现代畜禽养殖中抗生素的不合理使用,导致了病原菌耐药性、畜产品药物残留、畜禽机体免疫力低下与双重感染和环境污染等诸多问题[1]。目前,我国饲料中全面禁止添加抗生素,因而抗生素的替代越来越受到广大研究者的关注,其中通过细菌群体感应(quorum sensing,QS)实现肠道健康来替代抗生素是一种新的方法。QS是细菌用来调节集体行为的细胞间交流过程,它依赖于细菌群体密度而调控其生理行为[2]。细菌在生长过程中会分泌化学信号分子,伴随细菌的分裂生长和群体密度的增加,胞外信号分子浓度也随之增加,细菌会通过胞外信号分子的浓度而感知其群体密度。当胞外信号分子浓度达到某一阈值时,细菌会启动一系列基因的表达,从而调节细菌群体行为,致使宿主产生正面或负面应答。肠道作为宿主微生物的聚集地和营养素的主要吸收器官,它的生理状态直接影响宿主健康。QS可通过微生物的信息交流调控肠道屏障功能与营养素代谢,进而维持机体对营养素的吸收和肠道健康[3]。因此,研究QS及群体感应抑制剂(quorum sensing inhibitor,QSI)和QS介导肠道菌群促进机体健康发生机制对于动物健康养殖具有重要意义。
1 QS系统科学家们研究费氏弧菌(Vibrio fischeri)的发光机理时发现其释放信息交流信号,此信号分子调控自身发光,是一种依赖于菌群密度系统而发生的生理行为,即QS系统。QS不仅能够调节细菌生物发光,还可以调节细菌色素合成、生物膜形成、致病性、抗生素的分泌[4-5]。同时,QS在调节细菌共生、细菌素的产生、遗传能力、细胞的程序性死亡等方面也具有重要作用[6-8]。多种信号分子介导细菌之间的信息交流,根据信号分子的种类和感应信号分子的作用机制将细菌QS系统分为以下几类:1)由N-酰基高丝氨酸内酯(N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones,AHLs)介导的自体诱导物分子1型(auto-inducer-1,AI-1)QS系统,是革兰氏阴性菌中常见的QS系统;2)由寡肽(autoinducing peptides,AIPs)介导的QS系统,是革兰氏阳性菌中常见的QS系统;3)由呋喃硼酸二酯类介导的自体诱导物分子2型(autoinducer-2,AI-2)QS系统,是细菌种间(内)信息交流的QS系统;4)除了以上3种主要的细菌QS系统外,还有自动诱导型信号分子,扩散信号因子等介导的QS系统。
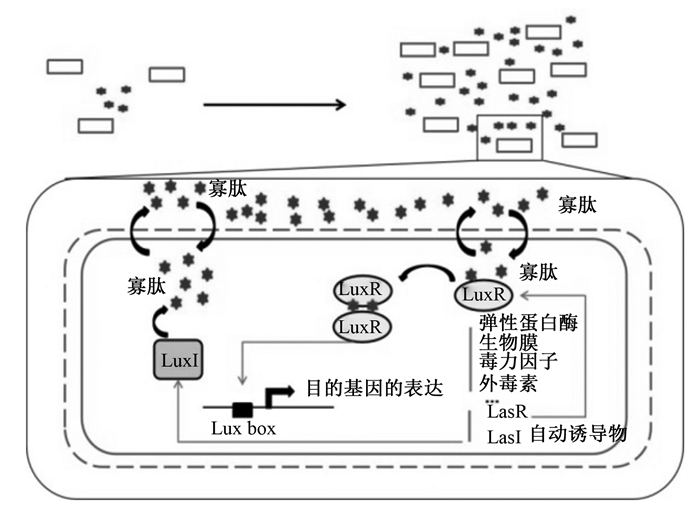
1.1 以AHLs为代表的革兰氏阴性细菌QS系统研究表明,革兰氏阴性细菌QS系统的信号分子主要为酰基高丝氨酸内酯类[9]。AHLs常作为自体诱导物介导革兰氏阴性细菌AI-1型QS的发生,此系统的发生过程为LuxI酶合成AHL,后者可以通过细胞膜自由扩散;在达到阈值浓度时,AHLs与其受体LuxR结合;该受体的二聚作用使LuxR能够在Lux盒上作为一个转录因子,进而触发参与细菌毒力的靶基因和AHLs系统LuxI/LuxR的表达(图 1)。
|
图 1 革兰氏阴性细菌中群体感应发生机制 Fig. 1 Mechanism of quorum sensing in Gram negative bacteria[10] |
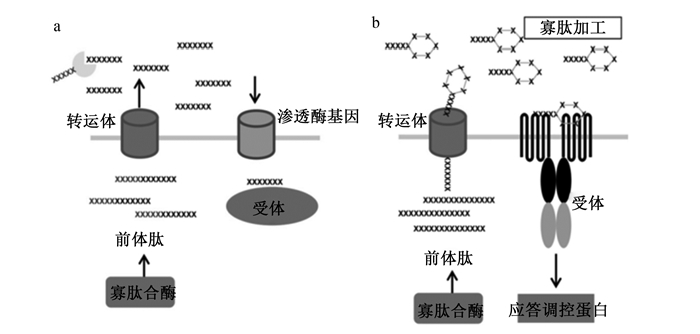
AIPs是革兰氏阳性细菌QS系统信息交流的主要信号分子,这些寡肽类分子不能自由透过细菌的细胞壁,需要一种通道蛋白或者一种名为ABC(ATP-binding-cassette)的转运系统帮助,此系统可以把AIPs转运出细胞从而发挥作用[11]。革兰氏阳性细菌QS发生信号转导系统感应AIPs信号由自动诱导肽由AIPs合成酶产生,其中单组分信号转导系统通过转运体释放到细胞外基质中进行AIPs修饰,被修饰后的AIPs转运回细胞质与受体结合发挥QS调控作用。然而,双组分信号转导系统转运体对产生的自动诱导肽进行翻译和修饰后将其释放到细胞外基质中,通过跨膜受体对其识别后,触发QS相关应答调节子基因的转录,从而发挥调控功能(图 2)。
|
a: 单组分QS系统one-component QS system;b: 2组分QS系统two-component QS system; SAH: Pfs:DPD: AI-2:自体诱导物分子2型autoinducer-2。 图 2 革兰氏阳性细菌中群体感应发生机制 Fig. 2 Mechanism of quorum sensing in Gram positive bacteria[12] |
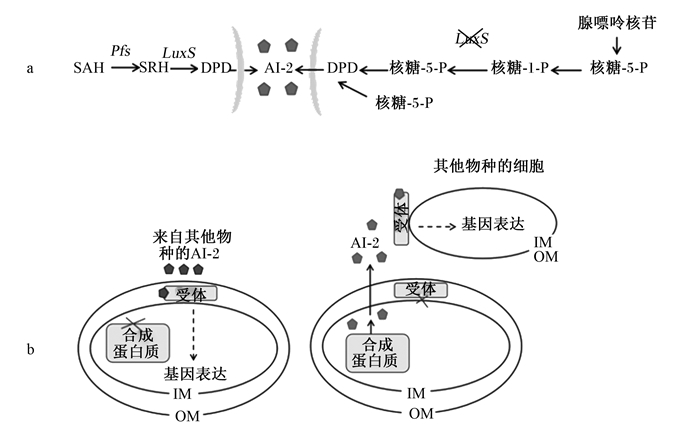
AI-2是革兰氏阳性细菌和阴性细菌共用的QS信号分子,AI-2型QS系统是由呋喃硼酸二酯类信号分子介导,几百种细菌都存在此系统[13]。由于AI-2型QS系统可以介导细菌在种间进行信息交流,因此,可以把它称为细菌之间的“共用语言系统”。在AI-2型QS系统中,进行调控的关键基因是LuxS,它参与了AI-2信号分子的合成。AI-2的合成取决于LuxS编码的合成酶,是一种将核糖基高半胱氨酸转化为高半胱氨酸和4,5-二羟基-2,3-戊二酮的代谢酶,对于没有AI-2合成蛋白或受体蛋白的细菌,AI-2用于种内/种间通讯,包括参与信号转导和调控其他微生物的下游基因表达(图 3)。
|
a: 有无LuxS的AI-2合成路线AI-2 synthetic routes with or without LuxS;b: AI-2的种内/种间通讯AI-2 intraspecific/interspecific communication; IM: 内膜intima; OM: 外膜outer membrane;SAH:S-腺苷高半胱氨酸S-adeno-sylhomocysteine;Pfs:S-腺苷同型半胱氨酸核苷酶S-adenosylhomocysteine nucleosidase;SRH:S-核糖高半胱氨酸S-ribosylhomocysteine;DPD:4, 5-二羟基2, 3-戊二酮4, 5-di-hydroxy 2, 3-pentanedione;AI-2:自体诱导物分子2型autoinducer-2。 图 3 细菌中的AI-2合成和感知 Fig. 3 AI-2 synthesis and perception in bacteria[14] |
有害菌QS活动可给宿主动物带来不利影响,目前主要利用QSI进行淬灭以阻断QS发生来消除其带来的不利影响。QSI主要包括植物来源和微生物来源。
2.1 QSI淬灭机制QSI主要通过以下4个方面来阻断QS发生:1)抑制有害菌QS系统中信号分子的合成;2)降解已合成的QS信号分子,使信号分子的浓度达不到调控阈值;3)干扰QS信号分子与对应受体蛋白结合;4)抑制参与信号转导的小分子,阻断QS的完整性。
2.2 QSI的种类及其作用效果目前,对QS有抑制作用的分子有如下几类,详情请见表 1。
|
|
表 1 QSI的种类、作用途径及效果 Table 1 Types, action pathways and effects of quorum sensing inhibitors |
有研究报道,从17种中草药中筛选得到了蒲公英、连翘、独活、杜仲、板蓝根、白癣皮、白芷、马齿苋8种有效QSI,13种中草药粗提取物明显抑制铜绿假单胞菌的浮游迁移活动[31]。赵弘毅[32]研究表明,丁香、赤芍等中草药粗提取物具有良好的抑菌效果,部分中草药如何首乌、八角茴香、菊花等可通过干预信号分子与受体蛋白的结合来实现对细菌QS调控。冬凌草片中冬凌草甲素对铜绿假单胞菌毒力因子的产生有类似效果[33],决明子提取产物对铜绿假单胞菌PAO1的毒力因子和生物膜也有显著的抑制作用[34]。
