛高度和分泌功能[34]。
4 结论① 在本试验条件下,饲粮添加复合酸化剂可以增强伊拉兔免疫功能,改善空肠形态,提高平均日采食量,降低腹泻率。
② 综合本试验结果,以添加0.1%复合酸化剂效果较好。
| [1] |
潘孝青, 杨杰, 邵乐, 等. 有机酸化剂对断奶仔兔生产性能、营养物质表观消化率及血清生化指标的影响[C]//2012现代兔业发展大会暨兔产品博览会. 临沂: 中国畜牧业协会, 2012: 77-80. PAN X Q, YANG J, SHAO L, et al. Effects of organic acidifiers on production performance, apparent digestibility of nutrients and serum biochemical indexes of weaned rabbits[C]//2012 Modern Rabbit Industry Development Conference & Rabbit Products Expo. Linyi: China Animal Agriculture Assocation, 2012: 77-80. (in Chinese). |
| [2] |
MANZANILLA E G, NOFRARÍAS M, ANGUITA M, et al. Effects of butyrate, avilamycin, and a plant extract combination on the intestinal equilibrium of early-weaned pigs[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2006, 84(10): 2743-2751. DOI:10.2527/jas.2005-509 |
| [3] |
ROTH F X, KIRCHGESSNER M. Organic acids as feed additives for young pigs: nutritional and gastrointestinal effects[J]. Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 1998, 7: 25-33. DOI:10.22358/jafs/69953/1998 |
| [4] |
李建平, 单安山, 徐奇友. 不同类型酸化剂对早期断奶仔猪胃酸分泌、免疫功能和抗氧化机能的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2009, 40(4): 69-73. LI J P, DAN A S, XU Q Y. Effects of different acidifiers on gastric acid secretion, immunology and antioxidation of early weaned piglets[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2009, 40(4): 69-73 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2009.04.017 |
| [5] |
KLUGE H, BROZ J, EDER K. Effect of benzoic acid on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, nitrogen balance, gastrointestinal microflora and parameters of microbial metabolism in piglets[J]. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2006, 90(7/8): 316-324. |
| [6] |
苏永腾, 陈丽媛. 复合酸化剂对断奶仔猪生长性能和肠道健康的影响[J]. 饲料工业, 2017, 38(1): 25-28. SU Y T, CHEN L Y. Effect of compound acidifier on growth performance and intestinal health in weaning piglets[J]. Feed Industry, 2017, 38(1): 25-28 (in Chinese). |
| [7] |
詹海杰, 曹亮, 郑建婷, 等. 饲粮中添加不同水平的复合酸化剂对商品肉兔生产性能和养分表观消化率的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(6): 2775-2781. ZHAN H J, CAO L, ZHENG J T, et al. Effects of diets with different supplemental levels of compound acidifier on performance and nutrient apparent digestibility of commercial meat rabbits[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(6): 2775-2781 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.06.037 |
| [8] |
DEBI M R, ISIAM K M S, AKBAR M A, et al. Response of growing rabbits to different levels of dietary citric acid[J]. Bangladesh Journal of Animal Science, 2010, 39(1/2): 125-133. |
| [9] |
韦良开, 贺晨晨, 蔡巧利, 等. 有机酸的功能及在断奶仔猪饲养中应用研究[J]. 饲料工业, 2018, 39(3): 20-25. WEI L K, HE C C, CAI Q L, et al. Research and application of organic acid function in weaned piglets production[J]. Feed Industry, 2018, 39(3): 20-25 (in Chinese). |
| [10] |
LUISE D, MOTTA V, SALVARANI C, et al. Long-term administration of formic acid to weaners: influence on intestinal microbiota, immunity parameters and growth performance[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2017, 232: 160-168. DOI:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.06.015 |
| [11] |
费洪标, 汤银根, 杨继峰, 等. 酸化剂对断奶獭兔生长性能、肠道消化酶活性和腹泻的影响[J]. 中国养兔, 2016(4): 21-23. FEI H B, TANG Y G, YANG J F, et al. Acidifier on growth performance of weaned Rex affect the digestive enzyme activity and intestinal diarrhea[J]. Chinese Journal of Rabbit Farming, 2016(4): 21-23 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-6327.2016.04.006 |
| [12] |