除中草药外,植物精油和植物提取物也具有抑制QS的作用。植物精油中的化合物香芹酚能显著抑制荧光假单胞菌的生物膜形成[35],绿薄荷精油和阿魏精油可作为与食品有关微生物和QSI[36-37]。在植物提取物方面,牡丹花中的酚类成分对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的生物膜抑制率达到87.03%和77.93%[38];大蒜提取物对紫色杆菌CVO26(Chromobacterium violaceum CVO26)QS有一定的抑制作用[39];芒果提取物和番石榴中的黄酮可抑制铜绿假单胞菌PAO1的毒力因子表达和生物膜形成[40-41];连翘提取物和花椒提取物分别抑制铜绿假单胞菌和嗜水气单胞菌QS发生[42-43]。此外,花椒提取物可通过降低嗜水气单胞菌AHLs的分泌,有效抑制其生物膜的形成和胞外蛋白酶活性。Lee等[44]研究发现,西兰花提取物对大肠杆菌O157 ∶ H7 QS和体内毒力有抑制作用。金银花中的重要成分之一绿原酸可在不影响荧光假单胞菌正常生长的情况下,明显抑制胞外蛋白酶、胞外脂肪酶活性、群集与泳动等相关腐败特性[45]。洋葱皮中的乙酸乙酯馏分(ONE),能显著抑制由QS介导毒力因子的产生,如紫色杆菌素、弹性蛋白酶[46]。余甘子多糖具有抑菌活性及QSI活性,当其终浓度为20 mg/mL时对紫色杆菌素生成量的抑制作用最大[47]。郭勋[48]研究证实,穿心莲中主要的活性成分穿心莲内酯能显著降低引起鸡败血症、气囊炎、输卵管炎的致病性大肠杆菌-O78中AI-2的分泌。从牛至、百里香等植物中提取的百里香酚能介导QS来调控动物肠道菌群[49]。由上述可见,植物相关来源的物质在QS发生上有较好的作用效果和应用前景。
2.2.2 微生物来源QSI益生菌在畜禽胃肠道中可抢占某些细菌和真菌的生存空间和资源,竞争性抑制QS活性和生物膜的形成。如林洋等[50]从发酵酸豆角中分离得到了能抑制嗜水气单胞菌群体感应和生物膜形成的植物乳杆菌AJS2-4。嗜酸菌La-5可分泌一种QS信号抑制分子,直接与细菌转录调控因子相互作用,控制参与定植的肠出血性大肠杆菌(enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli,EHEC)O157 ∶ H7毒力基因的转录[51]。Kim等[52]在断奶仔猪的研究中,发现嗜酸乳杆菌30SC细胞提取物可显著抑制EHEC O157 ∶ H7中AI-2活性。此外,乳杆菌也能够通过抑制QS活性抑制有害菌生物膜的形成。Melian等[53]研究发现,乳杆菌素AL705能通过QS机制抑制李斯特菌生物膜的形成。枯草芽孢杆菌分泌的枯草杆菌素能有效抑制大肠杆菌、李斯特菌生物膜的形成[54],芽孢杆菌分泌的芽孢杆菌脂肽可以通过抑制金黄色葡萄球菌QS来消除其在人体内定植[55]。枯草芽孢杆菌作为一种畜禽常用益生菌,在与嗜水气单胞菌共培养表明,其可以显著减少嗜水气单胞菌毒力因子的分泌[56]。因此,益生素介导QS对于维持动物肠道健康具有重要作用。
3 QS介导的肠道健康肠道中存在着大量且复杂的微生物,这些微生物菌群对宿主养分消化、吸收、能量供应和维持正常生理和免疫功能等具有重要意义。
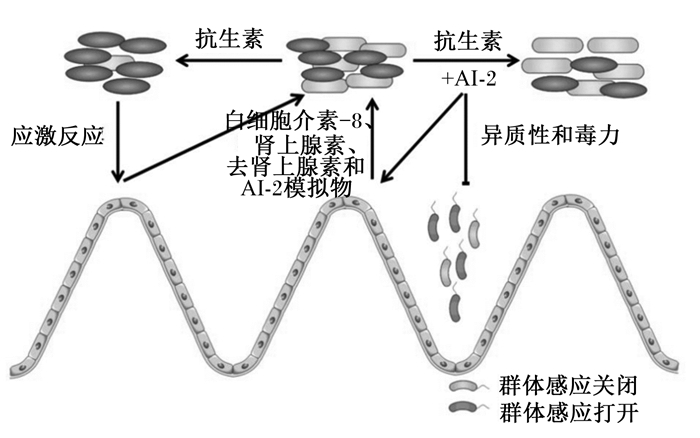
3.1 QS与肠道交流机制在肠道上百万个微生物中,细菌的占比超过了99%[57],肠道中的微生物被形象的称作动物体内移动的器官,也可作为一种生物屏障保护肠道健康[58]。在哺乳动物肠道中,通过抗生素处理可改变肠道微生物组成,进而引起AI-2水平变化,细菌感应AI-2产生白细胞介素-8(IL-8)、肾上腺素和去甲肾上腺素和AI-2模拟物来影响生物膜的形成(图 4)。
|
图 4 哺乳动物肠道中AI-2介导的群体感应 Fig. 4 AI-2-mediated quorum sensing in mammalian gut[59] |
QS可作为桥梁来介导肠道、营养素和一些代谢物促进肠道健康,如QS介导的葡聚糖、果聚糖、甘露糖、葡萄糖、木糖、果胶、淀粉、母乳和多酚的低聚物等益生元在促进胃肠道健康方面起到了积极作用[60]。研究表明,0.1%和0.5%的葡萄糖显著下调QS中LuxS系统影响的大肠杆菌O157 ∶ H7的毒力基因Lee的表达量[61],浓度超过0.05%的葡萄糖显著抑制嗜水气单胞菌QS活性、生物膜形成、蛋白酶产生以及群集和泳动[62]。肠道微生物在宿主屏障功能、氨基酸等养分代谢方面具有重要作用[63]。有研究表明,QS信号分子(3OC12-HSL)可通过肠道屏障功能和氨基酸代谢影响低出生体重仔猪健康[3]。在以仔猪小肠上皮细胞IPEC-J2为模型的研究中发现,不同来源QS信号分子刺激对宿主细胞相关基因表达产生显著影响[64]。有研究报道,赖氨酸、色氨酸显示出抗QS和显著的抗生物膜活性[65-66],限制碳源会抑制QS系统的激活[67]。乳酸盐和丙酮酸盐可增强小鼠机体免疫反应,对肠道沙门氏菌感染具有抵抗性[68];丁酸盐可减少沙门氏菌等有害菌的定植和引起的腹泻[69]。乳酸对铜绿假单胞菌QS信号分子、弹性蛋白酶、蛋白酶、吡氰素的产生和生物膜的形成具有抑制作用[70],醋酸盐可通过QS激活乳酸菌对细菌素的合成[71]。
一种来源于藏灵菇发酵奶的马克斯克鲁维酵母菌代谢产物乙酸色醇,可阻断革兰氏阴性菌的QS,干扰肠道霍乱弧菌的CAI-1 QS级联,进而显著改变其生物膜的形成和形态,降低细菌毒力[72]。Kim等[73]利用大肠杆菌和沙门氏菌成功证实,小鼠肠道内微生物菌群种内和种间基于QS的信号传递,表明细菌QS与肠道健康有密不可分的关系。在抗生素治疗引起的小鼠肠道微生物群失衡的情况下,大肠杆菌会增加肠道AI-2水平,进而影响微生物菌群的组成改变,改善机体肠道健康[74]。铜绿假单胞菌QS转录因子MvfR(PqsR)控制着多种毒力因子的表达和有毒产物的合成。Adiliaghdam等[75]研究表明,抑制铜绿假单胞菌QS系统可通过维持肠道屏障和免疫功能来缓解肠道通透性过高,减少细菌耐药性的发展,并保留有益的肠道微生物。肠道微生物生态系统具有多重抗感染、抗炎和免疫调节作用,对肠道内环境稳定起决定性作用,其会通过基于QS的代谢和免疫机制来抵抗肠道病原体,从而保护宿主健康[76]。产气荚膜梭菌C型可导致人和动物产生肠毒血症和出血性腹泻等严重疾病。Nava等[77]研究发现,用产气荚膜梭菌C型菌株CN3685感染人肠道细胞后,由QS调控的产气荚膜梭菌Agr样(clostridium perfringens Agr-like,CpAL)系统介导的用于评估肠道屏障功能的肠道细胞跨上皮抵抗力(trans-epithelial resistance,TEER)显著下降。对金鱼肠道细菌基因序列鉴定和产生AHL能力筛选中发现,当AHLs浓度达到一定阈值时,气单胞菌和希瓦氏菌属细菌可通过QS系统相互交流[78]。Tao等[79]研究发现,肠道中革兰氏阴性细菌产生的AHLs群体感应分子可以影响肠上皮稳态。N-3-(氧十二烷酰基)-高丝氨酸内酯(C12-HSL)会通过诱导线粒体功能障碍和激活细胞凋亡显著降低细胞活力,导致黏蛋白表达降低。QS分子酰基高丝氨酸内酯,被认为能调节肠出血性大肠杆菌的基因表达,从而帮助该病原体在动物胃肠道中存活。从猪肠道中分离的嗜水气单胞菌菌株YZ2研究发现,其能产生N-丁酰基高丝氨酸内酯(C4-HSL),用质谱分析该菌与大肠杆菌共培养的上清液显示,该菌的LuxI同系物可以使大肠杆菌具有合成AHLs的能力,并影响大肠杆菌的运动性和耐酸性[80]。此外,乳酸菌的AI-2群体信号传递可能是适应宿主生态系统和在肠道环境中相互作用的一种方式[81]。QS信号分子AI-2可通过耐药基因tetA调控禽致病大肠杆菌金霉素耐药性,对于治疗耐药型禽致病大肠杆菌提供了新的药物靶标与治疗思路[82]。
Ismail等[83]发现,哺乳动物肠道中产生的AI-2类似物可以激活其肠道中细菌的QS系统,这种类似物可以被细菌AI-2受体LuxP/LsrB检测到,从而激活系统控制相关基因的表达。肠道黏膜可以通过降解细菌自体诱导物AIs或分泌AI模拟物来干扰细菌AIs,从而实现肠道微生物群与宿主之间的域间信号传递,这为未来肠道微生物群相关疾病的治疗提供了新的靶点[84]。由此可见,群体感应与肠道健康关系密切,如果能抑制有害菌的QS活动,对于促进畜禽机体健康,提高其生产性能具有重要意义。
4 小结与展望目前,对于细菌QS的相关研究主要关注QS与有害菌之间的关系,而QS介导的肠道与营养素及微生物代谢物之间和有益菌的作用研究较少,多是一些表征性的因果关系,缺乏QS调控畜禽肠道微生物活动相关机制的阐述。肠道是一个非常复杂的消化器官,通过蛋白组学、代谢组学、微生物组学等多组学技术解析QS介导有益菌和有害菌定植与代谢、营养素与宿主代谢将会是研究的重要方向,对于以QS为靶标的促进畜禽肠道健康替抗产品开发也具有广阔的前景。
| [1] |
陈红英, 王月颖, 傅思武. 抗生素在养殖业中的应用现状[J]. 现代畜牧科技, 2019(5): 1-3. CHEN H Y, WANG Y Y, FU S W. Application status of antibiotics in aquaculture[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry Science & Technology, 2019(5): 1-3 (in Chinese). |