LUISE D, CORREA F, BOSI P, et al. A review of the effect of formic acid and its salts on the gastrointestinal microbiota and performance of pigs[J]. Animals, 2020, 10(5): 887. DOI:10.3390/ani10050887 |
| [13] |
曹娜, 张亚伟, 吴浩, 等. 丙酸盐在反刍动物中的应用[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2017, 44(12): 3519-3524. CAO N, ZHANG Y W, WU H, et al. Research progress on propionate application in ruminant[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 44(12): 3519-3524 (in Chinese). DOI:10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2017.12.018 |
| [14] |
LONG S F, XU Y T, PAN L, et al. Mixed organic acids as antibiotic substitutes improve performance, serum immunity, intestinal morphology and microbiota for weaned piglets[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2018, 235: 23-32. DOI:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.08.018 |
| [15] |
BOSI P, SARLI G, CASINI L, et al. The influence of fat protection of calcium formate on growth and intestinal defence in Escherichia coli K88-challenged weanling pigs[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2007, 139(3/4): 170-185. |
| [16] |
吴秋玉, 吴艺鑫, 郑远鹏. 有机酸对断奶仔猪生长性能及腹泻率的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2019(2): 81-84. WU Q Y, WU Y X, ZHENG Y P. Effect of the organic acid on growth performance and diarrhea rate of weaned piglets[J]. China Feed, 2019(2): 81-84 (in Chinese). |
| [17] |
冯国亮, 曹亮, 詹海杰, 等. 复合酸化剂对断奶幼兔生长性能、养分表观消化率、免疫器官及肉品质的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(12): 5875-5883. FENG G L, CAO L, ZHAN H J, et al. Effects of mixed acidifier on growth performance, nutrient apparent digestibilities, immune organ and meat quality of weaned rabbits[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(12): 5875-5883 (in Chinese). |
| [18] |
李万军. 酸化剂对肉鸡生长及免疫的影响[J]. 饲料研究, 2012(4): 75-77. LI W J. Effects of acidifier on growth and immunity of broilers[J]. Feed Research, 2012(4): 75-77 (in Chinese). |
| [19] |
卢德勋. 论动物机体自我防御功能的系统观及其实践应用(一)[J]. 饲料工业, 2022, 43(3): 1-9. LU D X. The systemic concept on body self-defense function and its practical application[J]. Feed Industry, 2022, 43(3): 1-9 (in Chinese). |
| [20] |
WANG Y, KUANG Y W, ZHANG Y L, et al. Rearing conditions affected responses of weaned pigs to organic acids showing a positive effect on digestibility, microflora and immunity[J]. Animal Science Journal, 2016, 87(10): 1267-1280. DOI:10.1111/asj.12544 |
| [21] |
程远之, 周洪彬, 虞财华, 等. 不同类型酸化剂对断奶仔猪生长性能和免疫功能的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(5): 2575-2584. CHENG Y Z, ZHOU H B, YU C H, et al. Effects of different types of acidifiers on growth performance and immune function of weaned piglets[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(5): 2575-2584 (in Chinese). |
| [22] |
KUANG Y, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of dietary combinations of organic acids and medium chain fatty acids as a replacement of zinc oxide on growth, digestibility and immunity of weaned pigs[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2015, 208: 145-157. |
| [23] |
HAN Y S, TANG C H, ZHAO Q Y, et al. Effects of dietary supplementation with combinations of organic and medium chain fatty acids as replacements for chlortetracycline on growth performance, serum immunity, and fecal microbiota of weaned piglets[J]. Livestock Science, 2018, 216: 210-218. |
| [24] |
汪晶晶. 酸化剂和微生态制剂对哺乳母猪生产性能及乳成分的影响[D]. 硕士学位论文. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2018. WANG J J. Effects of acidifier and probiotics on production performance and milk composition of lactating sows[D]. Master's Thesis. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese) |