| [2] |
PACZKOWSKI J E, MUKHERJEE S, MCCREADY A R, et al. Flavonoids suppress Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence through allosteric inhibition of quorum-sensing receptors[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2017, 292(10): 4064-4076. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M116.770552 |
| [3] |
TAO S Y, XIONG Y, WANG Z Y, et al. N-Acyl-homoserine lactones may affect the gut health of low-birth-weight piglets by altering intestinal epithelial cell barrier function and amino acid metabolism[J]. The Journal of Nutrition, 2021, 151(7): 1736-1746. DOI:10.1093/jn/nxab104 |
| [4] |
AMARA N, MASHIACH R, AMAR D, et al. Covalent inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(30): 10610-10619. DOI:10.1021/ja903292v |
| [5] |
KHAN M S A, ZAHIN M, HASAN S, et al. Inhibition of quorum sensing regulated bacterial functions by plant essential oils with special reference to clove oil[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2009, 49(3): 354-360. DOI:10.1111/j.1472-765X.2009.02666.x |
| [6] |
LI Y H, TIAN X L. Quorum sensing and bacterial social interactions in biofilms[J]. Sensors, 2012, 12(3): 2519-2538. DOI:10.3390/s120302519 |
| [7] |
THOMPSON J A, OLIVEIRA R A, XAVIER K B. Chemical conversations in the gut microbiota[J]. Gut Microbes, 2016, 7(2): 163-170. DOI:10.1080/19490976.2016.1145374 |
| [8] |
WATERS C M, BASSLER B L. Quorum sensing: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria[J]. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 2005, 21: 319-346. DOI:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.012704.131001 |
| [9] |
ZHANG C L, ZHU S Q, JATT A N, et al. Characterization of N-acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) producing bacteria isolated from vacuum-packaged refrigerated turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) and possible influence of exogenous AHLs on bacterial phenotype[J]. The Journal of General and Applied Microbiology, 2016, 62(2): 60-67. DOI:10.2323/jgam.62.60 |
| [10] |
COQUANT G, GRILL J P, SEKSIK P. Impact of N-acyl-homoserine lactones, quorum sensing molecules, on gut immunity[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2020, 11: 1827. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01827 |
| [11] |
SYVITSKI R T, TIAN X L, SAMPARA K, et al. Structure-activity analysis of quorum-sensing signaling peptides from Streptococcus mutans[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2007, 189(4): 1441-1450. DOI:10.1128/JB.00832-06 |
| [12] |
HAWVER L A, JUNG S A, NG W L. Specificity and complexity in bacterial quorum-sensing systems[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2016, 40(5): 738-752. DOI:10.1093/femsre/fuw014 |
| [13] |
PAPENFORT K, BASSLER B L. Quorum sensing signal-response systems in gram-negative bacteria[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(9): 576-588. DOI:10.1038/nrmicro.2016.89 |
| [14] |
ZHAO J, QUAN C S, JIN L M, et al. Production, detection and application perspectives of quorum sensing autoinducer-2 in bacteria[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 268: 53-60. DOI:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.01.009 |
| [15] |
THOMANN A, BRENGEL C, BÖRGER C, et al. Structure-activity relationships of 2-sufonylpyrimidines as quorum-sensing inhibitors to tackle biofilm formation and eDNA release of Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. ChemMedChem, 2016, 11(22): 2522-2533. DOI:10.1002/cmdc.201600419 |
| [16] |