| [25] |
连凯霞, 蒋国政, 李继昌. 复合酸化剂对饲料的防霉及酸化作用[J]. 中国饲料, 2013(13): 8-10. LIAN K X, JIANG G Z, LI J C. Anti-mould and acidification of compound acidifiers on feed[J]. China Feed, 2013(13): 8-10 (in Chinese). |
| [26] |
李运虎, 李美君, 彭兰丽, 等. 不同酸化剂对断奶仔猪胃肠道pH和消化酶活性的影响[J]. 饲料博览, 2019(2): 20-23. LI Y H, LI M J, PENG L L, et al. Effect of different acidifiers on gastrointestinal pH value and digestive enzyme activities in weaned piglets[J]. Feed Review, 2019(2): 20-23 (in Chinese). |
| [27] |
刘新泽, 胡友军, 赵晓南, 等. 饲粮中添加不同类型和水平的酸化剂对肉鸡生长性能、养分表观代谢率及血清生化、抗氧化和免疫指标的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34(5): 2949-2960. LIU X Z, HU Y J, ZHAO X N, et al. Effects of dietary different types and different levels of acidifiers on growth performance, nutrient apparent metabolic rates and serum biochemical, antioxidant and immune indexes of broilers[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34(5): 2949-2960 (in Chinese). |
| [28] |
秦枫, 潘孝青, 邵乐, 等. 延胡索酸对夏季幼兔生长性能、空肠发育及血清抗氧化和免疫指标的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30(3): 1103-1109. QIN F, PAN X Q, SHAO L, et al. Effects of fumaric acid on growth performance, jejunum development and serum antioxidant and immunity indicators of young rabbits in summer[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2018, 30(3): 1103-1109 (in Chinese). |
| [29] |
王铭洋, 胡颖, 黎明, 等. 饮水型酸化剂对蛋鸡免疫功能及血清、肝脏和肾脏相关生化指标的影响[J]. 中国家禽, 2021, 43(3): 47-52. WANG M Y, HU Y, LI M, et al. Effects of acidifiers supplementation by drinking water on physiological and biochemical function of laying hens[J]. China Poultry, 2021, 43(3): 47-52 (in Chinese). |
| [30] |
李马成, 李杰, 刘全新, 等. 代谢有机酸对育肥猪生长性能及抗氧化指标的影响[J]. 广东饲料, 2015, 24(6): 29-31. LI M C, LI J, LIU Q X, et al. Effects of metabolic organic acids on growth performance and antioxidant indexes of fattening pigs[J]. Guangdong Feed, 2015, 24(6): 29-31 (in Chinese). |
| [31] |
卫旭彪, 张璐璐, 马广, 等. 酵母菌对猪肠道绒毛、隐窝及菌群的影响[J]. 饲料工业, 2016, 37(4): 61-64. WEI X B, ZHANG L L, MA G, et al. Effects of yeasts on intestinal villus, crypt and flora in pigs[J]. Feed Industry, 2016, 37(4): 61-64 (in Chinese). |
| [32] |
周嘉鑫, 黄义强, 高玉云, 等. 甲酸+木质磺酸对黄羽肉鸡生产性能、屠宰性能、肌肉品质、肠道结构的影响[C]//中国畜牧兽医学会2018年学术年会禽病学分会第十九次学术研讨会论文集. 南宁: 中国畜牧兽医学会, 2018: 324. ZHOU J X, HUANG Y Q, GAO Y Y, et al. Effects of formic acid + lignosulfonic acid on production performance, slaughter performance, muscle quality and intestinal structure of yellow feather broilers[C]//Proceedings of the 19th Symposium of the Avian Disease Branch of the 2018 Annual Meeting of the Chinese Society of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine. Nanning: Chinese Association of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 324. (in Chinese). |
| [33] |
CHEN J L, ZHENG P, ZHANG C, et al. Benzoic acid beneficially affects growth performance of weaned pigs which was associated with changes in gut bacterial populations, morphology indices and growth factor gene expression[J]. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2017, 101(6): 1137-1146. |
| [34] |
何博, 王勤, 郑淑容. 甲酸和二甲酸钾对肉鸡生长、免疫和肠道健康的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2019(22): 68-72. HE B, WANG Q, ZHENG S R. Effects of formic acid and potassium diformate on growth performance, immunity and intestinal health of broilers[J]. China Feed, 2019(22): 68-72 (in Chinese). |
| [35] |
TUGNOLI B, GIOVAGNONI G, PIVA A, et al. From acidifiers to intestinal health enhancers: how organic acids can improve growth efficiency of pigs[J]. Animals, 2020, 10(1): 134. |