INABA T, OBANA N, HABE H, et al. Biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans is enhanced by indole via the quorum sensing pathway[J]. Microbes and Environments, 2020, 35(2): ME19164. |
| [17] |
GAO B, CHI L, TU P C, et al. The organophosphate malathion disturbs gut microbiome development and the quorum-sensing system[J]. Toxicology Letters, 2018, 283: 52-57. DOI:10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.10.023 |
| [18] |
ZHOU S X, ZHANG A, YIN H P, et al. Bacillus sp. QSI-1 modulate quorum sensing signals reduce Aeromonas hydrophila level and alter gut microbial community structure in fish[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2016, 6: 184. |
| [19] |
KARATHANASI G, BOJER M S, BALDRY M, et al. Linear peptidomimetics as potent antagonists of Staphylococcus aureus agr quorum sensing[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 3562. DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-21951-4 |
| [20] |
RYU E J, SIM J, SIM J, et al. D-galactose as an autoinducer 2 inhibitor to control the biofilm formation of periodontopathogens[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2016, 54(9): 632-637. DOI:10.1007/s12275-016-6345-8 |
| [21] |
KIM E K, LEE K A, HYEON D Y, et al. Bacterial nucleoside catabolism controls quorum sensing and commensal-to-pathogen transition in the Drosophila gut[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2020, 27(3): 345-357. |
| [22] |
PATEL B, KUMARI S, BANERJEE R, et al. Disruption of the quorum sensing regulated pathogenic traits of the biofilm-forming fish pathogen Aeromonas hydrophila by tannic acid, a potent quorum quencher[J]. Biofouling, 2017, 33(7): 580-590. DOI:10.1080/08927014.2017.1336619 |
| [23] |
WANG H, CHU W H, YE C, et al. Chlorogenic acid attenuates virulence factors and pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by regulating quorum sensing[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(2): 903-915. DOI:10.1007/s00253-018-9482-7 |
| [24] |
AMRUTHA B, SUNDAR K, SHETTY P H. Effect of organic acids on biofilm formation and quorum signaling of pathogens from fresh fruits and vegetables[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis, 2017, 111: 156-162. DOI:10.1016/j.micpath.2017.08.042 |
| [25] |
MOSTAFA I, ABBAS H A, ASHOUR M L, et al. Polyphenols from Salix tetrasperma impair virulence and inhibit quorum sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(6): 1341. DOI:10.3390/molecules25061341 |
| [26] |
RASAMIRAVAKA T, NGEZAHAYO J, POTTIER L, et al. Terpenoids from Platostoma rotundifolium (Briq.) A. J. Paton alter the expression of quorum sensing-related virulence factors and the formation of biofilm in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2017, 18(6): 1270. DOI:10.3390/ijms18061270 |
| [27] |
HEIDARI A, NOSHIRANZADEH N, HAGHI F, et al. Inhibition of quorum sensing related virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by pyridoxal lactohydrazone[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis, 2017, 112: 103-110. DOI:10.1016/j.micpath.2017.09.043 |
| [28] |
RIEKHOF W R, NICKERSON K W. Quorum sensing in Candida albicans: farnesol versus farnesoic acid[J]. FEBS Letters, 2017, 591(12): 1637-1640. DOI:10.1002/1873-3468.12694 |
| [29] |
OUYANG J, SUN F, FENG W, et al. Quercetin is an effective inhibitor of quorum sensing, biofilm formation and virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2016, 120(4): 966-974. DOI:10.1111/jam.13073 |
| [30] |
FORSCHNER-DANCAUSE S, POULIN E, MESCHWITZ S. Quorum sensing inhibition and structure-activity relationships of β-keto esters[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21(8): 971. DOI:10.3390/molecules21080971 |
| [31] |
石倩, 谢林香, 陈立志, 等. 17种中草药细菌群体感应抑制剂的筛选[J]. 广东农业科学, 2014, 41(10): 77-80, 2. SHI Q, XIE L X, CHEN L Z, et al. Screening of quorum-sensing inhibitors from 17 kinds of Chinese herbal medicine[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 41(10): 77-80, 2 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2014.10.019 |
| [32] |
赵弘毅. 从中草药中筛选多重耐药铜绿假单胞菌的群体感应抑制剂[D]. 硕士学位论文. 南宁: 广西大学, 2016: 10-88. ZHAO H Y. Screening of quorum sensing inhibitors from traditional Chinese herbal medicines on multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginos a[D]. Master's Thesis. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2016: 10-88. (in Chinese) |
| [33] |
黄靖. 群体感应抑制剂筛选及冬凌草甲素对铜绿假单胞菌QSI活性研究[D]. 硕士学位论文. 广州: 广东药科大学, 2018: 35-50. HUANG J. Screening of quorum sensing inhibitors and study on QSI activity of oridonin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa[D]. Master's Thesis. Guangzhou: Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2018: 35-50. (in Chinese) |
| [34] |
REKHA P D, VASAVI H S, VIPIN C, et al. A medicinal herb Cassia alata attenuates quorum sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2017, 64(3): 231-238. DOI:10.1111/lam.12710 |
| [35] |
王雅莹. 基于群体感应研究香芹酚对鱼源荧光假单胞菌单/混生物被膜的抑制作用[D]. 硕士学位论文. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2020: 57-77. WANG Y Y. Inhibitory of carvacrol against the mono/dual-biofilm of Pseudomonas fluorescens based on quorum sensing[D]. Master's Thesis. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2020: 57-77. (in Chinese) |
| [36] |
梅永超, 李婷婷, 刘楠, 等. 绿薄荷精油对温和气单胞菌群体感应现象及其腐败特性的抑制作用[J]. 食品科学, 2018, 39(15): 17-23. MEI Y C, LI T T, LIU N, et al. Effect of spearmint oil on quorum sensing and spoilage characteristics of Aeromonas sobria[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(15): 17-23 (in Chinese). DOI:10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201815003 |
| [37] |
王锦利, 周爱莲, 林其洋, 等. 阿魏植物精油对紫色杆菌群体感应的影响[J]. 现代食品科技, 2016, 32(10): 90-95. WANG J L, ZHOU A L, LIN Q Y, et al. Influence of herbal essential oil from Ferula spp.on quorum sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum[J]. Modern Food Science & Technology, 2016, 32(10): 90-95 (in Chinese). |
| [38] |
LI C C, JIANG C Y, JING H J, et al. Separation of phenolics from peony flowers and their inhibitory activities and action mechanism on bacterial biofilm[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2020, 104(10): 4321-4332. DOI:10.1007/s00253-020-10540-z |
| [39] |
綦国红, 杨志萍, 陈贵堂, 等. 大蒜提取物对紫色杆菌群体感应抑制作用研究[J]. 食品科技, 2018, 43(6): 250-253. QI G H, YANG Z P, CHEN G T, et al. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum by garlic extract[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2018, 43(6): 250-253 (in Chinese). |
| [40] |
HUSAIN F M, AHMAD I, AL-THUBIANI A S, et al. Leaf extracts of Mangifera indica L. inhibit quorum sensing-regulated production of virulence factors and biofilm in test bacteria[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 727. DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2017.00727 |
| [41] |
VASAVI H S, ARUN A B, REKHA P D. Anti-quorum sensing activity of Psidium guajava L. flavonoids against Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1[J]. Microbiology and Immunology, 2014, 58(5): 286-293. DOI:10.1111/1348-0421.12150 |
| [42] |
刘静雪, 李凤林, 曾英男, 等. 连翘提取物对铜绿假单胞菌群体感应系统的影响[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2019(3): 118-121, 182. LIU J X, LI F L, ZENG Y N, et al. Effect of forsythia extract on quorum sensing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2019(3): 118-121, 182 (in Chinese). |
| [43] |
李晴, 许腾腾, 张佳慧, 等. 花椒提取物对嗜水气单胞菌群体感应的抑制作用[J]. 生物加工过程, 2020, 18(2): 263-268. LI Q, XU T T, ZHANG J H, et al. Inhibition of Aeromonas hydrophila quorum sensing by extract from Zanthoxylum bungeanum[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2020, 18(2): 263-268 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2020.02.016 |
| [44] |
LEE K M, LIM J, NAM S, et al. Inhibitory effects of broccoli extract on Escherichia coli O157 ∶ H7 quorum sensing and in vivo virulence[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2011, 321(1): 67-74. DOI:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02311.x |
| [45] |
王虹懿, 吴海虹, 张新笑, 等. 绿原酸对荧光假单胞菌群体感应现象及其腐败特性的抑制作用[J]. 食品工业科技, 2020, 41(7): 95-101. WANG H Y, WU H H, ZHANG X X, et al. Inhibitory activity of chlorogenic acid on the quorum sensing of Pseudomonas fluorescens and its spoilage activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(7): 95-101 (in Chinese). |
| [46] |
AL-YOUSEF H M, AHMED A F, AL-SHABIB N A, et al. Onion peel ethylacetate fraction and its derived constituent quercetin 4'-O-β-D glucopyranoside attenuates quorum sensing regulated virulence and biofilm formation[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 1675. DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2017.01675 |
| [47] |
曹莉莉, 王芳, 杨贺忠, 等. 余甘子果实水溶性多糖抑菌及群体感应抑制活性初探[J]. 亚热带植物科学, 2015, 44(4): 289-292. CAO L L, WANG F, YANG H Z, et al. Inhibitory activity of antibacterial and quorum sensing of water-soluble polysaccharide from Phyllanthus emblica fruit[J]. Subtropical Plant Science, 2015, 44(4): 289-292 (in Chinese). DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-7791.2015.04.005 |
| [48] |
郭勋. 穿心莲内酯调控鸡致病性大肠杆菌群体感应系统的机制研究[D]. 硕士学位论文. 长春: 吉林大学, 2015: 20-31. GUO X. Study on the mechanism of andrographolide interfering quorum sensing of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli[D]. Master's Thesis. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015: 20-31. (in Chinese) |
| [49] |
李振翼, 彭芳, 贺喜, 等. 百里香酚调控动物肠道菌群的可能机制及其在畜禽生产中替代抗生素的应用[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(7): 3072-3079. LI Z Y, PENG F, HE X, et al. Thymol: possible mechanisms of controlling intestinal flora of animals and application in antibiotic substitution of livestock and poultry production[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(7): 3072-3079 (in Chinese). |
| [50] |
林洋, 崔天琦, 吕欣然, 等. 传统发酵蔬菜中抑制嗜水气单胞菌群体感应及生物膜形成乳酸菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 中国食品学报, 2019, 19(8): 199-207. LIN Y, CUI T Q, LV X R, et al. Screening and identification lactic acid bacteria with inhibitory activity against quorum sensing and biofilm formation of Aeromonas hydrophila from traditional fermented vegetables[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2019, 19(8): 199-207 (in Chinese). |
| [51] |
MEDELLIN-PEÑA M J, WANG H F, JOHNSON R, et al. Probiotics affect virulence-related gene expression in Escherichia coli O157 ∶ H7[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 73(13): 4259-4267. DOI:10.1128/AEM.00159-07 |
| [52] |
KIM J, KIM J, KIM Y, et al. Influences of quorum-quenching probiotic bacteria on the gut microbial community and immune function in weaning pigs[J]. Animal Science Journal, 2018, 89(2): 412-422. DOI:10.1111/asj.12954 |
| [53] |
MELIAN C, SEGLI F, GONZALEZ R, et al. Lactocin AL705 as quorum sensing inhibitor to control Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2019, 127(3): 911-920. DOI:10.1111/jam.14348 |
| [54] |
ALGBURI A, ZEHM S, NETREBOV V, et al. Subtilosin prevents biofilm formation by inhibiting bacterial quorum sensing[J]. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins, 2017, 9(1): 81-90. DOI:10.1007/s12602-016-9242-x |
| [55] |
PIEWNGAM P, ZHENG Y, NGUYEN T H, et al. Pathogen elimination by probiotic Bacillus via signalling interference[J]. Nature, 2018, 562(7728): 532-537. DOI:10.1038/s41586-018-0616-y |
| [56] |
任雨薇. 枯草芽孢杆菌对嗜水气单胞菌毒力的影响以及群体感应基因luxS的表达[D]. 硕士学位论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017: 14-31. REN Y W. The Influences of Bacillus subtilis on the virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila and the expression of quorum sensing luxS gene[D]. Master's Thesis. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017: 14-31. (in Chinese) |
| [57] |
周殿元, 潘令嘉. 肠道菌群失调及治疗进展[J]. 胃肠病学, 2001, 6(4): 258-260. ZHOU D Y, PAN L J. Intestinal flora imbalance and its treatment progress[J]. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology, 2001, 6(4): 258-260 (in Chinese). |
| [58] |
TURNER J R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease[J]. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2009, 9(11): 799-809. DOI:10.1038/nri2653 |
| [59] |
THOMPSON J A, OLIVEIRA R A, DJUKOVIC A, et al. Manipulation of the quorum sensing signal AI-2 affects the antibiotic-treated gut microbiota[J]. Cell Reports, 2015, 10(11): 1861-1871. DOI:10.1016/j.celrep.2015.02.049 |
| [60] |
SANDERS M E, MERENSTEIN D J, REID G, et al. Author correction: probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: from biology to the clinic[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2019, 16(10): 642. |
| [61] |
DELCENSERIE V, LAPOINTE G, CHARASLERTRANGSI T, et al. Glucose decreases virulence gene expression of Escherichia coli O157 ∶ H7[J]. Journal of Food Protection, 2012, 75(4): 748-752. DOI:10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-11-384 |
| [62] |
JAHID I K, LEE N Y, KIM A, et al. Influence of glucose concentrations on biofilm formation, motility, exoprotease production, and quorum sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila[J]. Journal of Food Protection, 2013, 76(2): 239-247. DOI:10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-12-321 |
| [63] |
WANG H Y, XU R Y, ZHANG H, et al. Swine gut microbiota and its interaction with host nutrient metabolism[J]. Animal Nutrition, 2020, 6(4): 410-420. |
| [64] |
刘云. 细菌群体感应信号分子3OC12-HSL对仔猪小肠上皮细胞IPEC-J2的影响[D]. 硕士学位论文. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2017: 2-41. LIU Y. Effect of bacterial quorum sensing signal 3OC12-HSL on intestine porcine epithelial cell line IPEC-J2[D]. Master's Thesis. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2017: 2-41. (in Chinese) |
| [65] |
CHAMPALAL L, KUMAR U S, KRISHNAN N, et al. Modulation of quorum sensing-controlled virulence factors in Chromobacterium violaceum by selective amino acids[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2018, 365(23): 1-8. |
| [66] |
CHAKRABORTY P, DAWARE A V, KUMARI M, et al. Free tryptophan residues inhibit quorum sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a potential approach to inhibit the development of microbial biofilm[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2018, 200(10): 1419-1425. DOI:10.1007/s00203-018-1557-4 |
| [67] |
ZHAO K L, LI J, YUAN Y, et al. Nutrient factor-dependent performance of bacterial quorum sensing system during population evolution[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2020, 202(8): 2181-2188. DOI:10.1007/s00203-020-01937-5 |
| [68] |
MORITA N, UMEMOTO E, FUJITA S, et al. GPR31-dependent dendrite protrusion of intestinal CX3CR1+ cells by bacterial metabolites[J]. Nature, 2019, 566(7742): 110-114. DOI:10.1038/s41586-019-0884-1 |
| [69] |
KREUZER M, HARDT W D. How food affects colonization resistance against enteropathogenic bacteria[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2020, 74: 787-813. DOI:10.1146/annurev-micro-020420-013457 |
| [70] |
KIYMACI M E, ALTANLAR N, GUMUSTAS M, et al. Quorum sensing signals and related virulence inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by a potential probiotic strain's organic acid[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis, 2018, 121: 190-197. DOI:10.1016/j.micpath.2018.05.042 |
| [71] |
MENG F Q, ZHAO H Z, NIE T, et al. Acetate activates Lactobacillus bacteriocin synthesis by controlling quorum sensing[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2021, 87(13): e0072021. |
| [72] |
MALKA O, KALSON D, YANIV K, et al. Cross-kingdom inhibition of bacterial virulence and communication by probiotic yeast metabolites[J]. Microbiome, 2021, 9(1): 70. DOI:10.1186/s40168-021-01027-8 |
| [73] |
KIM S, KERNS S J, ZIESACK M, et al. Quorum sensing can be repurposed to promote information transfer between bacteria in the mammalian gut[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(9): 2270-2281. DOI:10.1021/acssynbio.8b00271 |
| [74] |
BIVAR XAVIER K. Bacterial interspecies quorum sensing in the mammalian gut microbiota[J]. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 2018, 341(5): 297-299. DOI:10.1016/j.crvi.2018.03.006 |
| [75] |
ADILIAGHDAM F, ALMPANI M, GHAREDAGHI M H, et al. Targeting bacterial quorum sensing shows promise in improving intestinal barrier function following burn-site infection[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports, 2019, 19(5): 4057-4066. |
| [76] |
IACOB S, IACOB D G, LUMINOS L M. Intestinal microbiota as a host defense mechanism to infectious threats[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 3328. |
| [77] |
NAVA P, VIDAL J E. The CpAL system regulates changes of the trans-epithelial resistance of human enterocytes during Clostridium perfringens type C infection[J]. Anaerobe, 2016, 39: 143-149. |
| [78] |
SUGITA H, KITAO S, NARISAWA S, et al. Diversity of culturable bacterial communities in the intestinal tracts of goldfish (Carassius auratus) and their ability to produce N-acyl homoserine lactone[J]. Folia Microbiologica, 2017, 62(3): 263-267. |
| [79] |
TAO S Y, LUO Y W, HE B, et al. Paraoxonase 2 modulates a proapoptotic function in LS174T cells in response to quorum sensing molecule N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 28778. |
| [80] |
YANG Y, ZHOU M X, HARDWIDGE P R, et al. Isolation and characterization of N-acyl homoserine lactone-producing bacteria from cattle rumen and swine intestines[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2018, 8: 155. |
| [81] |
YEO S, PARK H, JI Y, et al. Influence of gastrointestinal stress on autoinducer-2 activity of two Lactobacillus species[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2015, 91(7): fiv065. |
| [82] |
刘志超. AI-2群体感应对禽致病大肠杆菌金霉素耐药性的调控机制[D]. 硕士学位论文. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2018: 5-38. LIU Z C. The regulatory mechanism of AI-2 quorum sensing of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli chlortetracycline drug resistance[D]. Master's Thesis. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2018: 5-38. (in Chinese) |
| [83] |
ISMAIL A S, VALASTYAN J S, BASSLER B L. A host-produced autoinducer-2 mimic activates bacterial quorum sensing[J]. Cell Host & Microbe, 2016, 19(4): 470-480. |
| [84] |
LI Q, REN Y X, FU X S. Inter-kingdom signaling between gut microbiota and their host[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2019, 76(12): 2383-2389. |




